RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults
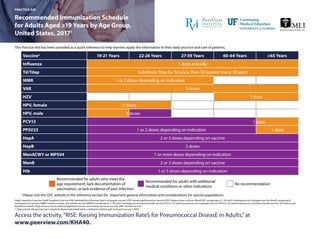
- 1. This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults Aged ≥19 Years by Age Group, United States, 20171 HepA: hepatitis A vaccine; HepB: hepatitis B vaccine; Hib: Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine; HPV: human papillomavirus vaccine; HZV: herpes zoster vaccine; MenACWY: serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal conjugate vaccine; MenB: serogroup B meningococcal vaccine; MMR: measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine; MPSV4: serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; PCV13: 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PPSV23: 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine; Td: tetanus and diphtheria toxoids; Tdap: tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine; VAR: varicella vaccine. 1. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/adult/adult-combined-schedule.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. PRACTICE AID Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Vaccinea 19-21 Years 22-26 Years 27-59 Years 60-64 Years ≥65 Years Influenza 1 dose annually Td/Tdap Substitute Tdap for Td once, then Td booster every 10 years MMR 1 or 2 doses depending on indication VAR 2 doses HZV 1 dose HPV, female 3 doses HPV, male PCV13 PPSV23 1 or 2 doses depending on indication 1 dose HepA 2 or 3 doses depending on vaccine HepB 3 doses MenACWY or MPSV4 1 or more doses depending on indication MenB 2 or 3 doses depending on vaccine Hib 1 or 3 doses depending on indication 3 doses 1 dose Recommended for adults who meet the age requirement, lack documentation of vaccination, or lack evidence of past infection a Please visit the CDC website in the reference section for important general information and considerations for special populations. Recommended for adults with additional medical conditions or other indications No recommendation
- 2. This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults Aged ≥19 Years by Medical Condition and Other Indications, United States, 20171 ESRD: end-stage renal disease; HepA: hepatitis A vaccine; HepB: hepatitis B vaccine; Hib: Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine; HPV: human papillomavirus vaccine; HZV: herpes zoster vaccine; MenACWY: serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal conjugate vaccine; MenB: serogroup B meningococcal vaccine; MMR: measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine; MPSV4: serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; MSM: men who have sex with men; PCV13: 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PPSV23: 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine; Td: tetanus and diphtheria toxoids; Tdap: tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine; VAR: varicella vaccine. 1. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/adult/adult-combined-schedule.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. PRACTICE AID Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Vaccinea Pregnancy Immuno- compromised (Excluding HIV Infection) HIV Infection CD4+ Count (cells/μL) Asplenia, Persistent Complement Deficiencies Kidney Failure, ESRD, on Hemodialysis Heart or Lung Disease, Chronic Alcoholism Chronic Liver Disease Diabetes Healthcare Personnel MSM <200 ≥200 Influenza 1 dose annually Td/Tdap 1 dose Tdap each pregnancy Substitute Tdap for Td once, then Td booster every 10 years MMR Contraindicated 1 or 2 doses depending on indication VAR Contraindicated 2 doses HZV Contraindicated 1 dose HPV, female Three doses 3 doses through age 26 years HPV, male 3 doses through age 26 years 3 doses through age 21 years 3 doses through age 26 years PCV13 PPSV23 HepA HepB MenACWY or MPSV4 MenB Hib 3 doses post-HSCT recipients only 1 dose 1, 2, or 3 doses depending on indication 2 or 3 doses depending on vaccine 1 dose 3 doses 1 or more doses depending on indication 2 or 3 doses depending on vaccine Recommended for adults who meet the age requirement, lack documentation of vaccination, or lack evidence of past infection Recommended for adults with additional medical conditions or other indications No recommendationContraindicated a Please visit the CDC website in the reference section for important general information and considerations for special populations.
- 3. This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. Information for Adult Patients 2017 Recommended Immunizations for Adults: By Age1 MenACWY: serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal conjugate vaccine; MenB: serogroup B meningococcal vaccine; MPSV4: meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; PCV13: 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PPSV23: 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. 1. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/adult/adult-schedule-easy-read.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. PRACTICE AID Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. May be recommended for you: This vaccine is recommended for you if you have certain risk factors due to your health condition or other. Talk to your healthcare professional to see if you need this vaccine Recommended for you: This vaccine is recommended for you unless your healthcare professional tells you that you do not need it or should not get it. Flu Influenza Td/Tdap Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis Shingles Zoster Pneumococcal Meningococcal MMR Measles, mumps, rubella HPV Human papillomavirus Chickenpox Varicella Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hib Haemophilus influenzae type bPCV13 PPSV23 MenACWY or MPSV4 MenB Women Men 19-21 years 22-26 years 27-59 years 60-64 years 65+ years You should get flu vaccine every year. You should get a Td booster every 10 years. You also need one dose of Tdap. Women should get a Tdap vaccine during every pregnancy to help protect the baby. You should get shingles vaccine even if you have had shingles before. You should get one dose of PCV13 and at least one dose of PPSV23 depending on your age and health condition. You should get this vaccine if you did not get it when you were a child. talk to your healthcare professional about these vaccines You should get HPV vaccine if you are a woman through age 26 years or a man through age 21 years and did not already complete the series. If you are this age, More information If you are traveling outside the United States, you may need additional vaccines. Ask your healthcare professional about which vaccines you may need at least 6 weeks before you travel.
