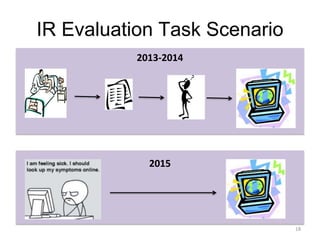
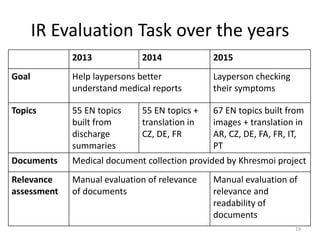
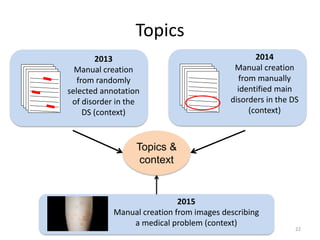
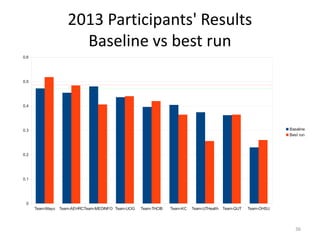
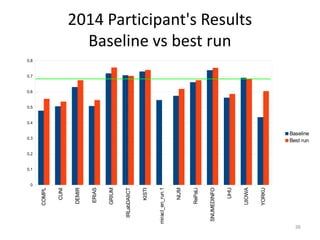
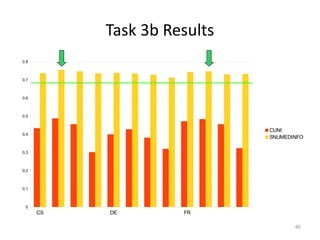
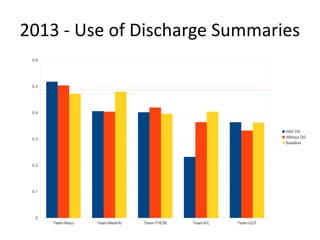
The document provides an overview of the CLEF eHealth evaluation tasks focused on medical information retrieval (IR) and its assessment, highlighting the significant gap in the patient-centered evaluation domain. It discusses the complexities faced by medical professionals and patients in finding relevant medical data, the methodologies used for IR evaluation, and the various tasks conducted between 2013 and 2015. Additionally, it emphasizes the creation of datasets and collaboration among participants to enhance IR systems for better healthcare solutions.













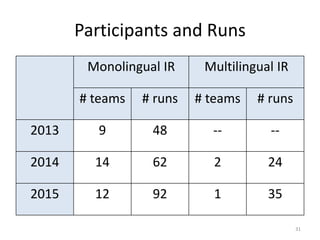
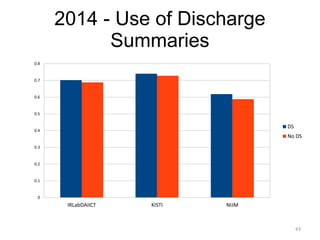
![Datasets - Summary
• Provided to the participants:
• Document collection
• Discharge summaries (optional) [2013-2014]
• Training set:
– 5 queries + qrels [2013]
– 5 queries (+ translation) + qrels [2014-2015]
• Test set:
– 50 queries [2013]
– 50 queries (+ translation) [2014]
– 62 queries (+ translation) [2015]
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-150518130228-lva1-app6892/85/Medical-Information-Retrieval-and-its-Evaluation-an-Overview-of-CLEF-eHealth-Evaluation-Task-24-320.jpg)


