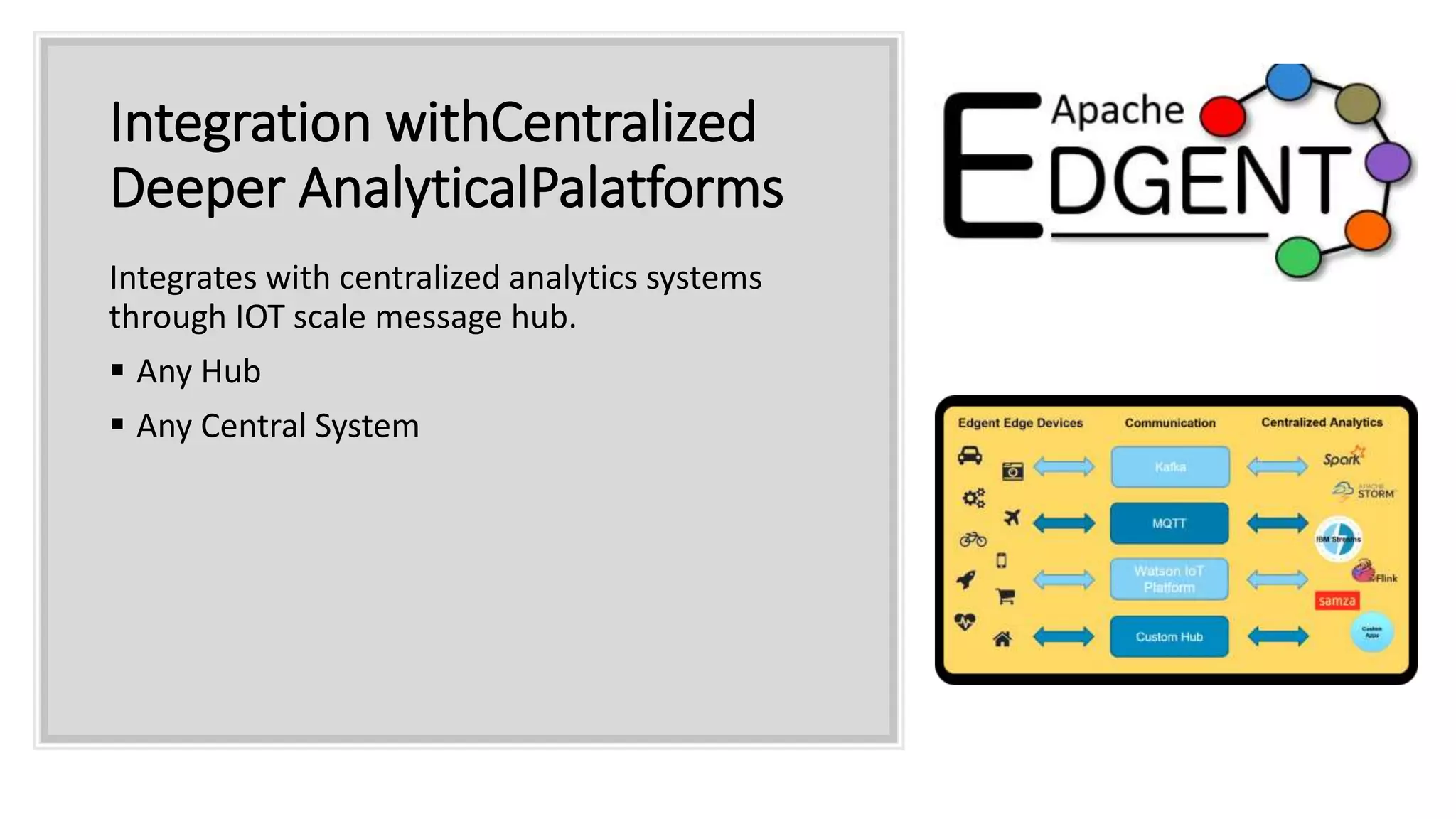
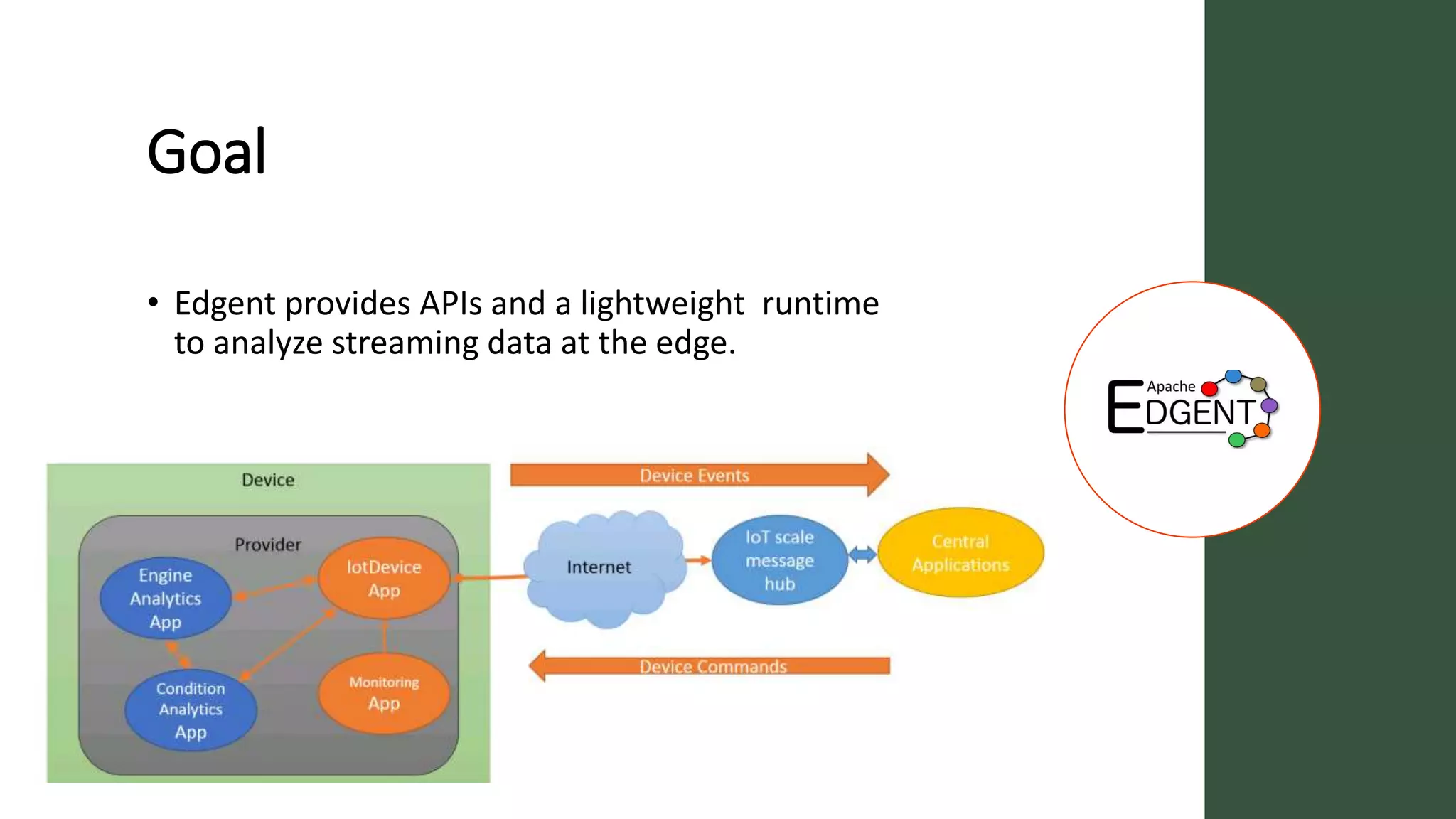
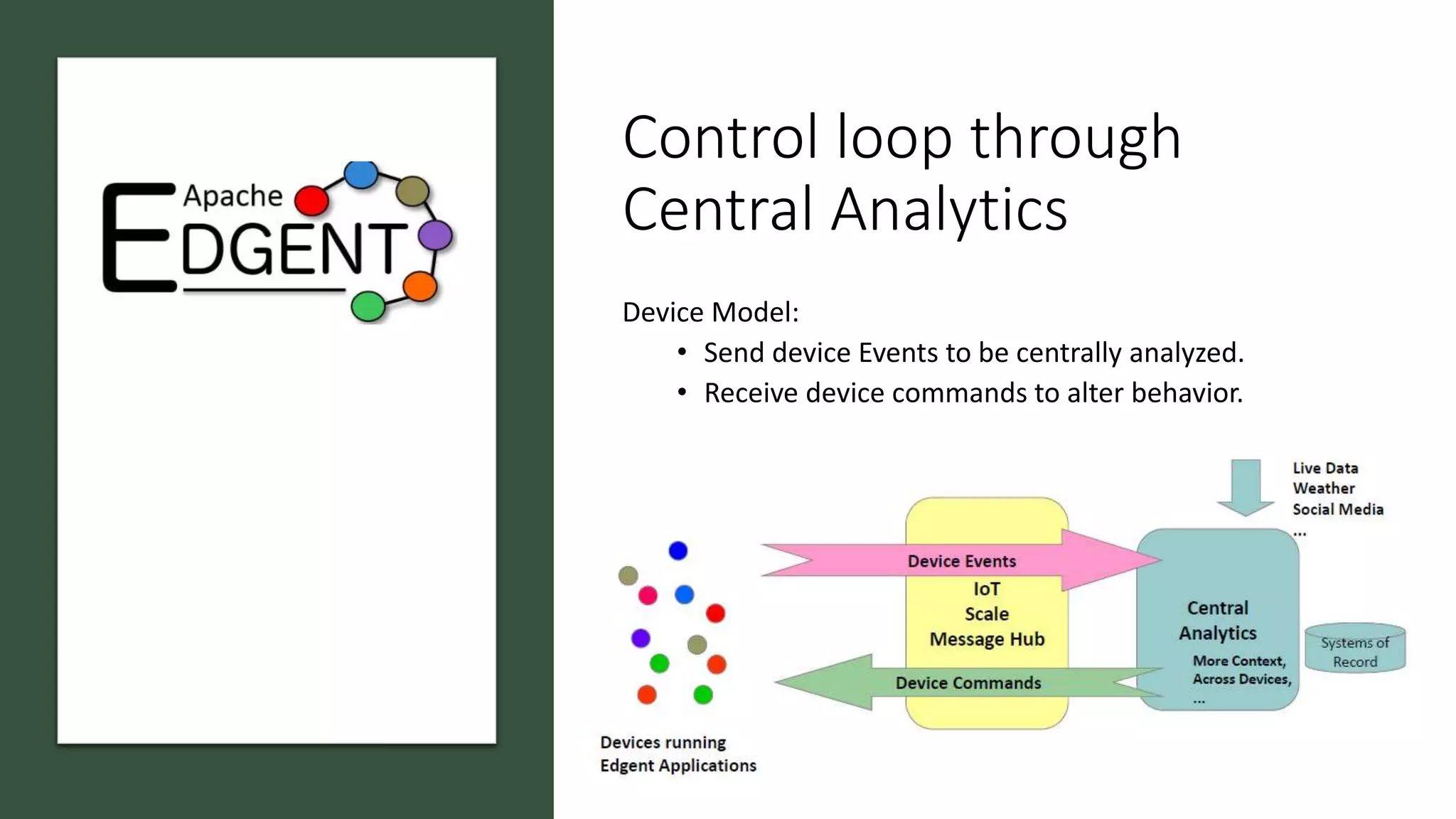
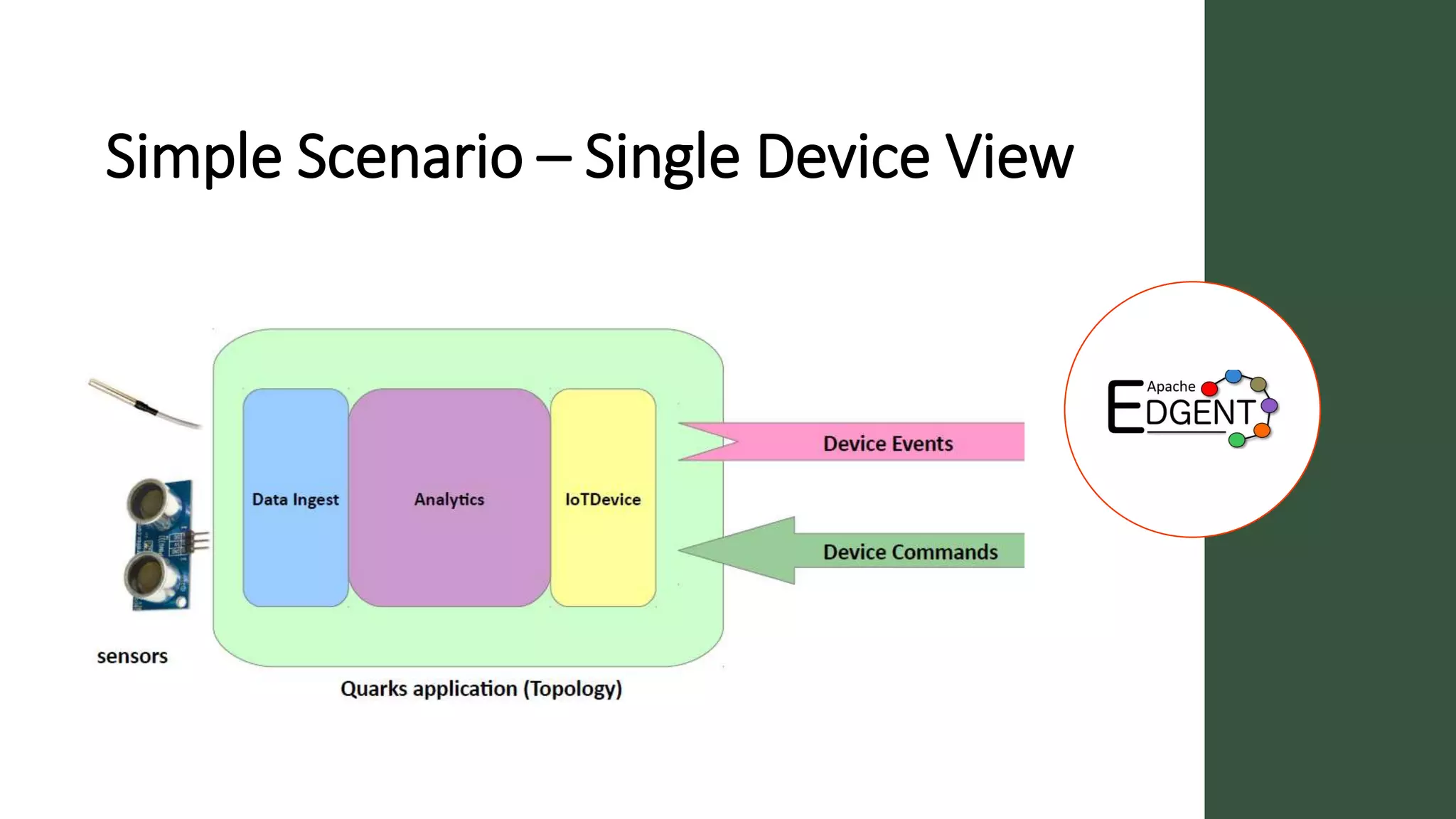
