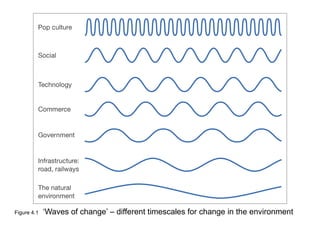
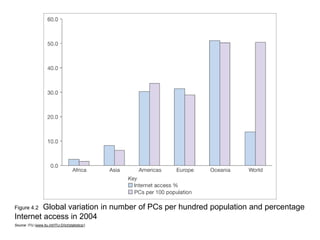
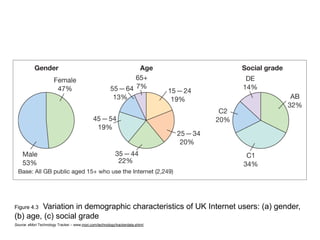
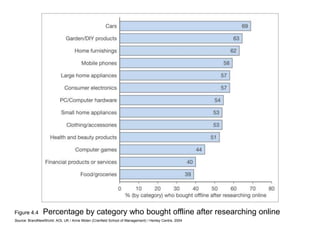
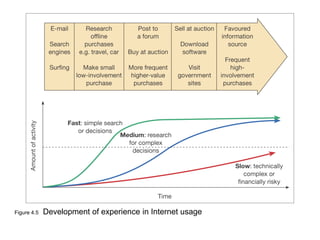
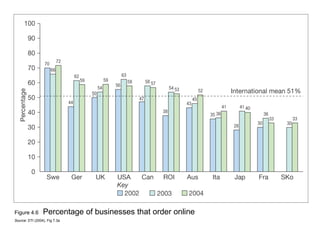
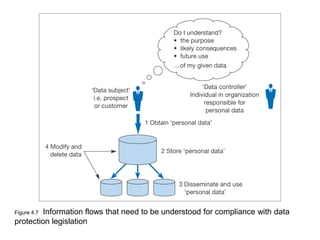
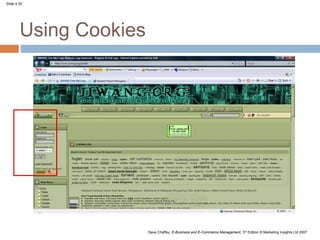
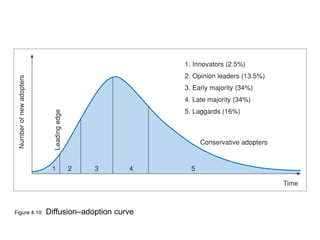
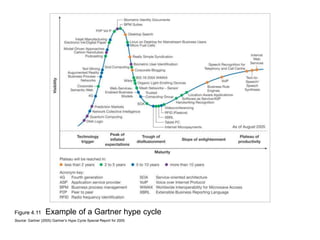
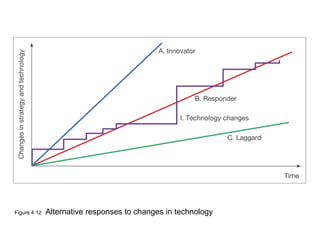
This document discusses the macro-environment factors that impact e-business and e-commerce strategy. It covers the SLEPT framework for analyzing social, legal, economic, political and technological factors. Specific issues covered include privacy, data protection legislation, cookies, spam laws, and how factors like access to technology, trust and costs influence adoption of digital services. Environmental scanning is important so companies can respond to changes and comply with regulations.