More Related Content
Similar to Prealg pssg g094
Surface area of a cuboid and a cube,cylinder,cone,sphere,volume of cuboid,cyl...Surface area of a cuboid and a cube,cylinder,cone,sphere,volume of cuboid,cyl...kamal brar
Similar to Prealg pssg g094 (20)
More from Nene Thomas (20)
Prealg pssg g094
- 1. NAME ______________________________________________ DATE ____________ PERIOD _____
11-5 Surface Area: Pyramids and
Cones (Pages 578–582)
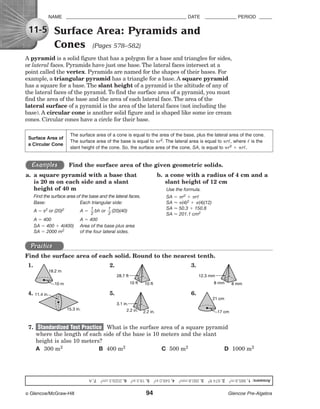
A pyramid is a solid figure that has a polygon for a base and triangles for sides,
or lateral faces. Pyramids have just one base. The lateral faces intersect at a
point called the vertex. Pyramids are named for the shapes of their bases. For
example, a triangular pyramid has a triangle for a base. A square pyramid
has a square for a base. The slant height of a pyramid is the altitude of any of
the lateral faces of the pyramid. To find the surface area of a pyramid, you must
find the area of the base and the area of each lateral face. The area of the
lateral surface of a pyramid is the area of the lateral faces (not including the
base). A circular cone is another solid figure and is shaped like some ice cream
cones. Circular cones have a circle for their base.
The surface area of a cone is equal to the area of the base, plus the lateral area of the cone.
Surface Area of
The surface area of the base is equal to r 2. The lateral area is equal to rᐉ, where ᐉ is the
a Circular Cone
slant height of the cone. So, the surface area of the cone, SA, is equal to r 2 ϩ rᐉ.
Examples Find the surface area of the given geometric solids.
a. a square pyramid with a base that b. a cone with a radius of 4 cm and a
is 20 m on each side and a slant slant height of 12 cm
height of 40 m Use the formula.
Find the surface area of the base and the lateral faces. SA ϭ r2 ϩ rᐉ
Base: Each triangular side: SA Ϸ (4)2 ϩ (4)(12)
1 1 SA Ϸ 50.3 ϩ 150.8
A ϭ s2 or (20)2 A ϭ ᎏ bh or ᎏ (20)(40)
2 2 SA Ϸ 201.1 cm2
A ϭ 400 A ϭ 400
SA ϭ 400 ϩ 4(400) Area of the base plus area
SA ϭ 2000 m2 of the four lateral sides.
Practice
Find the surface area of each solid. Round to the nearest tenth.
1. 2. 3.
18.2 m
28.7 ft 12.3 mm
10 m 10 ft 10 ft 8 mm 8 mm
4. 11.4 in. 5. 6.
21 cm
3.1 in.
15.3 in. 2.2 in. 2.2 in. 17 cm
7. Standardized Test Practice What is the surface area of a square pyramid
where the length of each side of the base is 10 meters and the slant
height is also 10 meters?
A 300 m2 B 400 m2 C 500 m2 D 1000 m2
Answers: 1. 885.9 m2 2. 674 ft2 3. 260.8 mm2 4. 548.0 in2 5. 18.5 in2 6. 2029.5 cm2 7. A
© Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 94 Glencoe Pre-Algebra