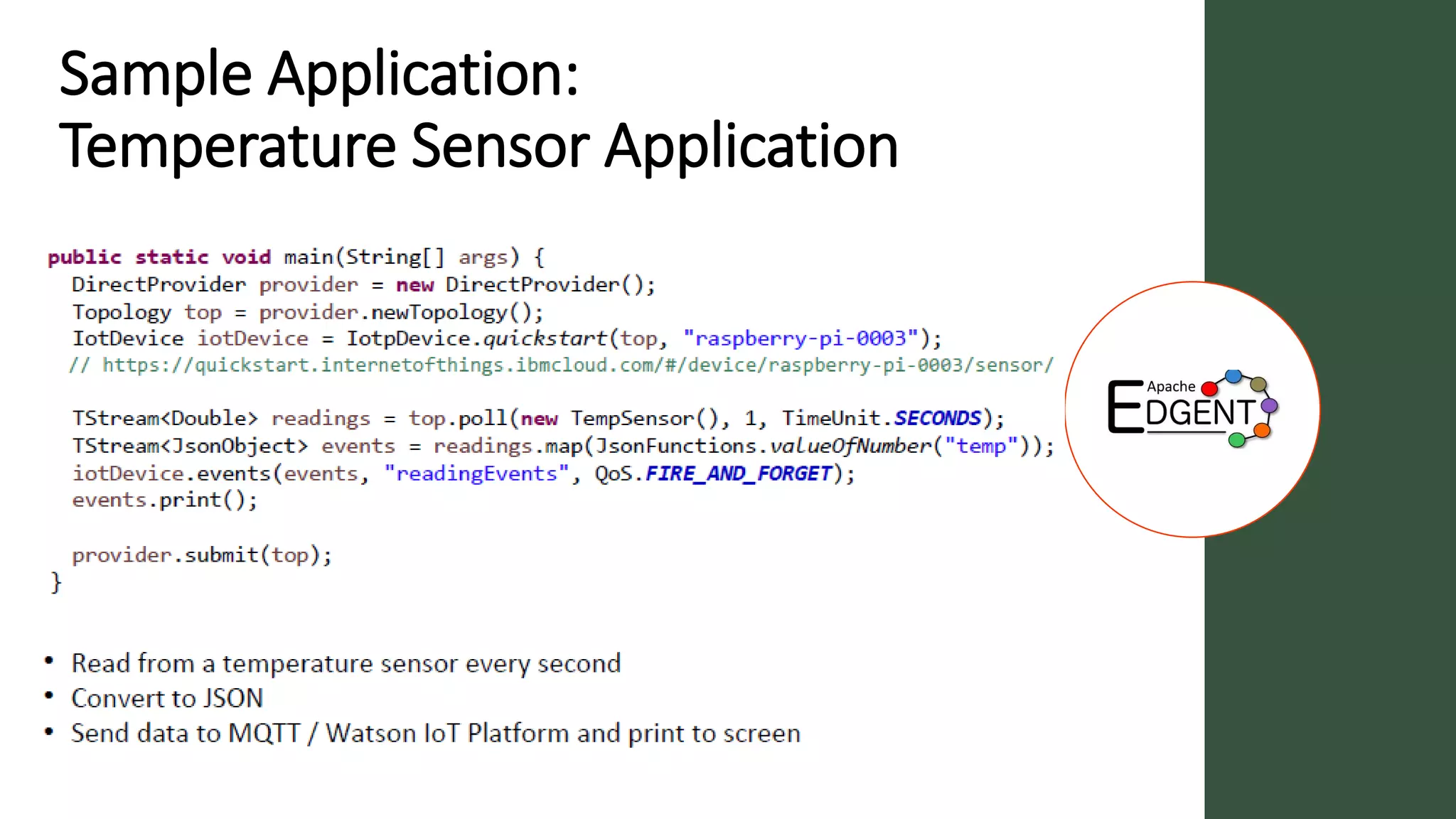
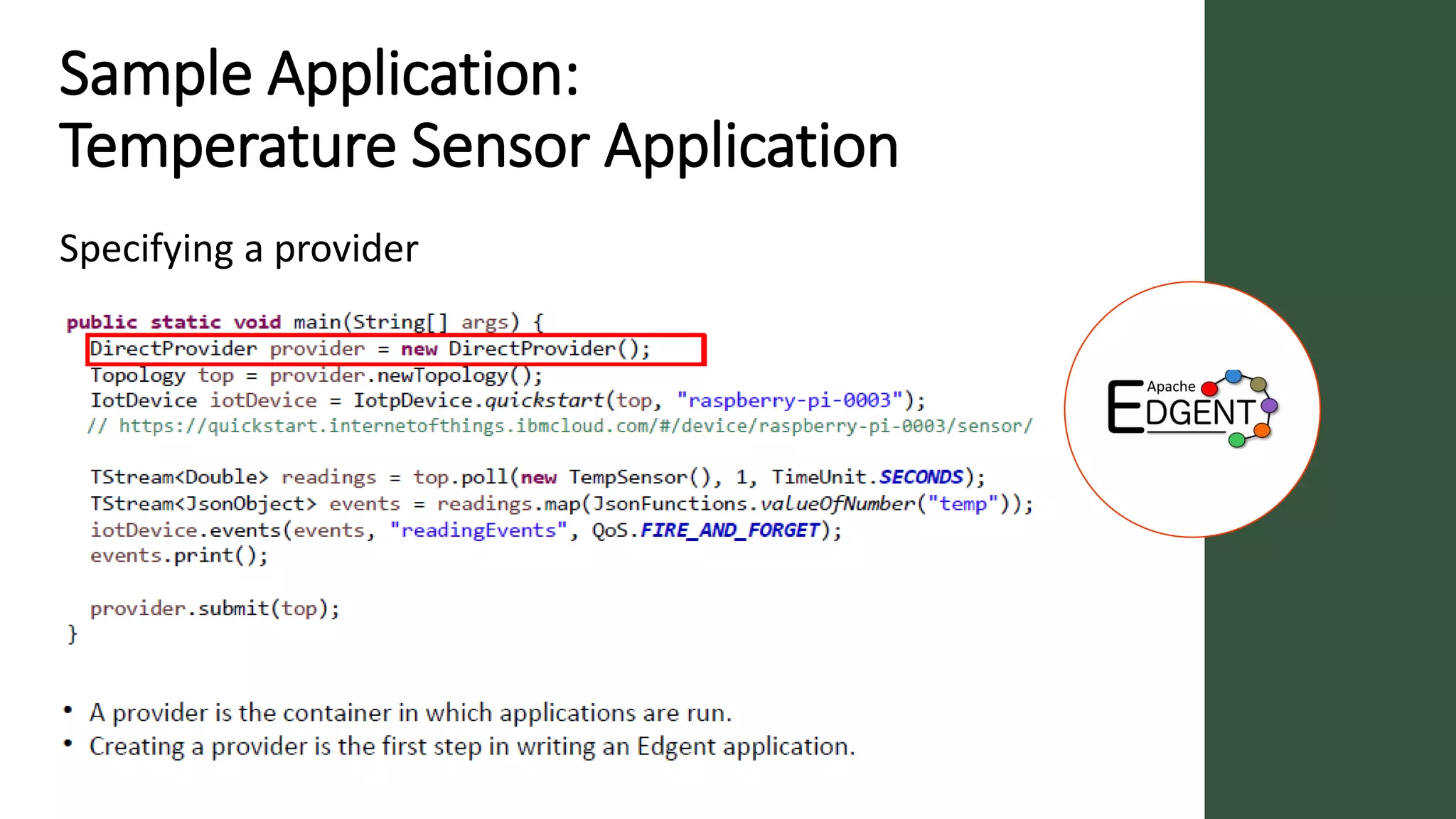
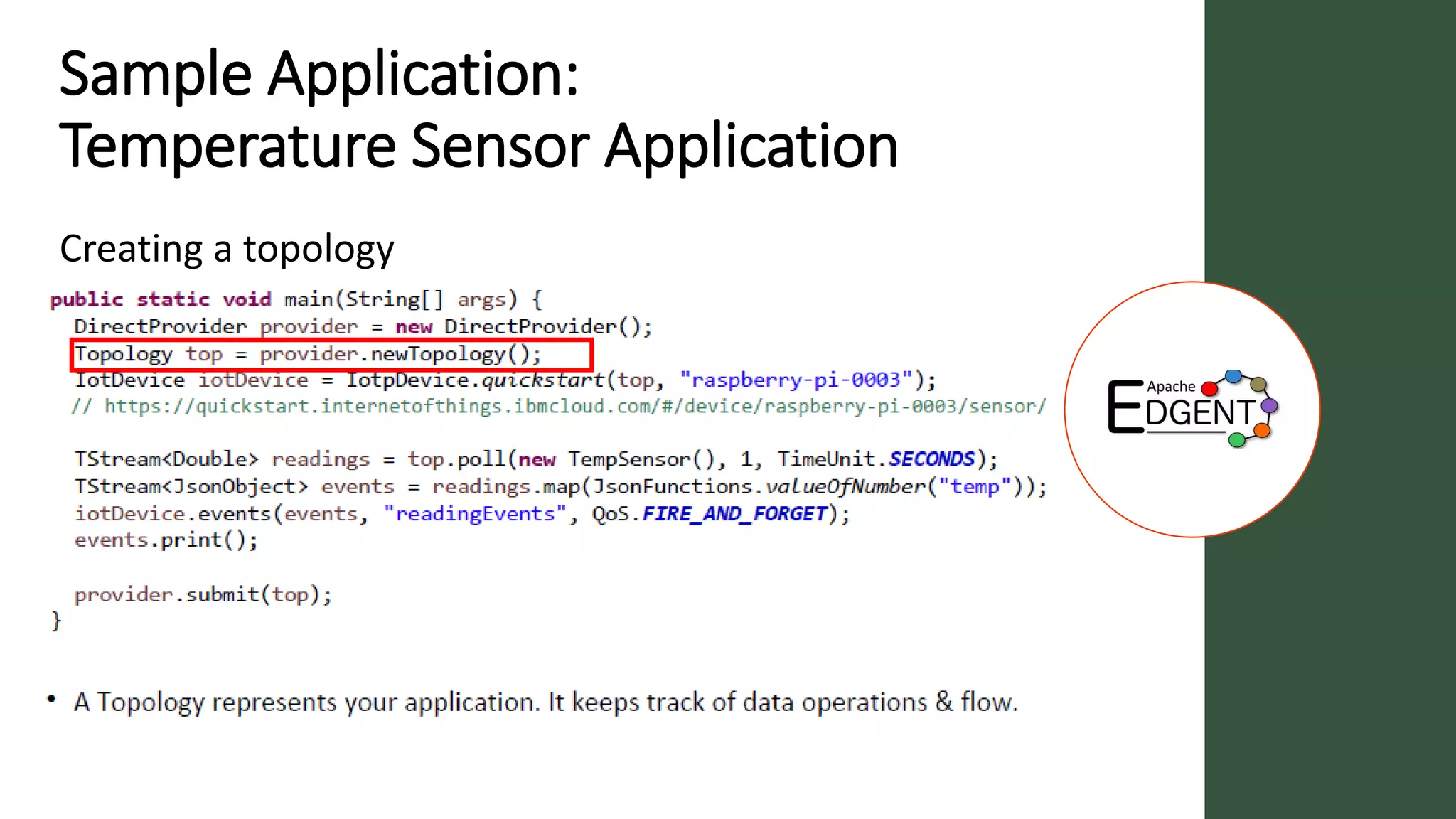
