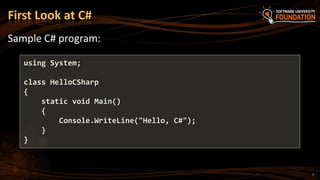
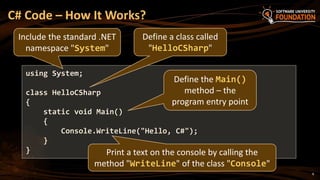
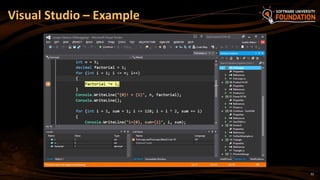
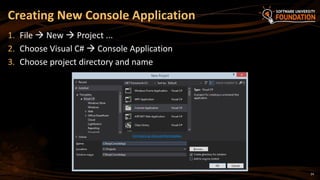
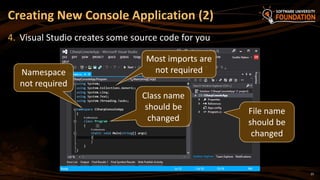
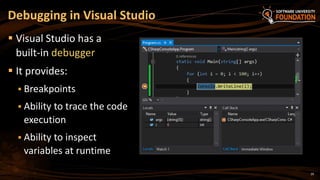
The document serves as an introduction to programming with a focus on C#, covering basic concepts of programming, the structure of a C# program, and the .NET framework. It includes details about Visual Studio as an integrated development environment, the importance of debugging, and how to utilize the MSDN library for documentation. The material is targeted towards beginners and provides a step-by-step guide for creating and running a C# program.




















![26
The process of compiling includes:
Syntactic checks
Type safety checks
Translation of the source code to lower level language (MSIL)
Creating executable files (assemblies)
You can start compilation by
Using Build->Build Solution/Project
Pressing [F6] or [Shift+Ctrl+B]
Compiling the Source Code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-200318122636/85/01-Introduction-to-Programming-26-320.jpg)
![27
The process of running application includes:
Compiling (if project not compiled)
Starting the application
You can run application by:
Using Debug->Start menu
By pressing [F5] or [Ctrl+F5]
* NOTE: Not all types of projects are able to be started!
Running Programs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-200318122636/85/01-Introduction-to-Programming-27-320.jpg)




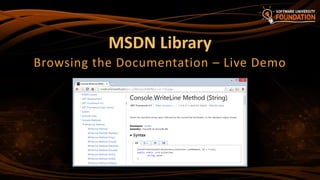
![37
Search in Google for certain class / method / property
E.g.
Or
Or
Use Visual Studio's built-in help system
Press [F1] in Visual Studio in the code
Browse http://msdn.microsoft.com
How to Use MSDN Library?
Press [F1] to view
the documentation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-200318122636/85/01-Introduction-to-Programming-37-320.jpg)