Embed presentation
Downloaded 78 times





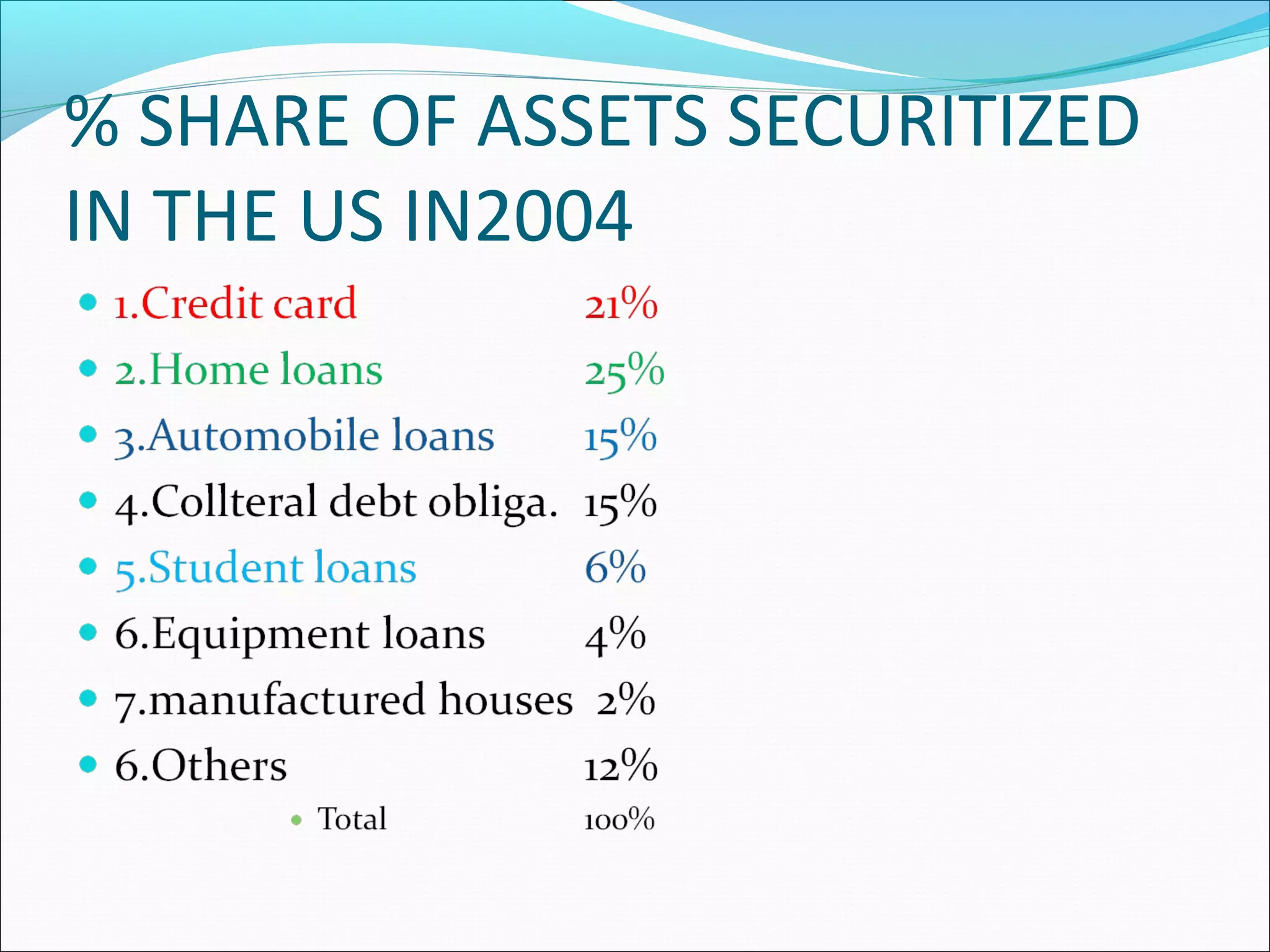
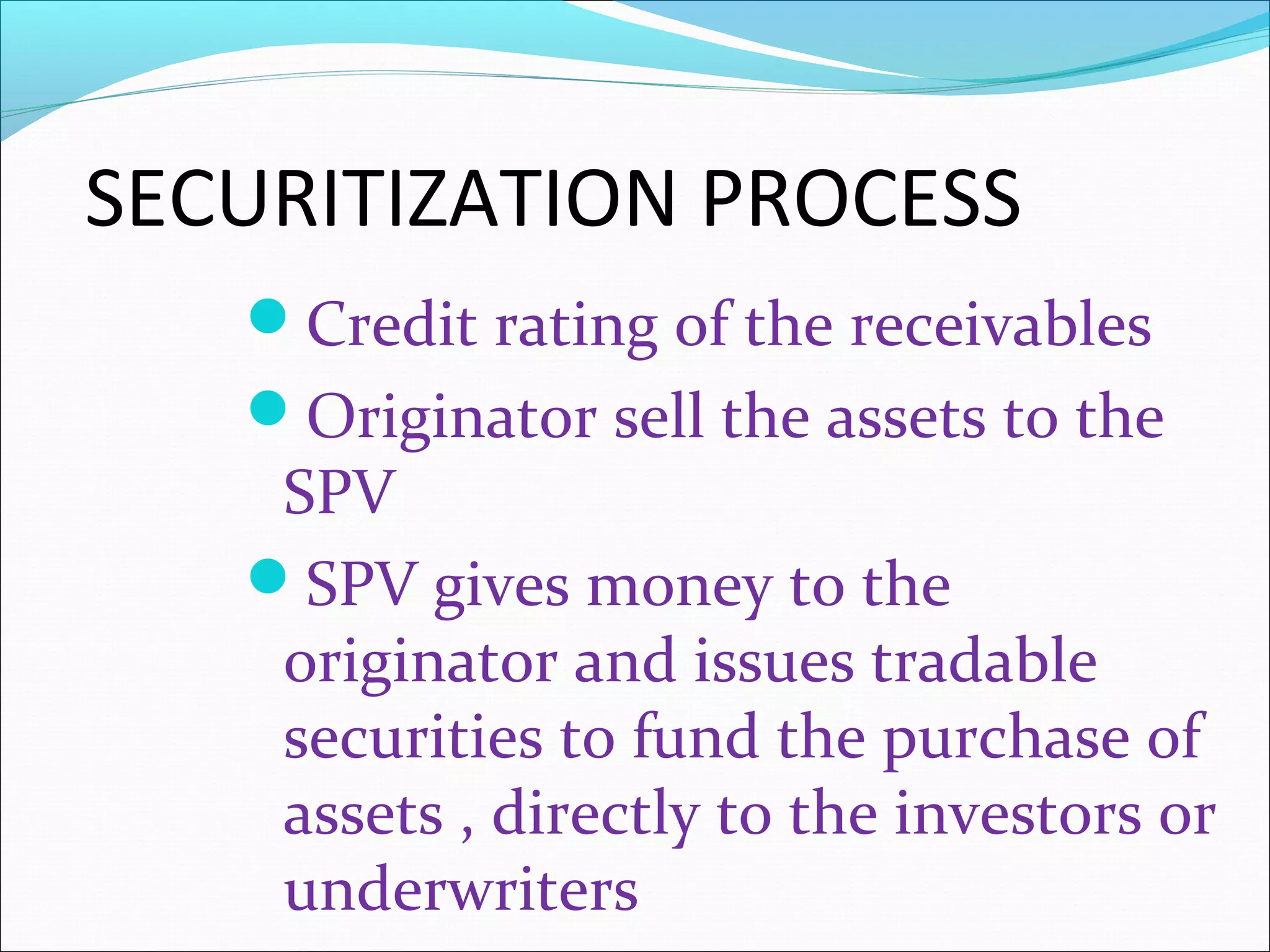
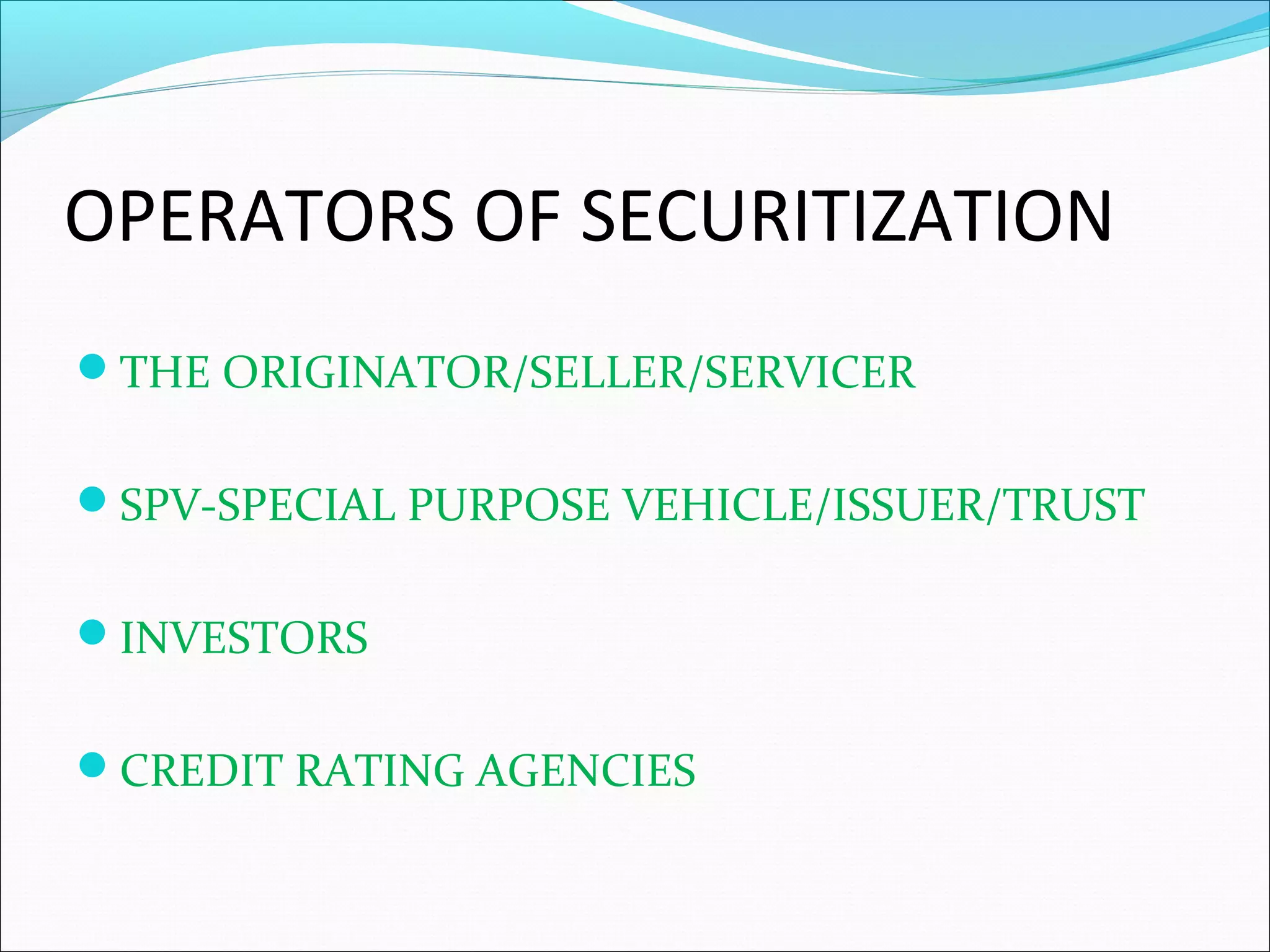

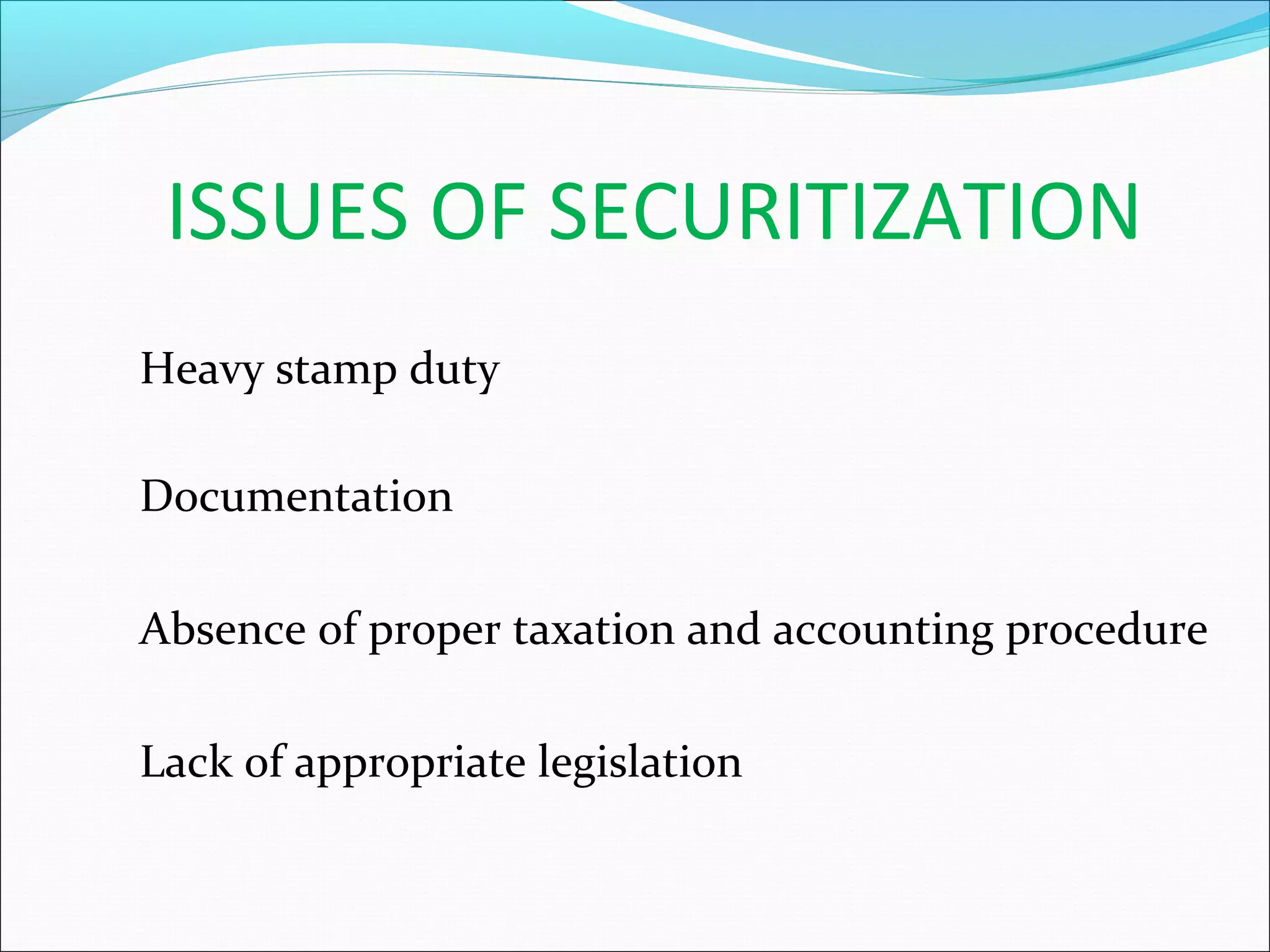



Securitization is a mechanism that pools illiquid assets and converts them into tradable securities. This transforms illiquid receivables into liquid assets and restructures balance sheets. Securitization serves as a powerful tool for financial reengineering. Common assets that are securitized include mortgages, loans, and receivables. Pioneers of securitization include the US, UK, France, Australia, and others. The first securitized asset was automobile loans. The securitization process involves credit rating the receivables, selling the assets to a special purpose vehicle which issues securities to investors to fund the asset purchase. Key players are the originator, SPV, investors, and credit rating agencies. Challenges











