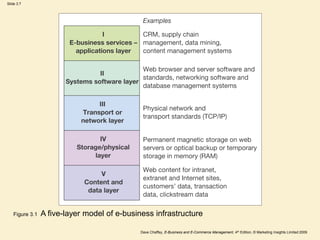
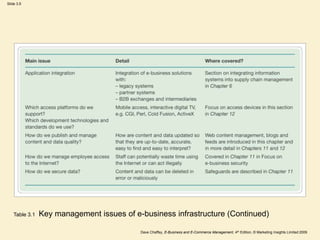
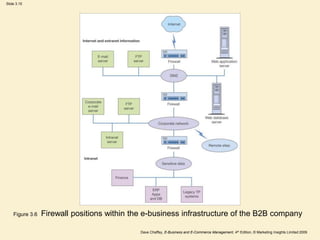
This document outlines the key components of an e-business infrastructure, including hardware, software, and management issues. It discusses the various layers of infrastructure, from physical infrastructure like servers and networks to applications and content. Several figures and tables illustrate examples like infrastructure models and common management issues. The document aims to describe the technical aspects and jargon involved in e-business infrastructure for business managers. It includes several activities for readers to identify infrastructure risks, components, and potential ways to increase usage of internal networks.