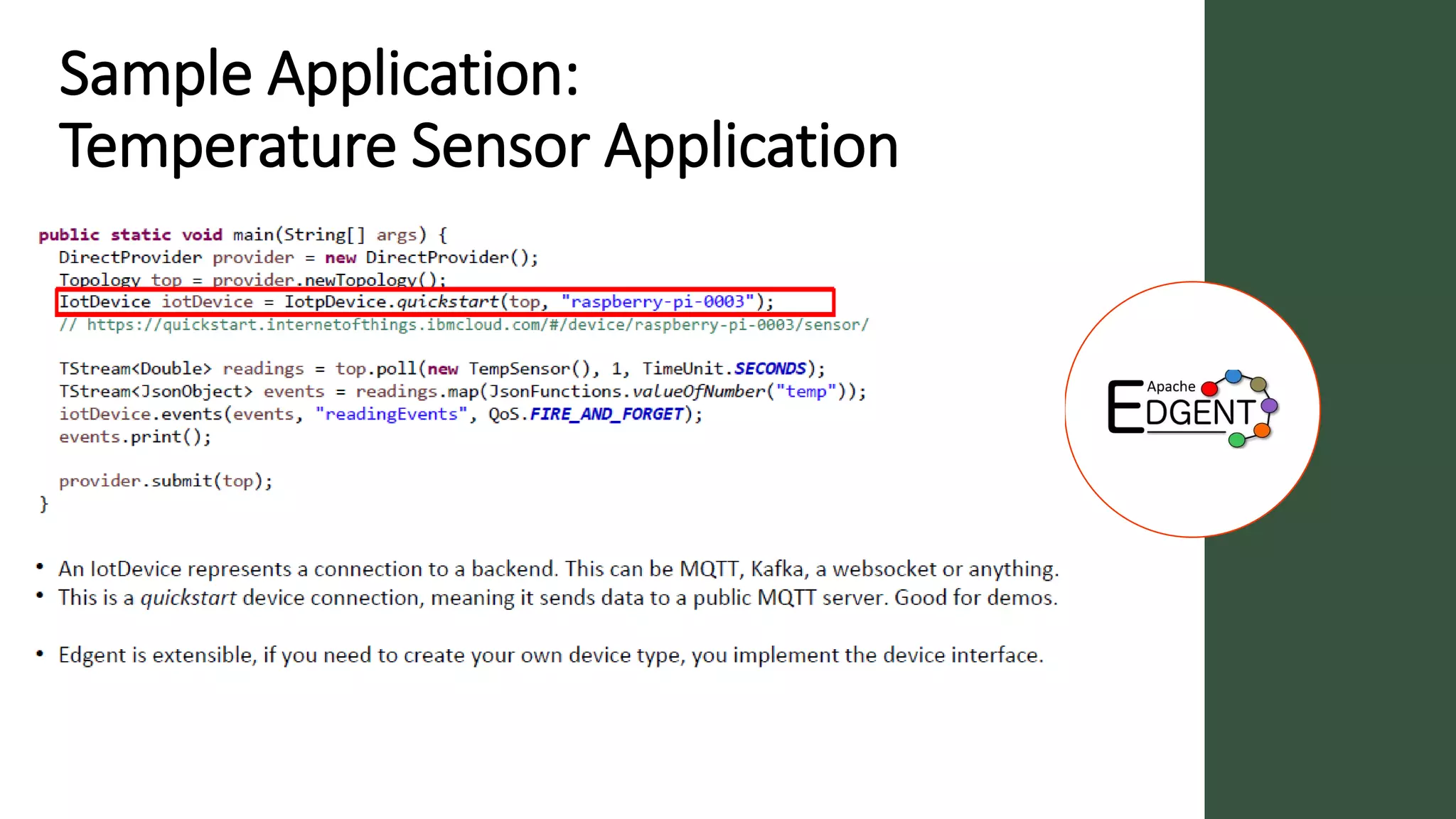
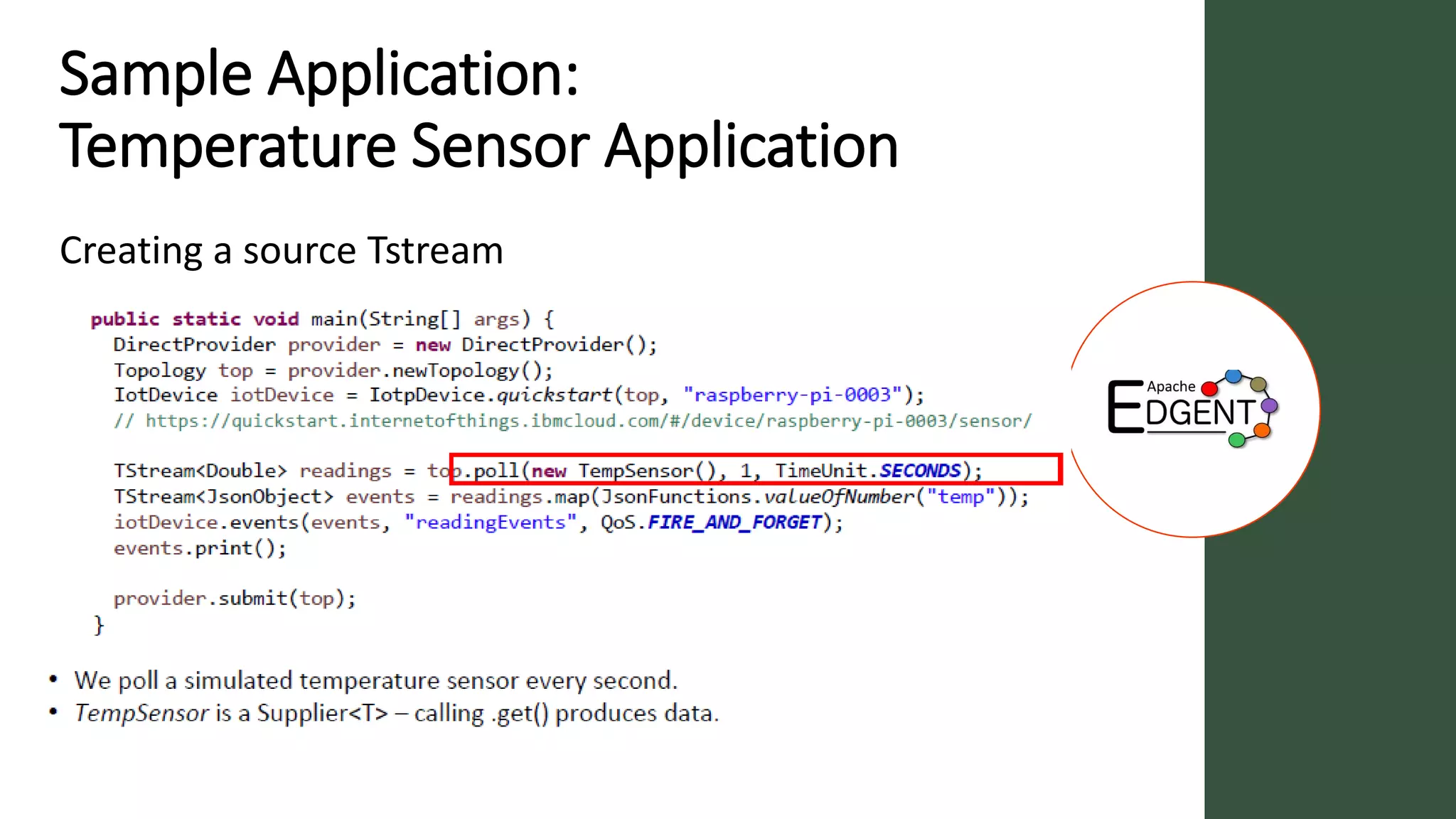
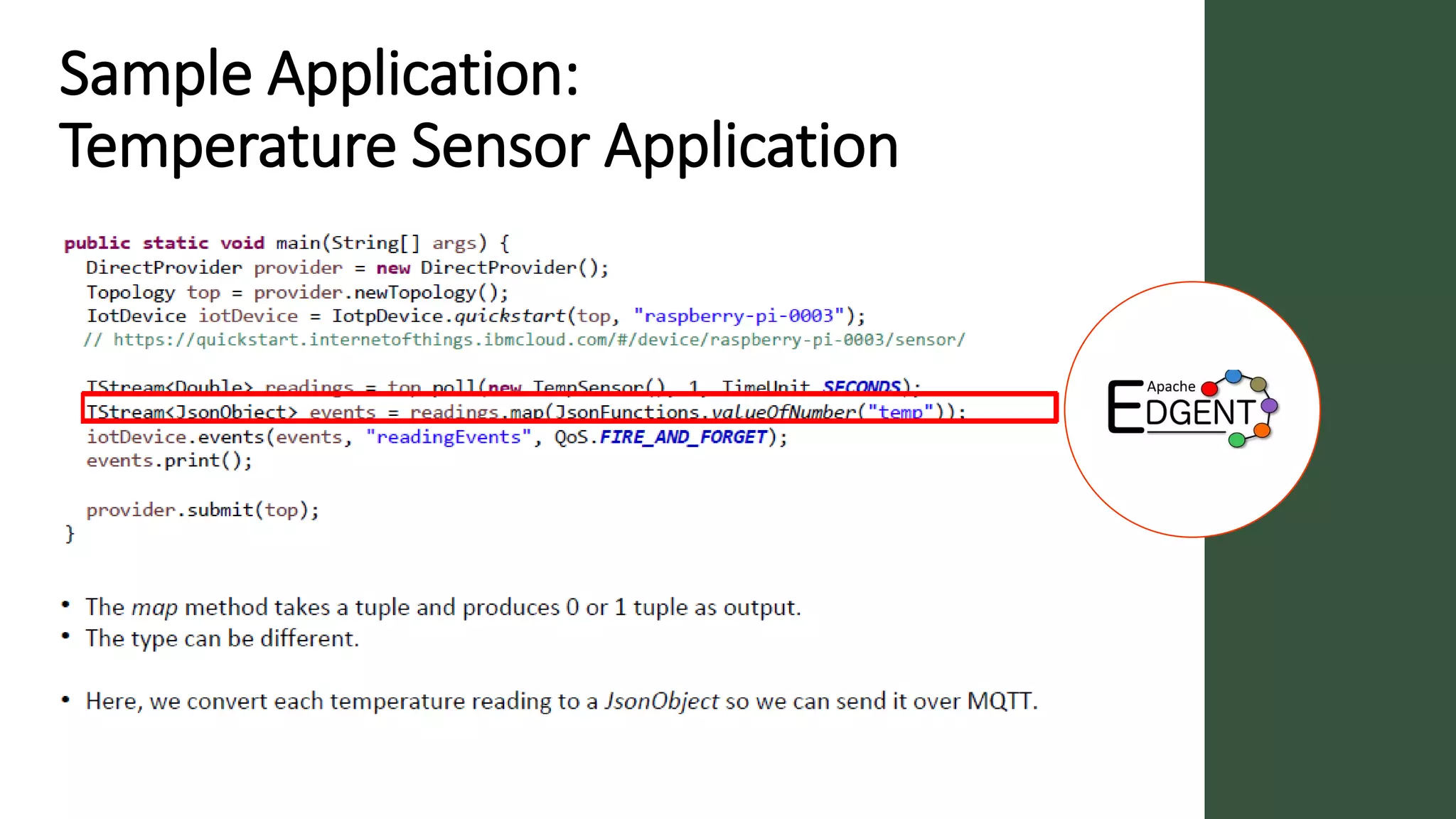
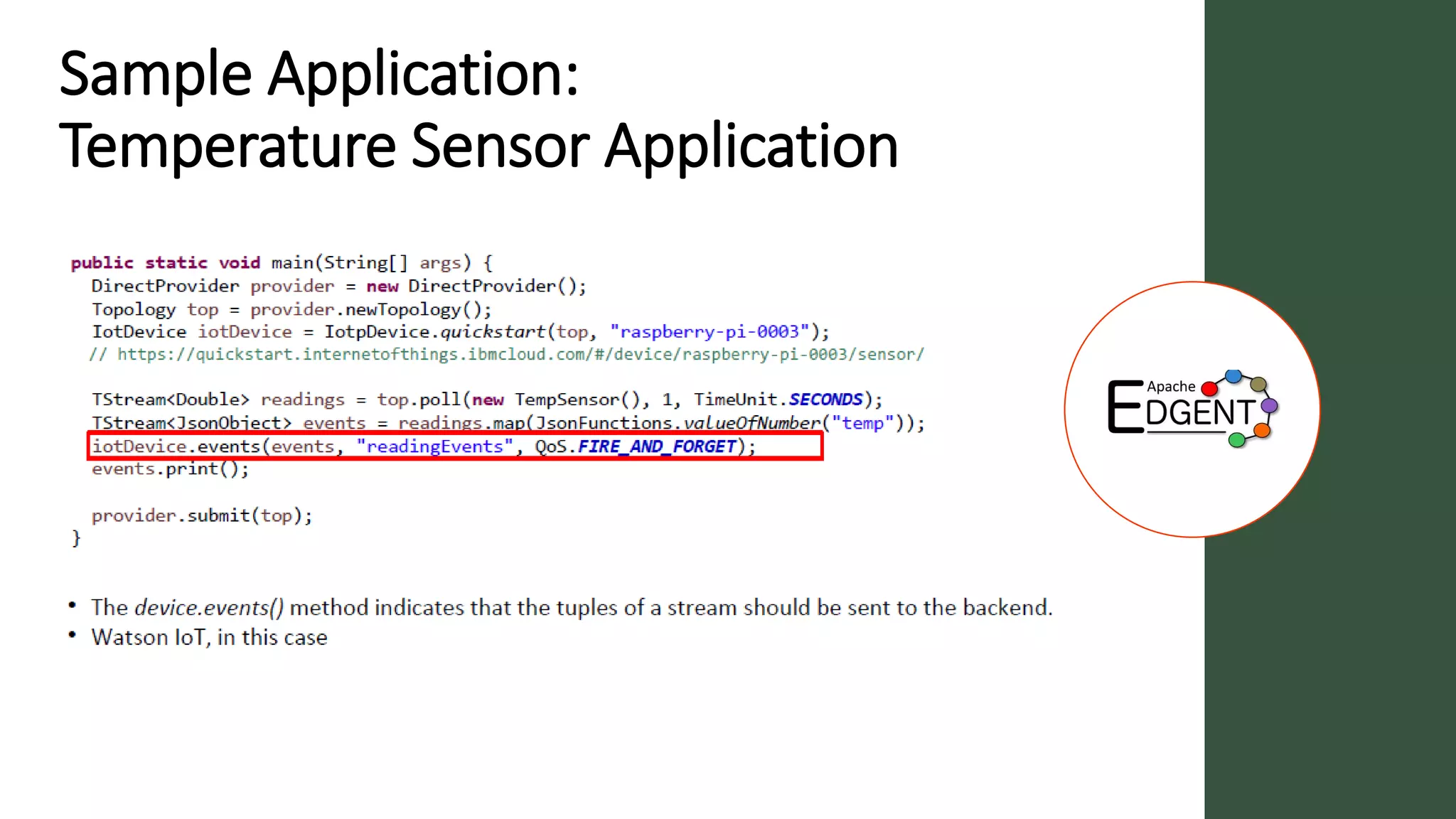
