MGT101 - Financial Accounting- Lecture 29
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•437 views
Virtual University Course MGT101 - Financial Accounting Lecture No 29 Instructor's Name: Mr. Mujahid Eshai Course Email: mgt101@vu.edu.pk
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (18)
MTH101 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry- Lecture 44

MTH101 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry- Lecture 44
More from Bilal Ahmed
More from Bilal Ahmed (20)
Recently uploaded
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
https://app.box.com/s/x7vf0j7xaxl2hlczxm3ny497y4yto33i80 ĐỀ THI THỬ TUYỂN SINH TIẾNG ANH VÀO 10 SỞ GD – ĐT THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH NĂ...

80 ĐỀ THI THỬ TUYỂN SINH TIẾNG ANH VÀO 10 SỞ GD – ĐT THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH NĂ...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Recently uploaded (20)
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions

Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...

Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...
80 ĐỀ THI THỬ TUYỂN SINH TIẾNG ANH VÀO 10 SỞ GD – ĐT THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH NĂ...

80 ĐỀ THI THỬ TUYỂN SINH TIẾNG ANH VÀO 10 SỞ GD – ĐT THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH NĂ...
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx

Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx
On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows

On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows
Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf

Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
MGT101 - Financial Accounting- Lecture 29
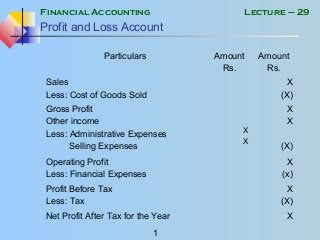
- 1. Financial Accounting 1 Lecture – 29 Profit and Loss Account Particulars Amount Rs. Amount Rs. Sales Less: Cost of Goods Sold X (X) Gross Profit Other income Less: Administrative Expenses Selling Expenses X X X X (X) Operating Profit Less: Financial Expenses X (x) Profit Before Tax Less: Tax X (X) Net Profit After Tax for the Year X
- 2. Financial Accounting 2 Lecture – 29 Profit and Loss Account • Sales Sales are the revenue against the sale of the product in which the organization deals. In case of a service organization, there will be Income Against Services Rendered instead of Sales and there will be no Cost of Sales or Gross Profit. • Cost of Goods Sold / Gross Profit It is the direct cost incurred to manufacture the goods that are sold during the period. Gross Profit = Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
- 3. Financial Accounting 3 Lecture – 29 Profit and Loss Account • Other Income Other income includes revenue from indirect source of income, such as return on investment, profit on PLS account, Sale of scrap etc. • Administrative and Selling Expenses All costs that are incurred for the purpose of business but are not directly related to production are classified in Admin and Selling Expenses. • All expenses should be distributed properly among the three classifications i.e. Cost of Goods Sold, Administrative Expenses and Selling Expenses to present the financial statements fairly.
- 4. Financial Accounting 4 Lecture – 29 Profit and Loss Account • Financial Expenses Financial expense are the cost / interest paid on loans taken by the organization. These are shown separately in the Profit and Loss Account
- 5. Financial Accounting 5 Lecture – 29 Profit and Loss Account • Income Tax Income Tax is paid on Net Profit. At the time of preparing annual financial statements, an estimate of expected tax liability is made. A provision is then created equal to that estimate. The treatment of Provision for tax is same as that of provision for Doubtful debts. i.e. provision is made at the time of preparing accounts which then adjusted accordingly at the time actual tax expense is known.
- 6. Financial Accounting 6 Lecture – 29 Balance Sheet (Assets) Particulars Amount Rs. Amount Rs. Assets Non Current Assets Fixed Assets Capital Work In Progress Deferred Costs Long Term Investments Current Assets Stocks Trade debtors and Other Receivables Prepayments Short Term Investments Cash and Bank Liabilities Capital x Profit x X X X X X X X X X x Long Term Liabilities Short Term Liabilities x x Total x Total x
- 7. Financial Accounting 7 Lecture – 29 Balance Sheet (Assets) Particulars Amount Rs. Amount Rs. Assets Non Current Assets Fixed Assets Capital Work In Progress Deferred Costs Long Term Investments X X X X Current Assets Stocks Trade debtors and Other Receivables Prepayments Short Term Investments Cash and Bank X X X X X X X Total X
- 8. Financial Accounting 8 Lecture – 29 Balance Sheet (Assets) • Fixed Assets Assets purchased not for resale are called fixed assets and these are presented at cost less accumulated depreciation OR revalued amount. • Capital Work in Progress A fixed asset under completion is shown under this head. At the time of completion it is transferred to fixed assets. • Deferred Costs These are revenue expenditures that benefit the organization for a period longer than one year. These are, therefore, initially shown in balance sheet and then charged to profit and loss (amortized) over the period they are expected to provide benefit to the organization.
- 9. Financial Accounting 9 Lecture – 29 Balance Sheet (Assets) • Long Term and Short Term Investments Investments made with the intention that they will be held for a period longer than twelve months are classified as long term and those made for a period shorter than 12 months are classified as short term.
- 10. Financial Accounting 10 Lecture – 29 Balance Sheet (Assets) Following things are important to note here: o Classification is to be made every time a balance sheet is prepared and the period is to be calculated from the date of balance sheet. o An investment may initially be made as a current investment. Subsequently, if it is decided to hold it for a longer period. Then, its classification will have to be changed accordingly and vice versa. Therefore, investments are checked for classification every time a balance sheet is prepared and presented accordingly.