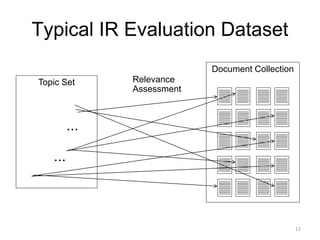
![Relevance Assessment
Manual relevance assessment conducted by medical
professionals and IR experts
4-point scale assessment mapped to a binary scale
– {0: non relevant, 1: on topic but unreliable} → non
relevant
– {2: somewhat relevant, 3: relevant} → relevant
4-point scale for NDCG and 2-point scale for precision
[2015] Manual assessment of the readability of the
documents conducted by the same assessors on a 4-
point scale
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-150518130228-lva1-app6892/85/Medical-Information-Retrieval-and-its-Evaluation-an-Overview-of-CLEF-eHealth-Evaluation-Task-27-320.jpg)














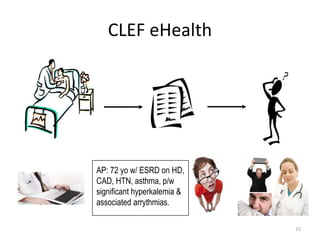
![Task 3a - Topic Generation Process (1)
Discharge Medications:
1. Aspirin 81 mg Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.) Sig: One (1) Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.) PO
DAILY (Daily). Disp:*30 Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.)(s)* Refills:*0*
2. Docusate Sodium 100 mg Capsule Sig: One (1) Capsule PO BID (2 times a day). Disp:*60
Capsule(s)* Refills:*0*
3. Levothyroxine Sodium 200 mcg Tablet Sig: One (1) Tablet PO DAILY (Daily).
Discharge Disposition:
Extended Care
Facility:
[**Hospital 5805**] Manor - [**Location (un) 348**]
Discharge Diagnosis:
Coronary artery disease.
s/p CABG
post op atrial fibrillation
54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-150518130228-lva1-app6892/85/Medical-Information-Retrieval-and-its-Evaluation-an-Overview-of-CLEF-eHealth-Evaluation-Task-54-320.jpg)
![Task 3a - Topic Generation Process (2)
Discharge Medications:
1. Aspirin 81 mg Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.) Sig: One (1) Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.) PO
DAILY (Daily). Disp:*30 Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.)(s)* Refills:*0*
2. Docusate Sodium 100 mg Capsule Sig: One (1) Capsule PO BID (2 times a day). Disp:*60
Capsule(s)* Refills:*0*
3. Levothyroxine Sodium 200 mcg Tablet Sig: One (1) Tablet PO DAILY (Daily).
Discharge Disposition:
Extended Care
Facility:
[**Hospital 5805**] Manor - [**Location (un) 348**]
Discharge Diagnosis:
Coronary artery disease.
s/p CABG
post op atrial fibrillation
55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-150518130228-lva1-app6892/85/Medical-Information-Retrieval-and-its-Evaluation-an-Overview-of-CLEF-eHealth-Evaluation-Task-55-320.jpg)
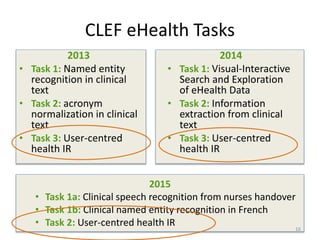
![Task 3a - Topic Generation Process (3)
Discharge Medications:
1. Aspirin 81 mg Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.) Sig: One (1) Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.) PO
DAILY (Daily). Disp:*30 Tablet, Delayed Release (E.C.)(s)* Refills:*0*
2. Docusate Sodium 100 mg Capsule Sig: One (1) Capsule PO BID (2 times a day). Disp:*60
Capsule(s)* Refills:*0*
3. Levothyroxine Sodium 200 mcg Tablet Sig: One (1) Tablet PO DAILY (Daily).
Discharge Disposition:
Extended Care
Facility:
[**Hospital 5805**] Manor - [**Location (un) 348**]
Discharge Diagnosis:
Coronary artery disease.
s/p CABG
post op atrial fibrillation
What is coronary heart disease?
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-150518130228-lva1-app6892/85/Medical-Information-Retrieval-and-its-Evaluation-an-Overview-of-CLEF-eHealth-Evaluation-Task-56-320.jpg)