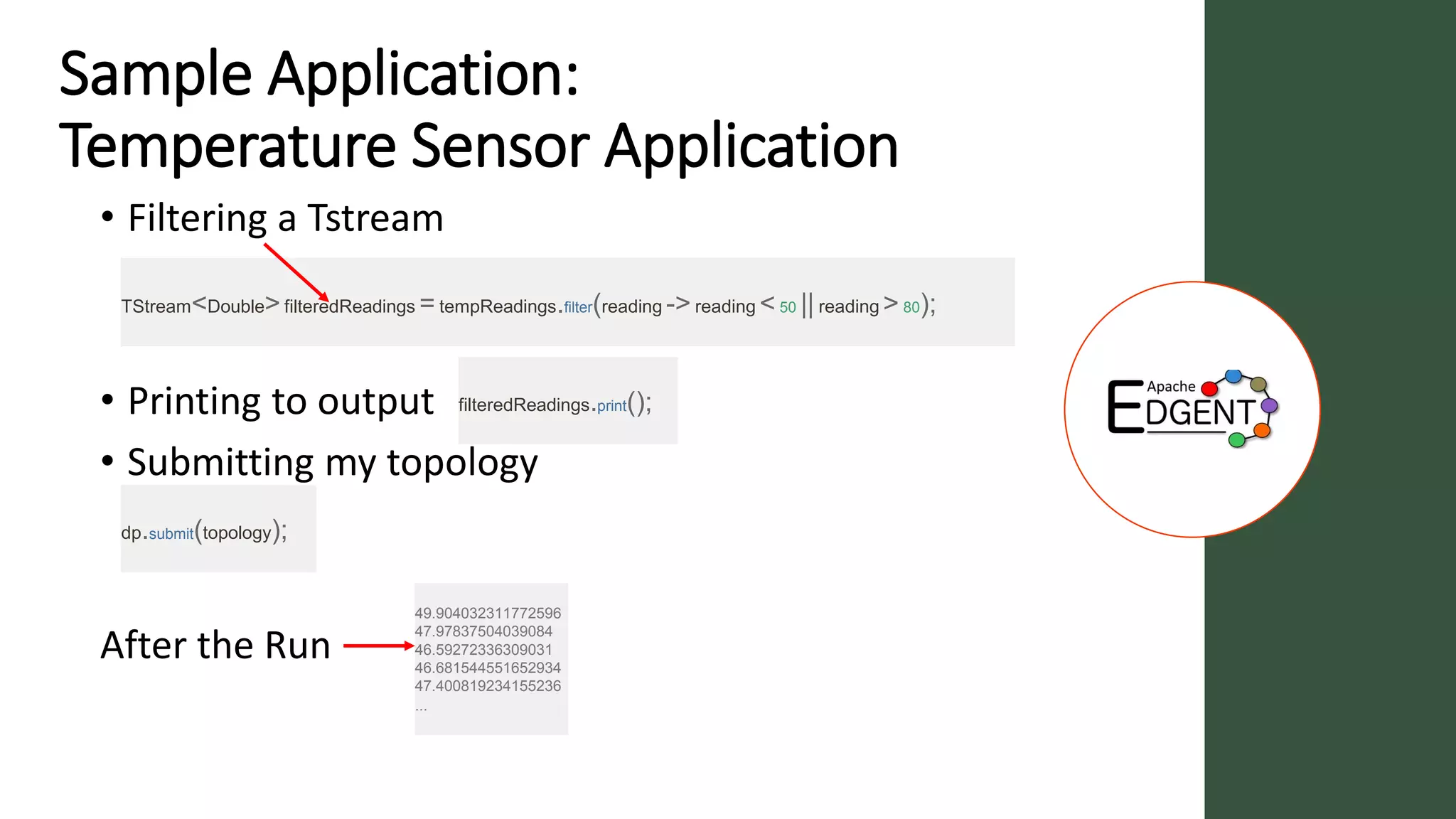
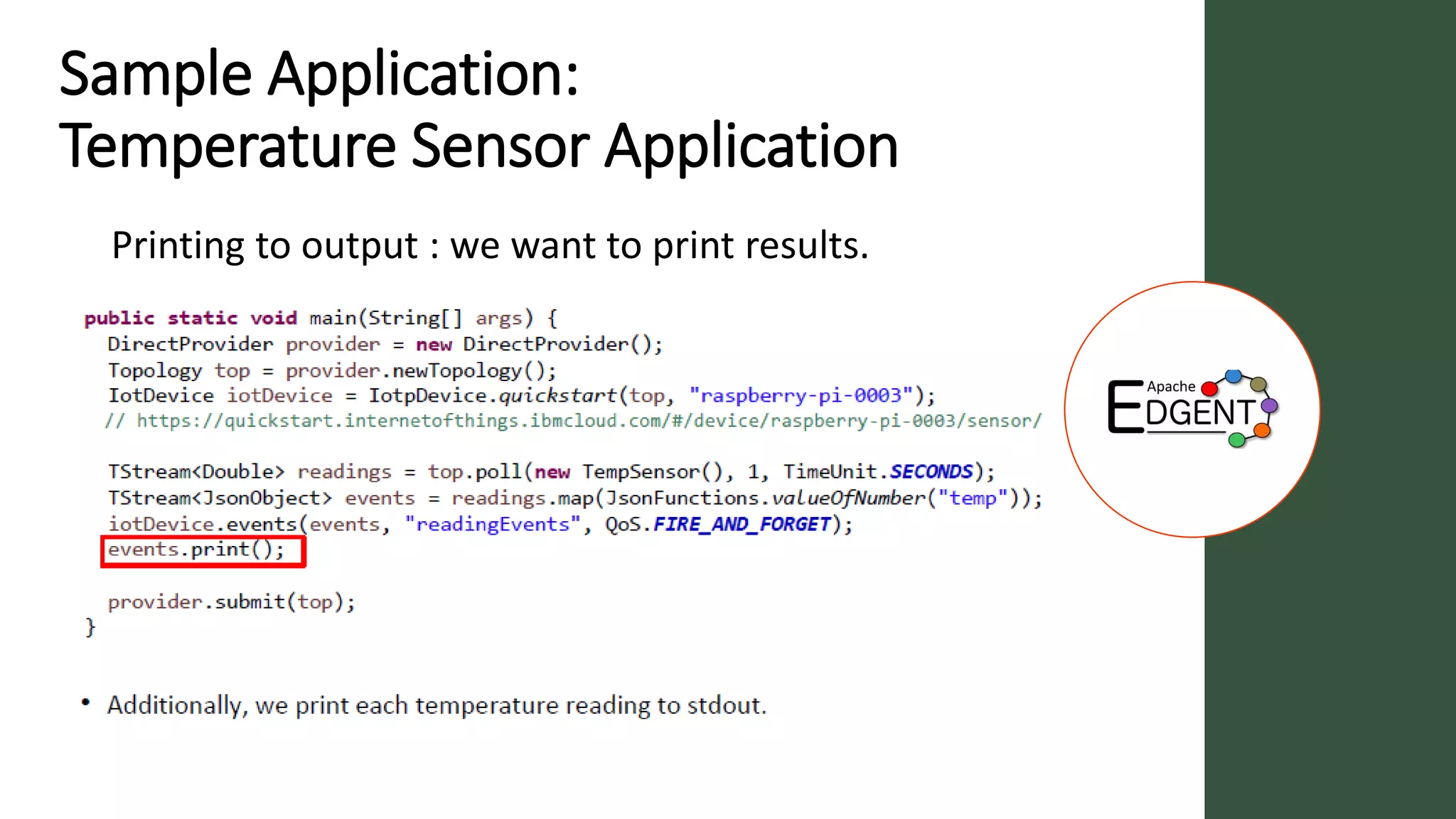
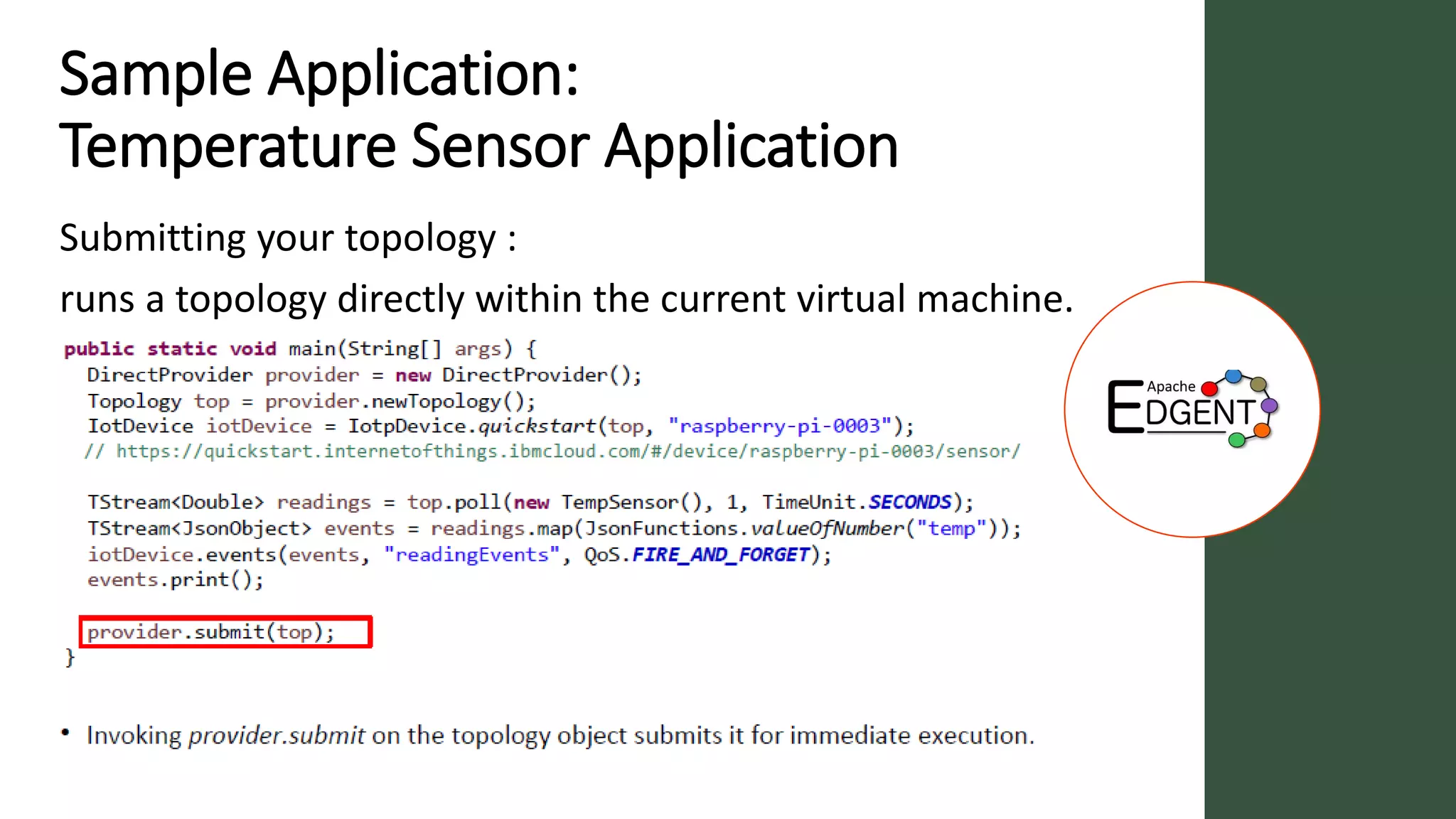
