Embed presentation
Download to read offline

![Type Casting/Type Conversion in Python
Int(x)
int (10)
int(10.20)
int('10')
int('10.20')
int(0b1010)
int(true)
int(A)
int(true)
float(x) complex(x,y) bool() str()
float (10)
float (10.20)
float ('10')
float ('10.20')
float (0b1010)
float (true)
float (A)
float (true)
complex(10)
complex(10.20)
complex('10')
complex('10.20')
complex(0b1010)
complex(true)
complex(A)
complex(true)
bool(0)
bool(0.0)
book(0+0j)
bool('')
bool([])
bool(0)
bool(none)
bool(* *)
str(complex(10,20))
srt('python')
str('10.20')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immutablevsmutabledatatypesinpython-210621105357/75/Immutable-vs-mutable-data-types-in-python-2-2048.jpg)
![A first fundamental distinction that Python makes on data
is about whether or not the value of an object changes.
If the value can change, the object is called mutable, while
if the value cannot change, the object is called immutable.
( ) Vs [ ]
Immutable vs Mutable Data Types in
Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immutablevsmutabledatatypesinpython-210621105357/75/Immutable-vs-mutable-data-types-in-python-4-2048.jpg)
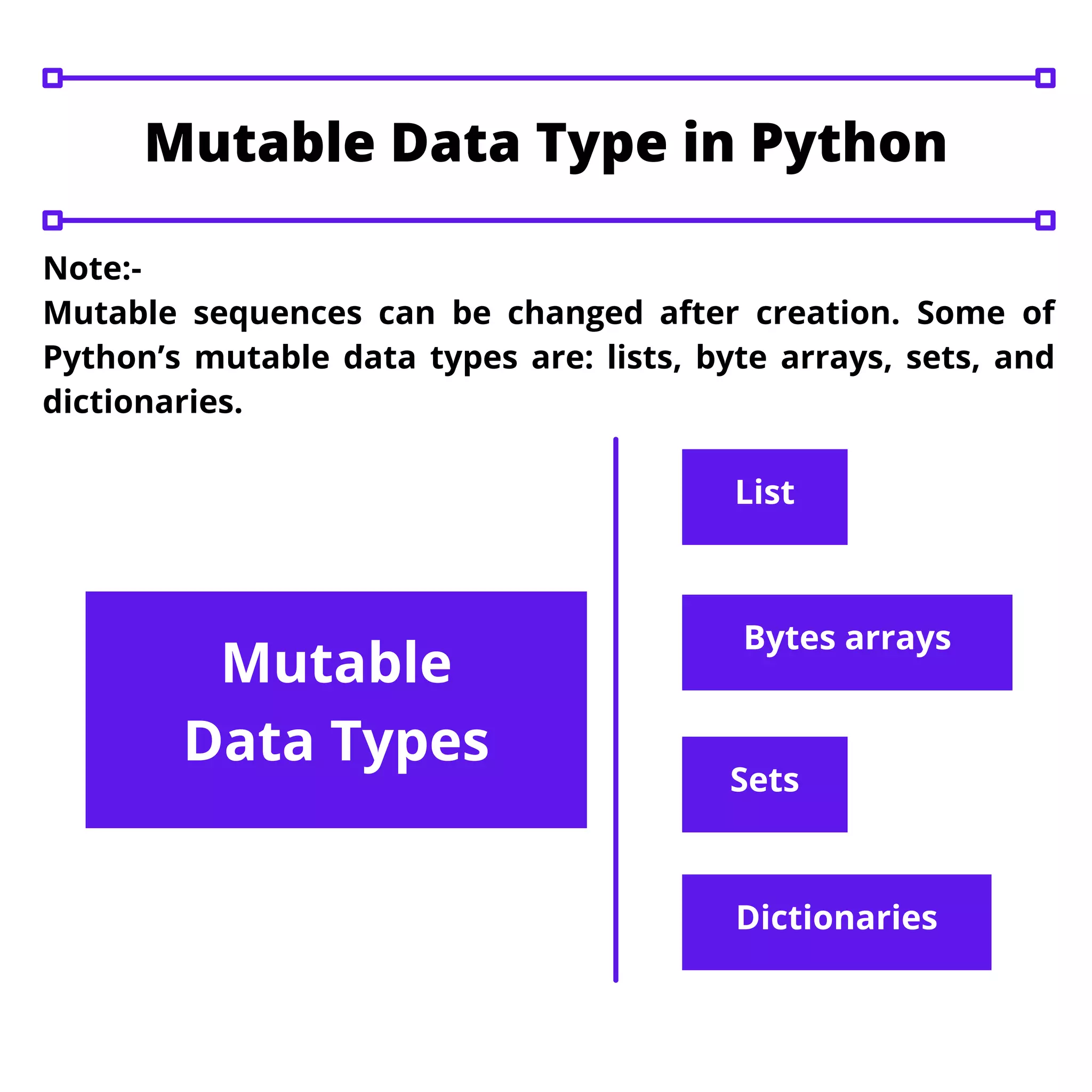


This document discusses data types in Python including type casting, immutable vs mutable data types. It provides examples of type casting integers, floats, booleans, strings and complexes to other types using functions like int(), float(), bool() etc. It explains that mutable data types like lists, bytes arrays, sets and dictionaries can be changed after creation while immutable types like numeric values, strings, frozen sets and tuples cannot be changed once created.

![Type Casting/Type Conversion in Python
Int(x)
int (10)
int(10.20)
int('10')
int('10.20')
int(0b1010)
int(true)
int(A)
int(true)
float(x) complex(x,y) bool() str()
float (10)
float (10.20)
float ('10')
float ('10.20')
float (0b1010)
float (true)
float (A)
float (true)
complex(10)
complex(10.20)
complex('10')
complex('10.20')
complex(0b1010)
complex(true)
complex(A)
complex(true)
bool(0)
bool(0.0)
book(0+0j)
bool('')
bool([])
bool(0)
bool(none)
bool(* *)
str(complex(10,20))
srt('python')
str('10.20')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immutablevsmutabledatatypesinpython-210621105357/75/Immutable-vs-mutable-data-types-in-python-2-2048.jpg)

![A first fundamental distinction that Python makes on data
is about whether or not the value of an object changes.
If the value can change, the object is called mutable, while
if the value cannot change, the object is called immutable.
( ) Vs [ ]
Immutable vs Mutable Data Types in
Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immutablevsmutabledatatypesinpython-210621105357/75/Immutable-vs-mutable-data-types-in-python-4-2048.jpg)


