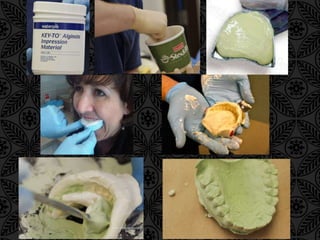
The document discusses impression materials used in dentistry. It defines an impression as a negative replica used to create a positive die or model. Desirable properties of impression materials include being soft and elastic to capture details, dimensionally stable, non-toxic, and economical. Materials are classified by their setting mechanism and elasticity, how they displace tissues, and their use for complete dentures versus dental impressions. The main classes are elastic materials like alginates and elastomers that change shape easily, and non-elastic materials like plaster that do not deform and are used for edentulous impressions.