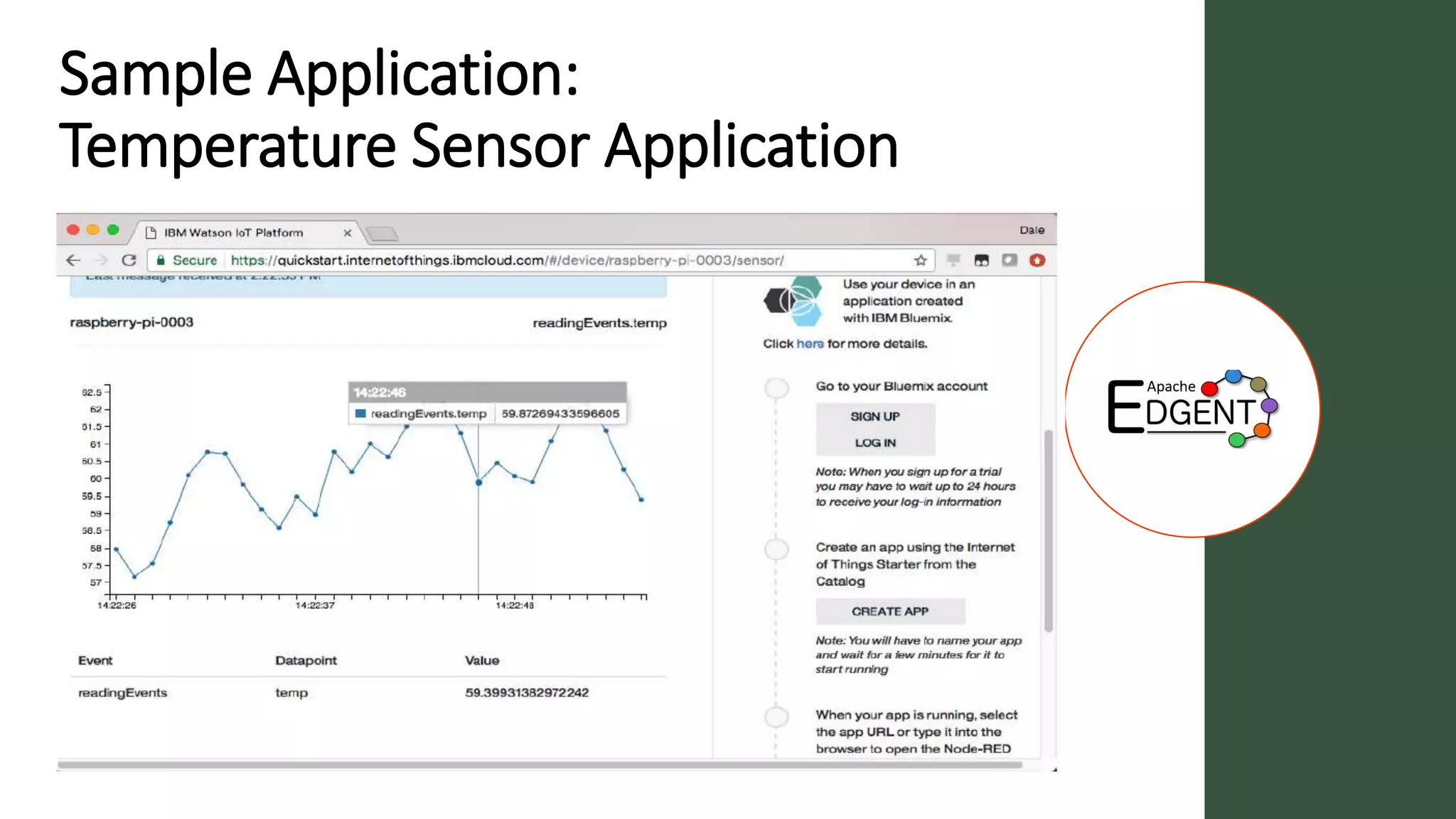
Apache Edgent is an open source project that provides a programming model and lightweight runtime for streaming analytics at the edge. It allows analyzing data and events locally on devices to reduce data transmission and storage costs. Edgent uses a functional flow API to apply operations like filtering and mapping to streams of data from sensors. It can integrate the results with centralized analytics platforms through messaging hubs. The goal is to enable local real-time analytics on continuous data streams at the edge in conjunction with backend systems.