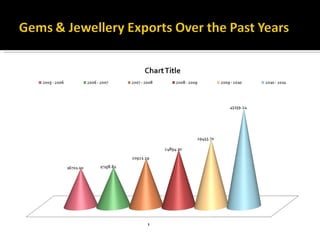
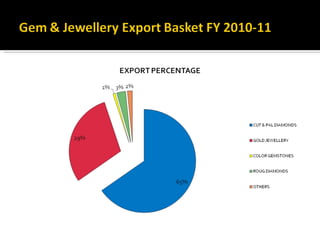
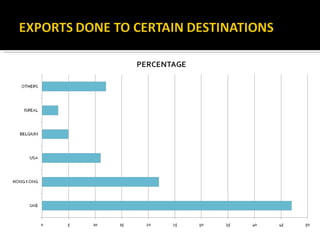
The Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) was established in 1966 to promote India's gem and jewelry exports. It has played a key role in developing the industry and establishing India as a prominent global player. GJEPC works to create a pool of trained artisans and designers to international standards to consolidate the Indian jewelry industry. It provides various export promotion services and advisory support to members and the government. GJEPC also operates several training institutions to develop skills and expertise in the industry.