More Related Content Similar to Mitosis and meiosis Similar to Mitosis and meiosis (20) More from Mustafa Y. G. Younis More from Mustafa Y. G. Younis (9) 2. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
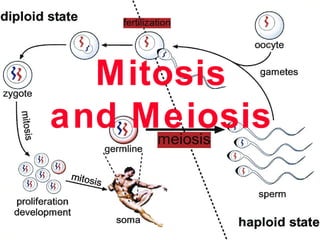
Chromosome number and genome size are reduced during a
specialized cell division called meiosis in order to keep the
genome size constant over successive generations.
3. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Mitosis: In The Beginning OneMitosis: In The Beginning One
Most of the organisms we see started out as one
cell
Humans start out as a single cell, the zygote,
formed by uniting a sperm and egg
The zygote divides to make approximately one
trillion cells
During the process of dividing, cells become
specialized to function in the various tissues and
organs of the body
Mitosis is the process of cell division in
eukaryotic cells
4. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Egg
1n
Haploid
nucleus
Fertilization Results In AFertilization Results In A
Diploid ZygoteDiploid Zygote
Sperm
1nHaploid
nucleus
5. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Sperm
1n
Fertilization Results In AFertilization Results In A
Diploid ZygoteDiploid Zygote
Egg
1n
Haploid
nucleus
Haploid
nucleus
6. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Sperm
1n
Fertilization Results In AFertilization Results In A
Diploid ZygoteDiploid Zygote
Egg
1n
Haploid
nucleus
Haploid
nucleus
7. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Sperm
1n
Fertilization Results In AFertilization Results In A
Diploid ZygoteDiploid Zygote
Egg
1n
Haploid
nucleus
Haploid
nucleus
8. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
From Zygote to EmbryoFrom Zygote to Embryo
Zygote
2n
Zygote
2n
9. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Cleavage
From Zygote to EmbryoFrom Zygote to Embryo
10. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Cleavage
From Zygote to EmbryoFrom Zygote to Embryo
11. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Cleavage
From Zygote to EmbryoFrom Zygote to Embryo
12. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Cleavage
From Zygote to EmbryoFrom Zygote to Embryo
14. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Why Cells Must DivideWhy Cells Must Divide
In multi-celled organisms (like humans) cells
specialize for specific functions thus the original
cells must divide to produce different kinds of
cells
Cells can only take in nutrients and excrete waste
products over the surface of the membrane that
surrounds them. The surface to volume ratio
decreases with the square of the volume (unless
special accommodations are made)
2 cm
Surface 24 cm2
/
volume 8 cm3
= 3
1 cm
Surface 6 cm2
/
volume 1cm3
= 6
15. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
The Cell LifecycleThe Cell Lifecycle
The cell lifecycle is well defined and can be
divided into four stages:
– Gap 1 (G1) - The growth phase in which most
cells are found most of the time
– Synthesis (S) - During which new DNA is
synthesized
– Gap 2 (G2) - The period during which no
transcription or translation occurs and final
preparations for division are made
– Mitosis - Cell division
16. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
G1
M
G2
S
The Cell Life CycleThe Cell Life Cycle
Gap 1 - Doubling
of cell size.
Regular cellular
activities.
transcription and
translation etc.
