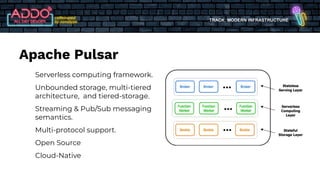
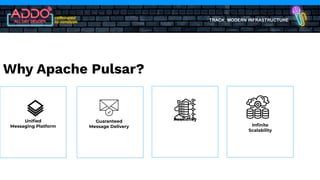
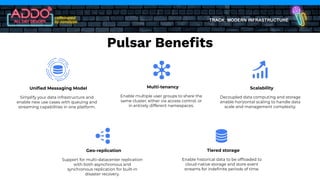
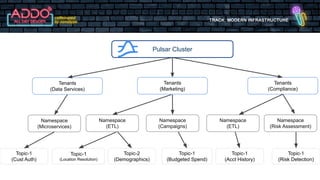
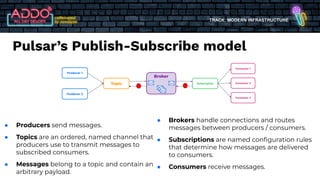
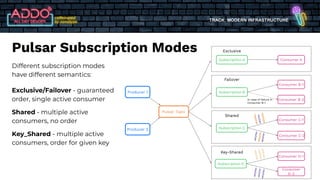
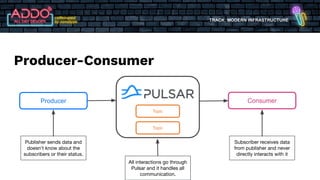
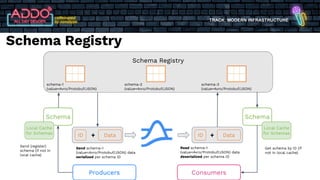
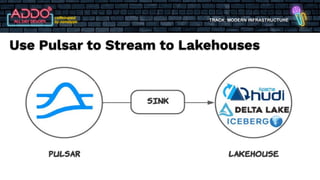
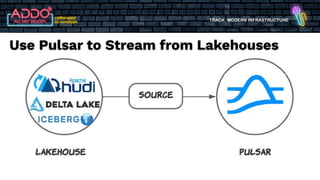
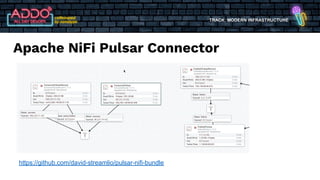
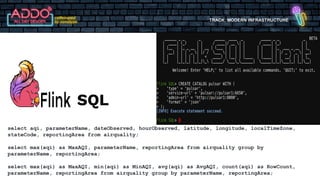
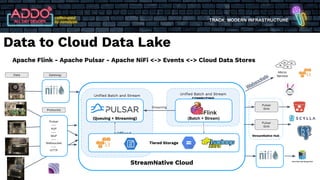
The document discusses the modern infrastructure utilizing Apache Pulsar, Flink, and NiFi for cloud data lakes and streaming systems. It highlights Pulsar's unified messaging platform that ensures guaranteed message delivery, scalability, and multi-tenant support for various data use cases, alongside insights into NiFi and Flink's functionalities for data processing. The document also features the benefits of combining these technologies to enhance data management and analytics capabilities.