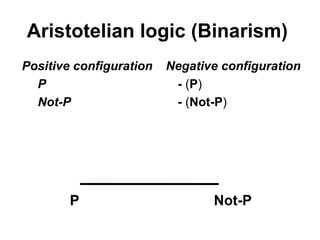
The document discusses the concept of catuskoti, or tetralemma, in relation to Aristotelian logic and its implications in mathematics, philosophy, and quantum computing. It highlights the complexities of relationships, subjective reality, and the overlap of subjective experiences, challenging the notion of objective reality. References to Buddhist philosophy and modern science are included to illustrate the differences in perspectives regarding existence and observation.