- 4. This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. Information for Adult Patients 2017 Recommended Immunizations for Adults: By Health Condition1 CD: cluster of differentiation; MenACWY: serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal conjugate vaccine; MenB: serogroup B meningococcal vaccine; MPSV4: meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; PCV13: 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PPSV23: 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. 1. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/adult/adult-schedule-easy-read.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. PRACTICE AID Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. May be recommended for you: This vaccine is recommended for you if you have certain risk factors due to your age, health condition, or other. Talk to your healthcare professional to see if you need this vaccine. YOU SHOULD NOT GET THIS VACCINE. Recommended for you: This vaccine is recommended for you unless your healthcare professional tells you that you do not need it or should not get it. Flu Influenza Td/Tdap Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis Shingles Zoster Pneumococcal Meningococcal MMR Measles, mumps, rubella HPV Human papillomavirus Chickenpox Varicella Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hib Haemophilus influenzae type bPCV13 PPSV23 MenACWY or MPSV4 MenB Women Men Pregnancy Weakened immune system HIV: CD4 count <200 HIV: CD4 count ≥200 Kidney disease or poor kidney function Asplenia (if you do not have a spleen or if it does not work well) Heart disease Lung disease Chronic alcoholism Diabetes (type 1 or type 2) Chronic liver disease You should get flu vaccine every year. You should get a Td booster every 10 years. You also need one dose of Tdap vaccine. Women should get Tdap vaccine during every pregnancy. You should get shingles vaccine if you are aged 60 years or older, even if you have had shingles before. You should get Hib vaccine if you do not have a spleen, have sickle cell disease, or received a bone marrow transplant. You should get one dose of PCV13 and at least one dose of PPSV23 depending on your age and health condition. You should get this vaccine if you did not get it when you were a child. You should get HPV vaccine if you are a woman through age 26 years or a man through age 21 years and did not already complete the series. If you have this health condition, More information talk to your healthcare professional about these vaccines
- 5. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Vaccine Information Statement Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13) What You Need to Know1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. 1. Why get vaccinated? 2. PCV13 vaccine 3. Some people should not get this vaccine 4. Risks of vaccine reaction Vaccination can protect both children and adults from pneumococcal disease. Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria that can spread from person to person through close contact. It can cause ear infections, and it can also lead to more serious infections of the • Lungs (pneumonia) • Blood (bacteremia) • Covering of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis) Pneumococcal pneumonia is most common among adults. Pneumococcal meningitis can cause deafness and brain damage, and it kills about 1 child in 10 who get it. Anyone can get pneumococcal disease, but children under 2 years of age and adults 65 years and older, people with certain medical conditions, and cigarette smokers are at the highest risk. Before there was a vaccine, the United States saw the following in children under 5 each year from pneumococcal disease: • More than 700 cases of meningitis • About 13,000 blood infections • About 5 million ear infections • About 200 deaths Since a vaccine became available, severe pneumococcal disease in these children has fallen by 88%. About 18,000 older adults die of pneumococcal disease each year in the United States. Treatment of pneumococcal infections with penicillin and other drugs is not as effective as it used to be, because some strains of the disease have become resistant to these drugs. This makes prevention of the disease, through vaccination, even more important. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (called PCV13) protects against 13 types of pneumococcal bacteria. PCV13 is routinely given to children at 2, 4, 6, and 12–15 months of age. It is also recommended for children and adults 2 to 64 years of age with certain health conditions, and for all adults 65 years of age and older. Your doctor can give you details. Anyone who has ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to a dose of this vaccine, to an earlier pneumococcal vaccine called PCV7, or to any vaccine containing diphtheria toxoid (for example, DTaP), should not get PCV13. Anyone with a severe allergy to any component of PCV13 should not get the vaccine. Tell your doctor if the person being vaccinated has any severe allergies. If the person scheduled for vaccination is not feeling well, your healthcare provider might decide to reschedule the shot on another day. With any medicine, including vaccines, there is a chance of reactions. These are usually mild and go away on their own, but serious reactions are also possible. Problems reported following PCV13 varied by age and dose in the series. The most common problems reported among children were • About half became drowsy after the shot, had a temporary loss of appetite, or had redness or tenderness where the shot was given • About 1 out of 3 had swelling where the shot was given • About 1 out of 3 had a mild fever, and about 1 in 20 had a fever over 102.2°F • Up to about 8 out of 10 became fussy or irritable Adults have reported pain, redness, and swelling where the shot was given; also mild fever, fatigue, headache, chills, or muscle pain. Young children who get PCV13 along with inactivated flu vaccine at the same time may be at increased risk for seizures caused by fever. Ask your doctor for more information.
