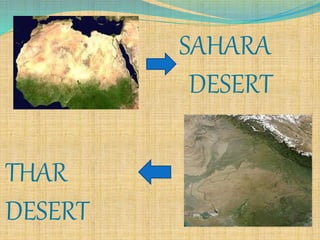
Sahara and Thar Desert Comparison
- 2. The Sahara is also known as ‘The Great Desert’ is the largest Subtropical hot desert and third largest desert after Antarctica and the Arctic. The Thar Desert also known as ‘The Great Indian Desert’ is a large, arid region in the northwestern part of the Indian Subcontinent that forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 9th largest subtropical desert.
- 3. Saharaspreads over 9,400,000 square kilometres and covers most of North Africa . . The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea in the east, including parts of the Mediterranean, to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. To the south, it is delimited by the Sahel, a belt of semi-arid tropical savanna that composes the northern region of central and western Sub-Saharan Africa.
- 4. The desert landforms of the Sahara are shaped by wind or by extremely rare rainfall and include sand dunes and dune fields or sand seas, stone plateaus , gravel plains , dry valleys , dry lakes and salt flats. Unusual landforms include the Richat Structure in Mauritania. Several deeply dissected mountains and mountain ranges, many volcanic, rise from the desert, including the Aïr Mountains, Ahaggar Mountains, Saharan Atlas, Tibesti Mountains, Adrar des Iforas, and the Red Sea hills. The highest peak in the Sahara is Emi Koussi, ashield volcano in the Tibesti range of northern Chad.
- 5. The soil of the Thar Desert remains dry for much of the year and is prone to wind erosion. High velocity winds blow soil from the desert, depositing some on neighboring fertile lands, and causing shifting sand dunes within the desert. . Sand dunes are stabilised by erecting micro-windbreak barriers with scrub material and subsequent afforestation of the treated dunes with seedlings of shrubs such as phog,senna, castor oil plant and trees such as gum acacia, Prosopis juliflora and lebbek tree.
- 9. Occupation The Thar Desert is one of most heavily populated desert areas in the world and the main occupations of people living here are agriculture and animal husbandry. Agriculture is not a dependable proposition in this area— after the rainy season, at least 33% of crops fail. Animal husbandry, trees and grasses, intercropped with vegetables or fruit trees, is the most viable model for arid, drought- prone regions. The region faces frequent droughts. Overgrazing due to high animal populations, wind and water erosion, mining and other industries result in serious land degradation.
- 10. FLORA And FAUNA The Saharan flora comprises around 2800 species of vascular plants. Approximately a quarter of these are endemic. About half of these species are common to the flora of the Arabian deserts. FAUNA comprises of many species like cheetah etc. The central Sahara is estimated to include five hundred species of plants, which is extremely low considering the huge extent of the area. Plants such as acacia trees, palms, succulents, spiny shrubs, and grasses have adapted to the arid conditions, by growing lower to avoid water loss by strong winds, by storing water in their thick stems to use it in dry periods, by having long roots that travel horizontally to reach the maximum area of water and to find any surface moisture and by having small thick leaves or needles to prevent water loss by evapo- transpiration. Plant leaves may dry out totally and then recover.
- 11. FLORA And FAUNA Stretches of sand in the desert are interspersed by hillocks and sandy and gravel plains. Due to the diversified habitat and ecosystem, the vegetation, human culture and animal life in this arid region is very rich in contrast to the other deserts of the world. About 23 species of lizard and 25 species of snakes are found here and several of them are endemic to the region. Some wildlife species, which are fast vanishing in other parts of India, are found in the desert in large numbers such as the blackbuck, chinkara and Indian wild ass in the Rann of Kutch. They have evolved excellent survival strategies, their size is smaller than other similar animals living in different conditions, and they are mainly nocturnal. There are certain other factors responsible for the survival of these animals in the desert. Due to the lack of water in this region, transformation of the grasslands into cropland has been very slow. The protection provided to them by a local community, the Bishnois, is also a factor. Other mammals of the Thar Desert include a subspecies of red fox and the caracal.
- 12. THAR DESERT
- 13. SAHARA DESERT
- 14. MAP OF SAHARA
- 15. MAP OF THAR
- 16. A NATURAL ROCK ARCH IN SAHARA DESERT