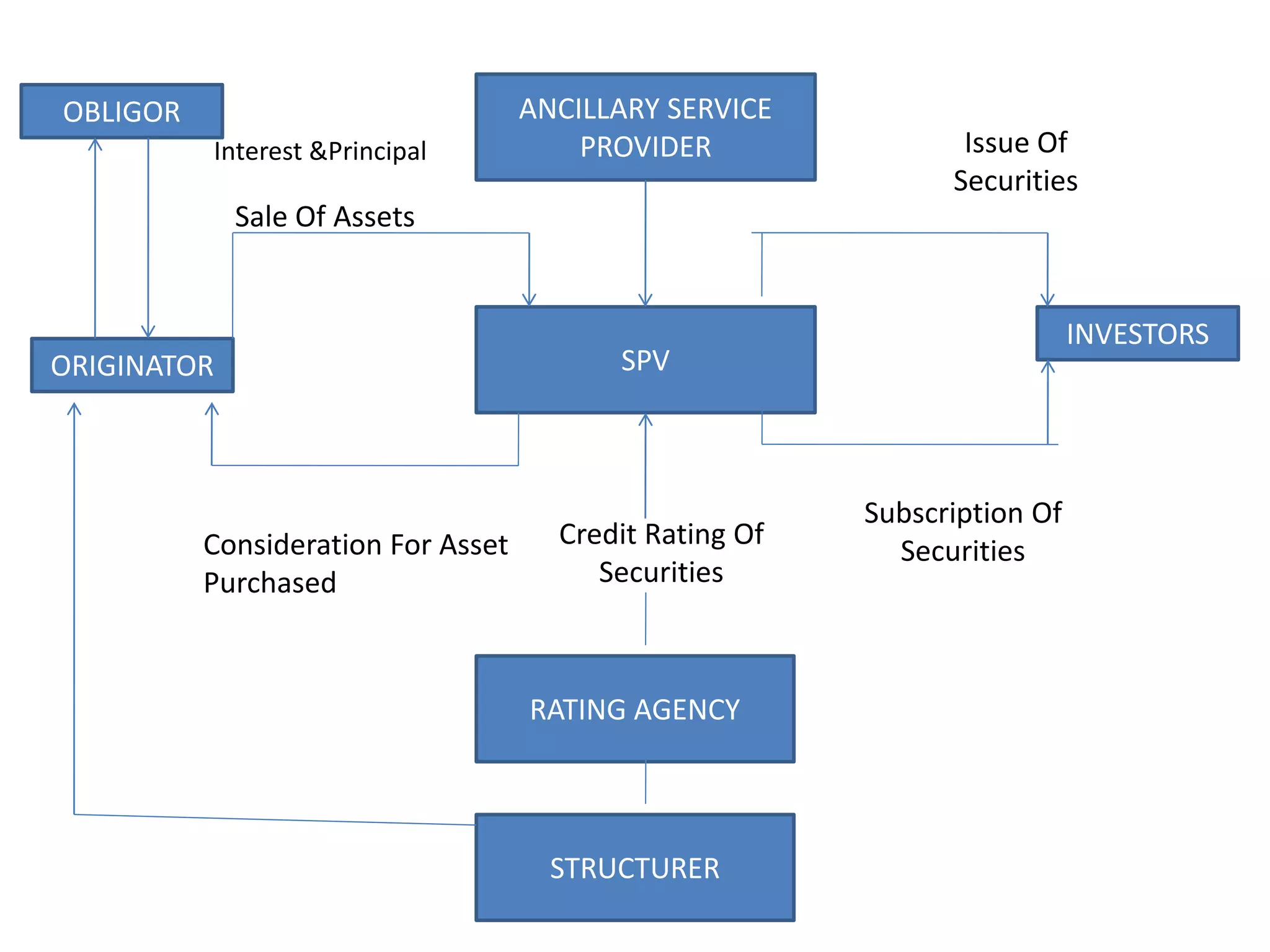
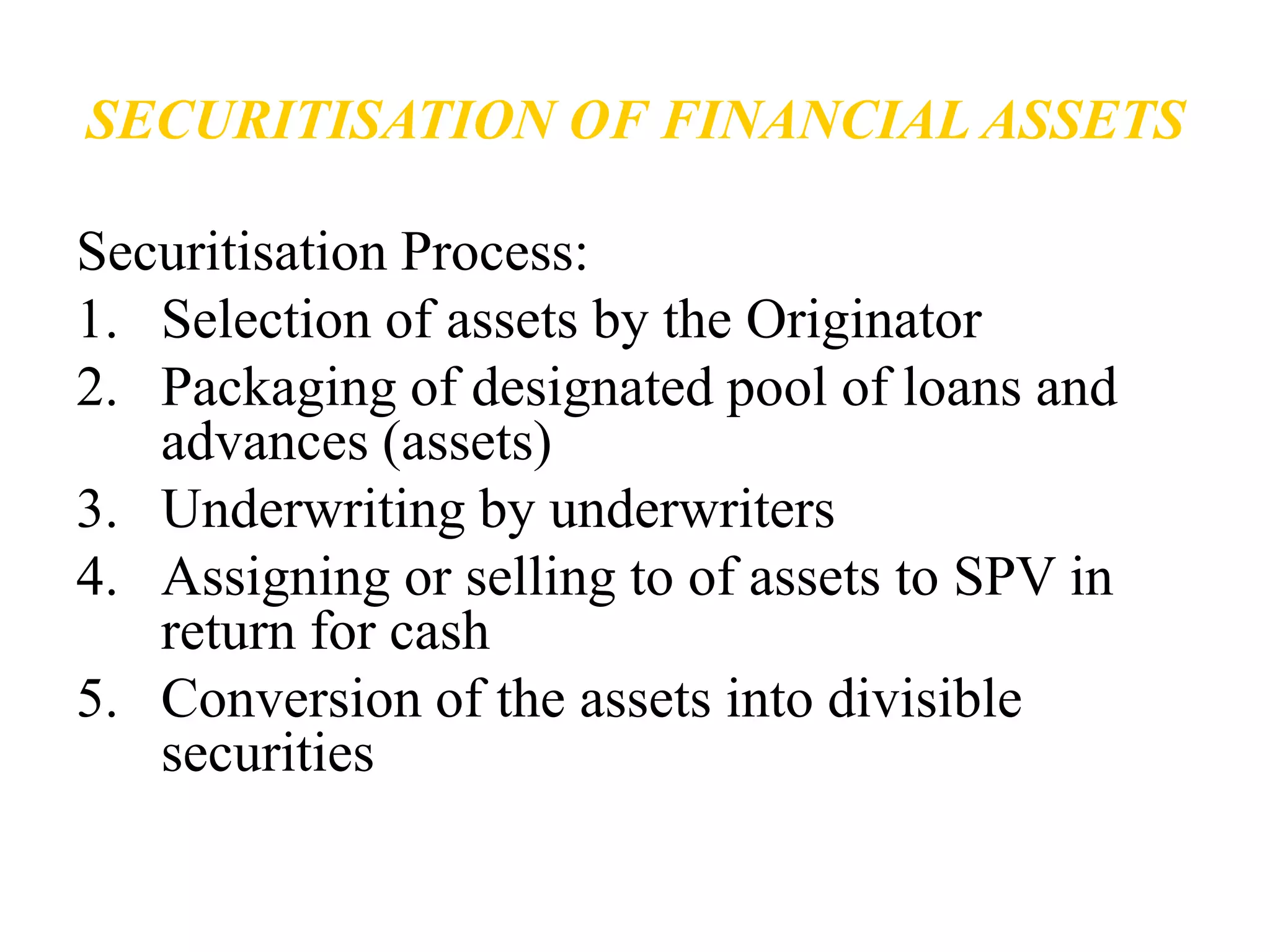
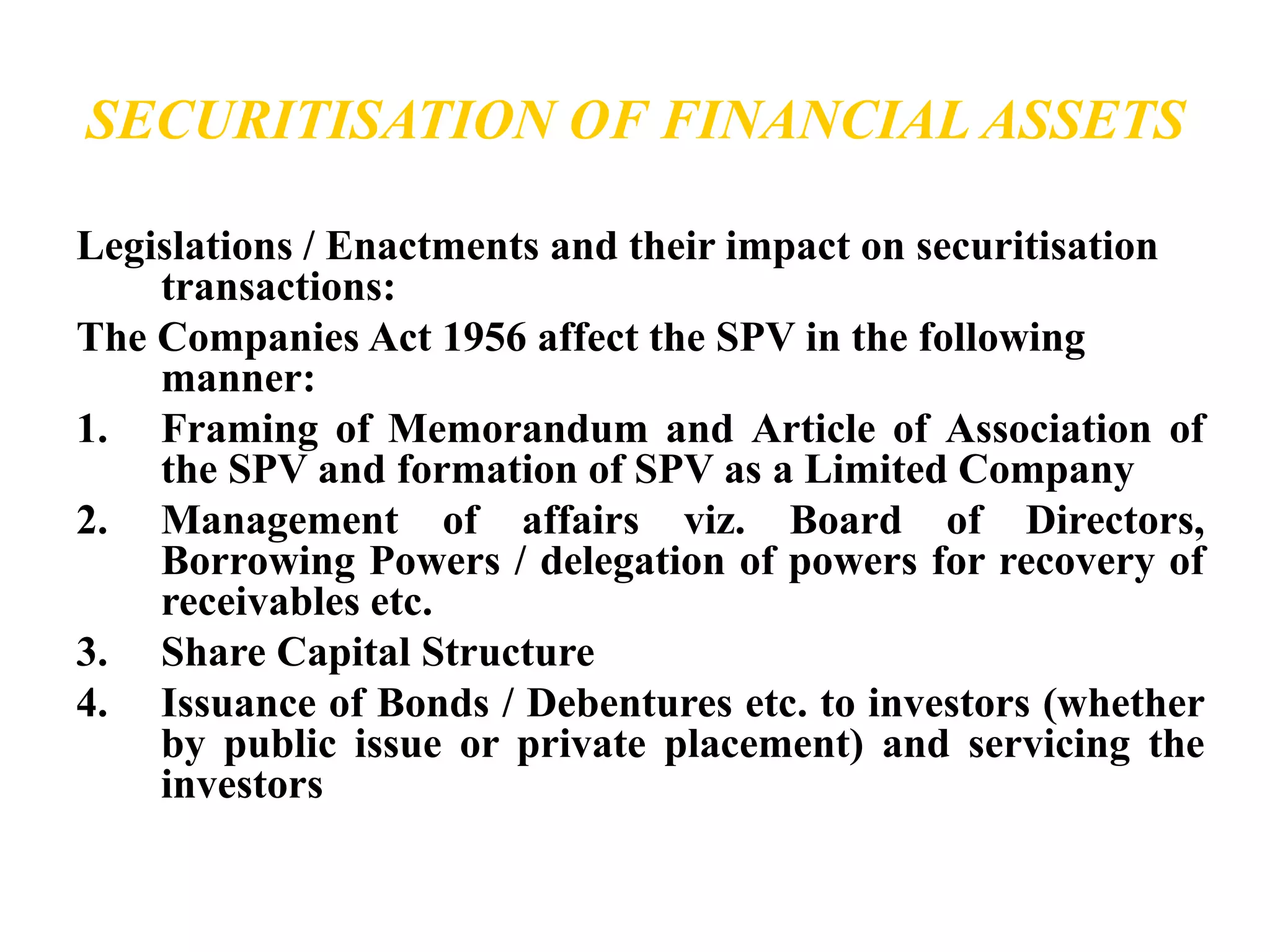
The document discusses securitization and mortgage loans. Securitization is the process of converting assets like mortgage loans into marketable securities that can be sold to investors. It allows banks to raise funds by pooling and repackaging their loans. The key aspects covered are the definition of securitization, the players involved like originators and SPVs, the securitization process, and some benefits like improving capital adequacy and providing an alternative funding source for banks. Examples of major mortgage companies in India and securitization companies are also provided.