Synthesis of DNA -
Regular cell
activities cease and
a copy of all nuclear
DNA is made
Gap 2 - Final
preparation for
division
Mitosis - Cell
division
17. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of MitosisStages Of Mitosis
During mitosis an exact copy of the
genetic material in the “mother” cell
must be distributed to each “daughter”
cell
Each stage of mitosis is designed to
achieve equal and exact distribution of
the genetic material which has been
copied during the S phase of the cell
cycle
18. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of InterphaseStages Of Interphase
Interphase - The in between stage - Originally
interphase was thought to be a resting stage. Now
we know that this is the stage most cells spend
their time in as they do the things cells do
including, if they are preparing to divide, growing
and replicating their DNA
G1
M
G2
S
Interphase
19. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of MitosisStages Of Mitosis
Prophase - The beginning phase - DNA which
was unraveled and spread all over the nucleus is
condensed and packaged
Metaphase - Middle stage - Condensed
chromosomes line up along the equator of the
cell
Anaphase - One copy of each chromosome
moves to each pole of the cell
Telophase - End stage - New nuclear membranes
are formed around the chromosomes and
cytokinesis (cytoplasm division) occurs resulting
in two daughter cells
20. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of MitosisStages Of Mitosis
Interphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Metaphase
Mitotic
spindle
Prophase
Nucleus with un-
condensed
chromosomes Equator
of the cell
Condensed
chromosomes
Disappearing
nuclear
membrane
Poles of
the cell
Mother cell
Two
daughter
cells
Metaphase
plate
21. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Controlling The Cell CycleControlling The Cell Cycle
CDC Mutants - Cell Division Cycle mutants helped
elucidate genetic control points of the cell cycle
Three major checkpoints controlled by Cyclin
dependant kinase (Cdk) proteins which add
phosphates to cyclin proteins changing their
activity:
1 G1S - Monitors cell size and checks for DNA
damage
2 G2M - Ensures physiological conditions are right
for division including completion of DNA
replication and any necessary repair
3 M - Checks for successful formation of the mitotic
22. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Meiosis: In The Beginning TwoMeiosis: In The Beginning Two
Humans and many other complex multi-
celled organisms incorporate genetic
recombination in their reproduction
Reproduction in which there is a re-mixing
of the genetic material is called sexual
reproduction
Two cells, a sperm and an egg, unite to form
a zygote, the single cell from which the
organism develops
Meiosis is the process of producing sperm
and eggs (gametes)
23. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Gametes Are HaploidGametes Are Haploid
Gametes must have half the genetic material of a
normal cell
If the genetic material in the gametes was not
halved, when they combined the zygote would
have more genetic material than the parents
Meiosis is specialized cell division resulting in
cells with half the genetic material of the parents
Gametes have exactly one set of chromosomes,
this state is called haploid (1n)
Regular cells have two sets of chromosomes, this
state is called diploid (2n)
24. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of MeiosisStages Of Meiosis
Meiosis resembles mitosis except that it is
actually two divisions not one
These divisions are called Meiosis I and
Meiosis II
Meiosis I results in haploid cells with
chromosomes made up of two chromotids
Meiosis II is essentially mitosis on haploid
cells
Stages of meiosis resemble mitosis with two
critical differences: 1) in prophase I 2)
Metaphase I
25. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of Meiosis - Meiosis IStages Of Meiosis - Meiosis I
Prophase I - The beginning phase -
– DNA which was unraveled and spread all
over the nucleus is condensed and packaged
– Homologous chromosomes (each made of
two identical chromatids) come together and
form tetrads (4 chromatids)
– Crossing over, in which chromatids within
tetrads exchange genetic material, occurs
Metaphase I - Middle stage - Tetrads line
up along the equator of the cell
26. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of Meiosis - Meiosis IStages Of Meiosis - Meiosis I
Anaphase I - One copy of each
chromosome still composed of two
chromatids moves to each pole of the cell
Telophase I - End stage - New nuclear
membranes are formed around the
chromosomes and cytokinesis (cytoplasm
division) occurs resulting in two haploid
daughter cells
27. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Stages Of Meiosis - Meiosis IIStages Of Meiosis - Meiosis II
Prophase II - Cells do not typically go into
interphase between meiosis I and II, thus
chromosomes are already condensed
Metaphase II - Chromosomes line up at the
equator of the two haploid cells produced in
meiosis I
Anaphase II - Chromosomes made up of two
chromatids split to make chromosomes with one
chromatid which migrate to the poles of the cells
Telophase II - Cytokinesis and reformation of
the nuclear membrane in haploid cells each with
one set of chromosomes made of one chromatid
28. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Interphase
Mother cell Stages Of Meiosis:Stages Of Meiosis:
Meiosis IMeiosis I
Meiosis II
Prophase I:
Tetrad formation/
crossing over
Metaphase I
Telophase I
Prophase I:
Condensing
Chromosomes
Anaphase I
29. Telophase I
Stages Of Meiosis:Stages Of Meiosis:
Meiosis IIMeiosis II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
The products of
mitosis are 2 diploid
cells with identical
chromosomes.
The products of meiosis are 4
haploid cells each with a
unique set of chromosomes.
Prophase II
30. ©2000 Timothy G. Standish
Prophase I:
Tetrad formation/
crossing over
Crossing OverCrossing Over
Anaphase I
Telophase II
Metaphase I
Telophase IBecause of crossing over, every
gamete receives a unique set of
genetic information.