More Related Content
Similar to AAI Poster Preeyam
Similar to AAI Poster Preeyam (20)
AAI Poster Preeyam
- 1. Early Exposure to Phosphorylcholine-Bearing Microbes Dampens
the Development of House Dust Mite Allergy During Adult Life
ABSTRACT
Preeyam Patel and John F. Kearney
Microbiology Theme; Graduate Biomedical Sciences at the University of Alabama at Birmingham
INTRODUCTION AND METHODS
A suggested mechanism to explain the dramatic rise in the incidence of allergic disease
among individuals living in developed countries has been an imbalance in the TH1/TH2
subsets; however, a majority of neonatal pathogens evoke potent B cell responses.
These B cell clones, with shared specificity for allergens, can be protective against the
development of allergic disease. Streptococcus pneumoniae and house dust mite (HDM)
bear similar phosphorylcholine epitopes. Therefore, we hypothesized that B cell clones
generated as a result of early pneumococcal exposure would dampen the development
of HDM allergy during adult life. To test our hypothesis, we immunized neonatal mice
with PC-deficient or PC-bearing pneumococcus and then challenged these mice with
HDM as adults. Mice receiving the PC-bearing pneumococcus had a large frequency of
PC-specific B cells that resided in their spleen and continually secreted antibodies. Upon
pulmonary exposure to PC-bearing HDM, these B cells migrated to the lung and
secreted antibody locally into the pulmonary space. As a result, mice immunized with
PC-bearing pneumococcus, presented with dampened production of serum IgE and
TH2-associated cytokines, development of airway hyperreactivity, and infiltration of
allergic mediators into the lung as compared to mice exposed to PC-devoid
pneumococcus as neonates. We further demonstrated that neonatal exposure to
bacteria was not sufficient enough to disrupt the balance in the TH1/TH2 subsets.
RESULTS
TH2$TH2$
TH2$TH2$T$
TH2$
IgE$
TH2$TH2$
TH2$TH2$
B$
B$
TH2$TH2$
IncidenceofInfectiousDiseases(%)
IncidenceofImmuneDiseases(%)
1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
0
50
100
100
200
300
400
Rheumatic Fever
Hepatitis A
Tuberculosis
Mumps
Measles
Chron’s Disease
Multiple Sclerosis
Type 1 Diabetes
Asthma
1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
IncidenceofInfectiousDiseases(%)
IncidenceofImmuneDiseases(%)
1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
0
50
100
100
200
300
400
Rheumatic Fever
Hepatitis A
Tuberculosis
Mumps
Measles
Chron’s Disease
Multiple Sclerosis
Type 1 Diabetes
Asthma
1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
Quest Diagnostics Health Trends; Allergy Report 2011
Development of Allergic DiseaseThe Hygiene Hypothesis
Graham-Rowe D, Nature 479; Nov 2011; Masoli M., Allergy 59; 2004
Adapted from: Bach J-F, NEJM 347 11; Sept 2002
CONCLUSIONS
0 10 20 30 40 50
1
2
3
4
Vaporized Methacholine (mM)
Rrs(cmH2O.s/mL)
**
GATA3 TBET
0
1
2
4
6
8
10
CellsintheLung(x103
)
*
GATA3 TBET
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.5
1.0
1.5
CellsintheBALF(x104
)
***
*
GATA3 TBET
0.0
0.2
0.4
1
2
3
CellsintheMLN(x104
)
***
**
IL-2 IL-12p70 IFNg
0
1
2
3
4
5
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-13 IL-9
0
1
2
3
20
40
60
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
* ***
* * *
**
*
CXCL1CXCL2RANTESCCL4
0
2
4
10
20
30
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
*
**
***
*
***
*
100μm"
50μm"
50μm"
PBS! R36A! T15 KI!JY2190!
