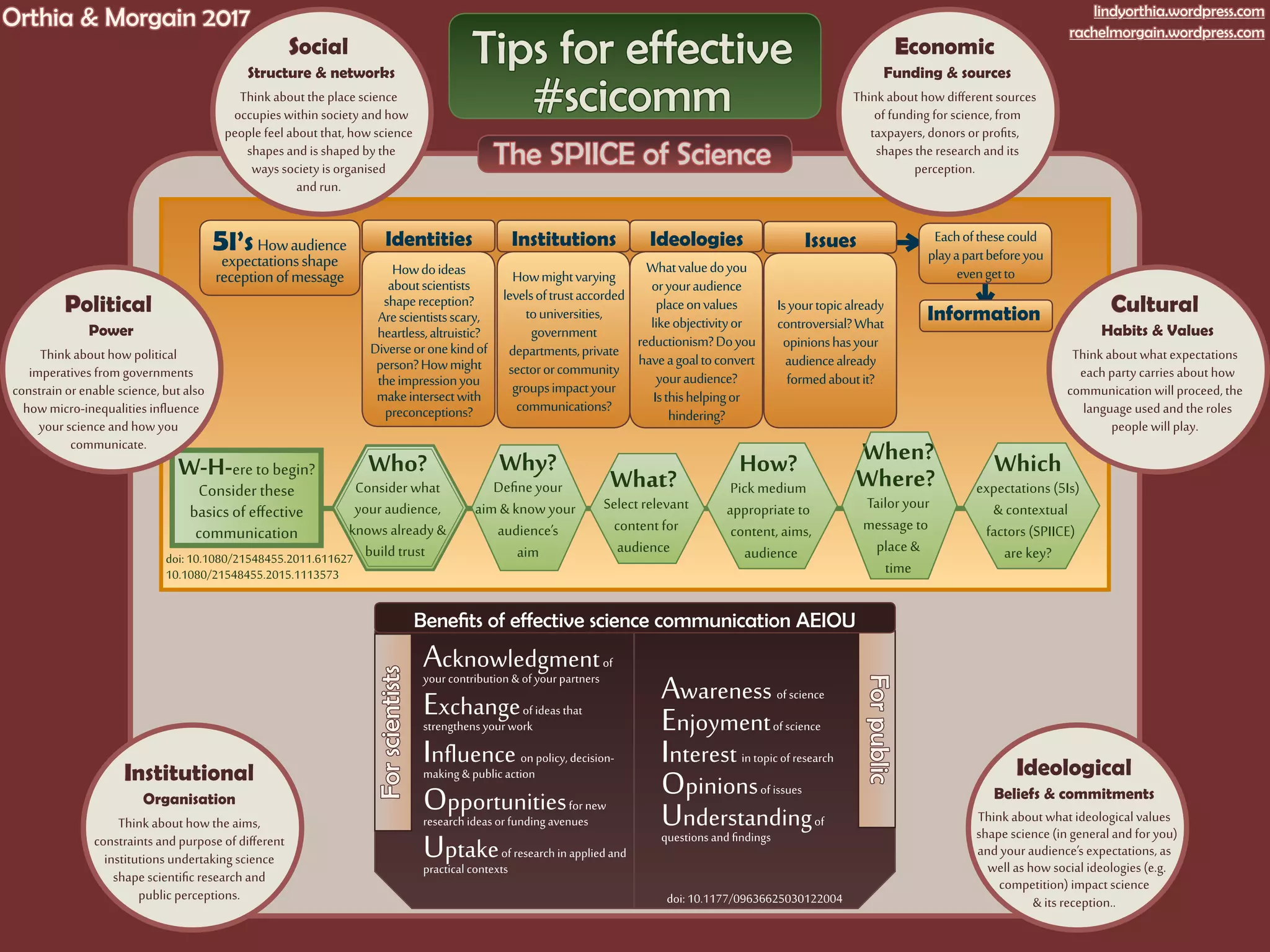
The document discusses the intricate relationship between science and society, emphasizing the influence of social structures, funding sources, and audience perceptions on scientific communication. It outlines key considerations for effective communication, including understanding audience expectations, political influences, and institutional contexts. Additionally, it highlights the importance of acknowledging contributions and the role of ideology in shaping both science and its reception.