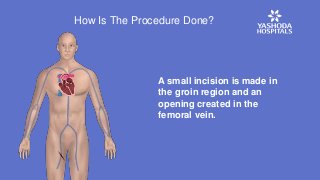
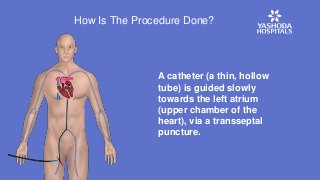
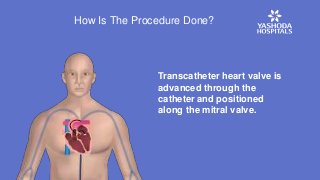
Heart valve replacements were conventionally done through open-heart surgery. But TMVR is giving new hope to patients with mitral valve disease.
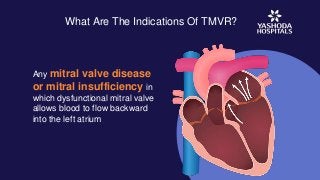
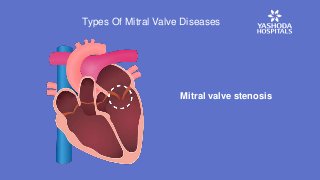
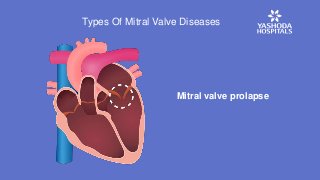
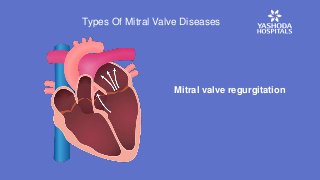
The disease may be caused either due to mitral valve stenosis or mitral valve regurgitation. In the former, the mitral valve narrows and obstructs the blood flow while in the latter, the valve allows blood to leak in both directions inside the heart.
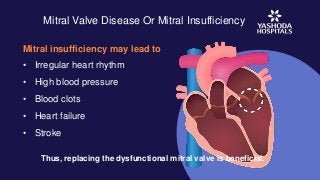
Mitral valve replacement is commonly performed to treat these conditions. The procedure requires the placement of a heart valve. It can be either a tissue heart valve or a metallic heart valve. They both offer different benefits. However, tissue heart valves are preferred for older patients as they require blood thinner medication for a shorter period of time.
However, tissue prosthetic valves can degenerate over time and not work properly. Traditionally, the management of such a case would require second open-heart surgery to replace the tissue heart valve. However, this increases the patient’s risk of complications.
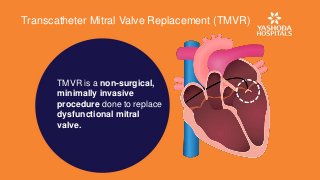
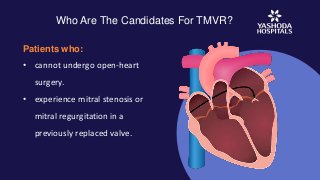
Transcatheter mitral valve replacement resolves the issue as it is a minimally invasive procedure that provides maximized benefits with minimal risk. It is a percutaneous procedure that helps to accomplish TMVI valve-in-valve procedure with reduced complications.
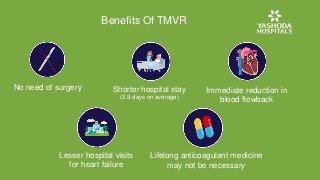
The procedure takes only an hour, and the patient can be discharged in 2-3 days. Medical technology has come a long way, and Yashoda Hospitals is keeping up!