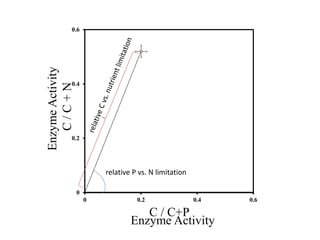
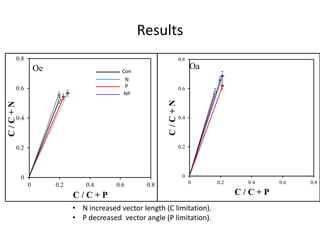
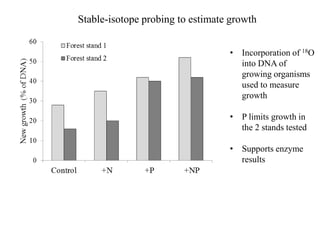
1) The study measured soil enzyme activities to determine whether nitrogen or phosphorus limits microbial decomposer growth.
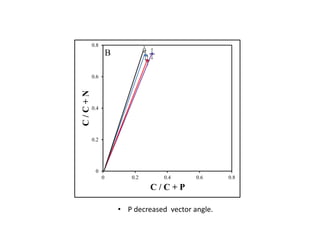
2) It found that phosphatase enzyme activity was higher, indicating higher microbial demand for and limitation by phosphorus.
3) Stable isotope probing also supported phosphorus as the limiting nutrient, showing lower microbial growth in soils with phosphorus limitation.