GATA 3 Tbet" GATA 3 Tbet" Vaporized Methacholine (mg/mL)"
CellsintheLung(x103)"
CellsintheBALF(x104)"
Rrs(cmH2O.s/mL)"
IL-2 IL-12p70 IFNg" IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-13 IL-9" CXCL1 CXCL2 RANTES CCL4"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
No HDM"
Neonatal Immunization with R36A Decreases Mucin Production and Cellular Infiltration in the Bronchioles
0 10 20 30 40 50
1
2
3
4
Vaporized Methacholine (mM)
Rrs(cmH2O.s/mL)
**
GATA3 TBET
0
1
2
4
6
8
10
CellsintheLung(x103
)
*
GATA3 TBET
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.5
1.0
1.5
CellsintheBALF(x104
)
***
*
GATA3 TBET
0.0
0.2
0.4
1
2
3
CellsintheMLN(x104
)
***
**
IL-2 IL-12p70 IFNg
0
1
2
3
4
5
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-13 IL-9
0
1
2
3
20
40
60
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
* ***
* * *
**
*
CXCL1CXCL2RANTESCCL4
0
2
4
10
20
30
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
*
**
***
*
***
*
100μm"
50μm"
50μm"
PBS! R36A! T15 KI!JY2190!
GATA 3 Tbet" GATA 3 Tbet" Vaporized Methacholine (mg/mL)"
CellsintheLung(x103)"
CellsintheBALF(x104)"
Rrs(cmH2O.s/mL)"
IL-2 IL-12p70 IFNg" IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-13 IL-9" CXCL1 CXCL2 RANTES CCL4"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
No HDM"
0 10 20 30 40 50
1
2
3
4
Vaporized Methacholine (mM)
Rrs(cmH2O.s/mL)
**
GATA3 TBET
0
1
2
4
6
8
10
CellsintheLung(x103
)
*
GATA3 TBET
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.5
1.0
1.5
CellsintheBALF(x104
)
***
*
GATA3 TBET
0.0
0.2
0.4
1
2
3
CellsintheMLN(x104
)
***
**
IL-2 IL-12p70 IFNg
0
1
2
3
4
5
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-13 IL-9
0
1
2
3
20
40
60
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
* ***
* * *
**
*
CXCL1CXCL2RANTESCCL4
0
2
4
10
20
30
CytokinesintheBALF(pg/mL)
*
**
***
*
***
*
100μm"
50μm"
50μm"
PBS! R36A! T15 KI!JY2190!
GATA 3 Tbet" GATA 3 Tbet" Vaporized Methacholine (mg/mL)"
CellsintheLung(x103)"
CellsintheBALF(x104)"
Rrs(cmH2O.s/mL)"
IL-2 IL-12p70 IFNg" IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-13 IL-9" CXCL1 CXCL2 RANTES CCL4"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
BALFCytokines(pg/mL)"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
PBS"
JY2190"
R36A"
T15 KI"
No HDM"
Neonatal Immunization with R36A Decreases the Production of TH2-, but not TH1-, Associated Cytokines in the Lung as
well as the Development of Airway Hyperresponsiveness (AHR)
PBSJY2190R36AT15 KI
0
100
200
300
ng/mLDerp1-specificIgE
*
***
PBSJY2190R36AT15 KI
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
ng/mLTotalIgE
*
**
total T cells eos neuts
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
2
4
6
CellsintheBALF(x106)
***
**
**
***
**
***
**
**
Baso Mast macs alv mac
0.00
0.01
1
3
6
9
CellsintheBALF(x105)
***
***
***
***
***
**
PBS! R36A! T15 KI!JY2190!
Cells(x106)!
Cells(x105)!
TotalIgE(ng/mL)!
Total T cells Eos Neuts! Baso Mast Macs Alv Macs! PBS JY2190 R36A T15 KI! PBS JY2190 R36A T15 KI!
A.M.!
A.M.!
neut!
neut!
eo!
eo!
A.M.!
neut!
eo!
20μm!
A.M.!
neut!
Derp1-IgE(ng/mL)!
PBS!
JY2190!
R36A!
T15 KI!
Neonatal Immunization with R36A Decreased the Number of Cells infiltrating the Bronchoalveolar Space and
IgE Production
mm
PBS
JY2190
R36A
T15 KI
CD44!
PBS! R36A! T15 KI!JY2190!
%ofMax!
Neonatal Immunization with R36A Decreases Priming of Antigen-Experienced T Cells in the Mediastinal Lymph
Node
CD44
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
CD4TCellMFI(x104)
***
*
CD4+ T Cells!
CD44MFI(x104)!
DCs imm DCs macs alv macs
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
CD86MFI(x103)
*
***
*
***
*
**
total T cells Eos Neuts
0.00
0.02
0.2
2
4
CellsintheLung(x107)
*
*
*
***
**
*** *
***
macs DCs Mast Baso
0.0
0.5
1.0
2
4
10
20
CellsintheLung(x105)
***
***
**
*** *
* **
*
Total T cells Eos Neuts ! Macs DCs Mast Baso!
Cells(x107)!
Cells(x105)!
DCs imm DCs macs alv macs!
CD86MFI(x103)!
PBS!
JY2190!
R36A!
T15 KI!
No HDM!
Neonatal Immunization with R36A Decreased Cellular Infiltration into the Pulmonary Parenchyma
PBSJY2190R36AT15 KI
0
10
20
30
ng/mLanti-PCIgM
**
*
NS
PBS JY2190 R36A T15 KI!
ng/mLanti-PCIgM!
PBS! JY2190! R36A! T15 KI!
PBS! JY2190!
R36A! T15 KI!
Neonatal Immunization with R36A Increased the Number of PC-Specific B Cells in the Lung
IgM!
PC-BSA!
Laminin!
PC-SpecificIgM-Expressing
50μg anti-PC
IgM ab i.t. 1
hour prior to
challenge with
5ug HDM!
ISO BH8!
mm!
CD44!
ISO!
BH8!
%ofMax!
Passive Antibody Administration
CD44
0
2
4
6
8
MLNCD4+TCells:MFI
uMT uMT uMT !
JY2190 R36A!
mm!
CD4+ T Cells!
CD44MFI!
DC imm DC macs
0
5
10
15
20
CD86MFI:Lung
CD86MFI!
DC imm DC Macs!
Mice Deficient in Mature B Cells
HDM (ISO)
S107 (IgA)
BH8 (IgM)
R36A (ISO)
S107 (IgA)
BH8 (IgM)
JY2190 (ISO)
S107 (IgA)
BH8 (IgM)
Streptococcus pneumoniae D. pteronyssinus
0.5mm!
ISO! BH8!
D. pteronyssinus
3-4 day
PFA-fixed
PC-bearing
pneumococcus
R36A
Neonatal Immunization TEPC15 KI mouse
Inc population of T15 id
PC-specific B cells
PFA-fixed
PC-devoid
pneumococcus
JY2190
HDM Allergy Model
5ug$ 5$x$5ug$
0$ 7$ 8$ 9$10$11$ 14$
OR
FSC! CD19! PC-BSA! PC-BSA! AB1-2!
PC-BSA! PC-BSA! PC-BSA! GATA3! GATA3!
SSC!
B220!
IgM!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
CD4!
CD4!
B220+CD19+!
IgM PC-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
TC68 PC-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
AB1-2 TC68!
0.81 3.8
FSC! CD19! PC-BSA! PC-BSA! AB1-2!
PC-BSA! PC-BSA! PC-BSA! GATA3! GATA3!
SSC!
B220!
IgM!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
CD4!
CD4!
B220+CD19+!
IgM PC-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
TC68 PC-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
AB1-2 TC68!
0.81 3.8
CD19! PC-BSA! PC-BSA! AB1-2!
PC-BSA! PC-BSA! GATA3! GATA3!
B220!
IgM!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
CD4!
CD4!
D19+!
-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
TC68 PC-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
AB1-2 TC68!
0.81 3.8
CD19! PC-BSA! PC-BSA! AB1-2!
PC-BSA! PC-BSA! GATA3! GATA3!
B220!
IgM!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
TC68!
CD4!
CD4!
CD19+!
C-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
TC68 PC-BSA!
B220+CD19+!
AB1-2 TC68!
0.81 3.8
0 10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
<PE-A>: CD11b/SiglecF
0
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
<APC-A>:Ly6G
85.9
2.59
0 50K 100K 150K 200K 250K
FSC-A
0
50K
100K
150K
200K
250K
SSC-A
13.5
94.4
SiglecF
Ly6G
Alveolar macrophages
Eosinophils
lymphocytes, monos
eosinophils
neutrophils
HDM onlyISO BH8 Media
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
CD86MFI(x103)
***
CD86!
CD86MFI(x103)!
Alv Mac Pulm APCsMac cell line
0
5
10
20
40
60
80
HDMPositiveCells(%)
HDM-ISO
HDM-10 BH8
HDM-20 BH8
*
**
*
**
*
**HDM only
HDMPositiveCells(%)!
Alv Mac Pulm APCs Mac cell line!
HDM ISO BH8 Media!
4!
3!
2!
1!
1 HDM!
2 ISO!
3 BH8!
4 Media!
Serum
Serum
+
100ug
BH
8
H
ISerum
H
ISerum
+
100ug
BH
8
0
2
4
6
8
10
HDMPositiveCells(%)
*
NS
*
BAL
BAL
+
100ug
BH
8
H
IBAL
H
IBAL
+
100ug
BH
8
0
5
10
15
20
HDMPositiveCells(%)
*
NS
*
NS
H
D
M
only
H
D
M
+
100ug
ISO
H
D
M
+
100ug
BH
8
0
2
4
6
HDMPositiveCells(%)
NS
***A! B! C!
Serum! +! +! +! +!
BH8! -! +! -! +!
HI! -! -! +! +!
BALF! +! +! +! +!
BH8! -! +! -! +!
HI! -! -! +! +!
HDMPositiveCells(%)!
HDMPositiveCells(%)!
Media! +! +! +!
BH8! -! -! +!
ISO! -! +! -!
HDMPositiveCells(%)!
Flow Cytometry
Identifying Antigen-Specific B Cells by Flow Cytometry IgM Antibodies Can Decrease Phagocytosis
Dendritic cells migrate from the lung to
the mediastinal lymph node, where they
prime a TH2-directed response.
Br!
Br!
Br!
Br!
V!
V!
V!
PBS! JY2190! R36A! T15 KI!
IgM!
Neonatal Immunization with R36A Results in Increased IgM Secretion in the Lung and Decreased Eosinophil Infiltration
Into the Lung
Br!
V!
V!
V!
V! Br!
Br!
Br!
Siglec-F!
CD11c!
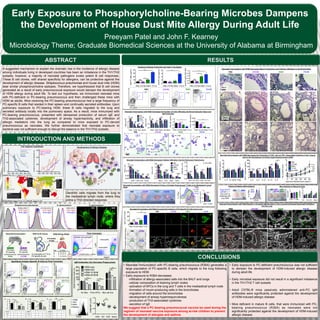
• Neonatal immunization with PC-bearing pneumococcus (R36A) generates a
large population of PC-specific B cells, which migrate to the lung following
exposure to HDM.
• Early exposure to R36A decreases:
-infiltration of allergy-associated cells into the BALF and lungs
-cellular composition of draining lymph nodes
-activation of APCs in the lung and T cells in the mediastinal lymph node
-formation of mucin-producing cells in the bronchioles
-migration of cells around the bronchioles
-development of airway hyperresponvieness
-production of TH2-associated cytokines
-secretion of IgE
We suggest that a PC-bearing pneumococcal vaccine be used during the
regimen of neonatal vaccine exposure among at-risk children to prevent
the development of allergies and asthma
• Early exposure to PC-deficient pneumococcus was not sufficient
to dampen the development of HDM-induced allergic disease
during adult life
• Early microbial exposure did not result in a significant imbalance
in the TH1/TH2 T cell subsets
• Adult C57BL/6 mice passively administered anti-PC IgM
antibodies were significantly protected against the development
of HDM-induced allergic disease
• Mice deficient in mature B cells, that were immunized with PC-
bearing pneumococcus (R36A) as neonates were not
significantly protected against the development of HDM-induced
allergic disease
6-8 weeks
of age
PBSJY2190R36AT15 KI
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
O.D.405
**
*
NS
PBS JY2190 R36A T15 KI
0
10
20
30
40
ug/mLanti-PCIgM
***
**
NS
PBSJY2190R36AT15 KI
0
2
4
6
8
ug/mLanti-PCIgA
***
PBS! JY2190! R36A! T15 KI!
TC68!
Anti-PCIgM(μg/mL)!
Anti-PCIgA(μg/mL)!
PBS JY2190 R36A T15 KI! PBS JY2190 R36A T15 KI! PBS JY2190 R36A T15 KI!
1.07! 1.11! 1.72! 4.71!
Anti-PCIgG3(OD405)!
Sustained Antibody Production and Cells in the Spleen
PC-BSA