- 6. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Vaccine Information Statement Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13) What You Need to Know1 PRACTICE AID 1. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/pcv13.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. 5. What if there is a serious reaction? 6. The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program 7. How can I learn more? Problems that could happen after any vaccine • People sometimes faint after a medical procedure, including vaccination. Sitting or lying down for about 15 minutes can help prevent fainting, and injuries caused by a fall. Tell your doctor if you feel dizzy, or have vision changes or ringing in the ears. • Some older children and adults get severe pain in the shoulder and have difficulty moving the arm where a shot was given. This happens very rarely. • Any medication can cause a severe allergic reaction. Such reactions from a vaccine are very rare, estimated at about 1 in a million doses, and would happen within a few minutes to a few hours after the vaccination. As with any medicine, there is a very small chance of a vaccine causing a serious injury or death. The safety of vaccines is always being monitored. For more information, visit: www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/. What should I look for? Look for anything that concerns you, such as signs of a severe allergic reaction, very high fever, or unusual behavior. Signs of a severe allergic reaction can include hives, swelling of the face and throat, difficulty breathing, a fast heartbeat, dizziness, and weakness—usually within a few minutes to a few hours after the vaccination. What should I do? If you think it is a severe allergic reaction or other emergency that can’t wait, call 9-1-1 or get the person to the nearest hospital. Otherwise, call your doctor. Reactions should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Your doctor should file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS website at www.vaers.hhs.gov, or by calling 1-800-822-7967. VAERS does not give medical advice. The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) is a federal program that was created to compensate people who may have been injured by certain vaccines. Persons who believe they may have been injured by a vaccine can learn about the program and about filing a claim by calling 1-800-338-2382 or visiting the VICP website at www.hrsa.gov/vaccinecompensation. There is a time limit to file a claim for compensation. • Ask your healthcare provider. He or she can give you the vaccine package insert or suggest other sources of information. • Call your local or state health department. • Contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) -- Call 1-800-232-4636 (1-800-CDC-INFO) -- Visit CDC’s website at www.cdc.gov/vaccines
- 7. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Vaccine Information Statement Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine What You Need to Know1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. 1. Why get vaccinated? 2. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) 3. Some people should not get this vaccine Vaccination can protect older adults (and some children and younger adults) from pneumococcal disease. Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria that can spread from person to person through close contact. It can cause ear infections, and it can also lead to more serious infections of the • Lungs (pneumonia) • Blood (bacteremia) • Covering of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis); meningitis can cause deafness and brain damage, and it can be fatal. Anyone can get pneumococcal disease, but children under 2 years of age, people with certain medical conditions, adults over 65 years of age, and cigarette smokers are at the highest risk. About 18,000 older adults die each year from pneumococcal disease in the United States. Treatment of pneumococcal infections with penicillin and other drugs used to be more effective. But some strains of the disease have become resistant to these drugs. This makes prevention of the disease, through vaccination, even more important. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) protects against 23 types of pneumococcal bacteria. It will not prevent all pneumococcal disease. PPSV23 is recommended for • All adults 65 years of age and older • Anyone 2 through 64 years of age with certain long-term health problems • Anyone 2 through 64 years of age with a weakened immune system • Adults 19 through 64 years of age who smoke cigarettes or have asthma Most people need only one dose of PPSV. A second dose is recommended for certain high-risk groups. People 65 and older should get a dose even if they have gotten one or more doses of the vaccine before they turned 65. Your healthcare provider can give you more information about these recommendations. Most healthy adults develop protection within 2 to 3 weeks of getting the shot. • Anyone who has had a life-threatening allergic reaction to PPSV should not get another dose. • Anyone who has a severe allergy to any component of PPSV should not receive it. Tell your provider if you have any severe allergies. • Anyone who is moderately or severely ill when the shot is scheduled may be asked to wait until they recover before getting the vaccine. Someone with a mild illness can usually be vaccinated. • Children less than 2 years of age should not receive this vaccine. • There is no evidence that PPSV is harmful to either a pregnant woman or to her fetus. However, as a precaution, women who need the vaccine should be vaccinated before becoming pregnant, if possible.
- 8. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Vaccine Information Statement Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine What You Need to Know1 PRACTICE AID https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/ppv.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. 4. Risks of vaccine reaction 5. What if there is a serious reaction? 6. How can I learn more? With any medicine, including vaccines, there is a chance of side effects. These are usually mild and go away on their own, but serious reactions are also possible. About half of people who get PPSV have mild side effects, such as redness or pain where the shot is given, which go away within about two days. Less than 1 out of 100 people develop a fever, muscle aches, or more severe local reactions. Problems that could happen after any vaccine • People sometimes faint after a medical procedure, including vaccination. Sitting or lying down for about 15 minutes can help prevent fainting, and injuries caused by a fall. Tell your doctor if you feel dizzy, or have vision changes or ringing in the ears. • Some people get severe pain in the shoulder and have difficulty moving the arm where a shot was given. This happens very rarely. • Any medication can cause a severe allergic reaction. Such reactions from a vaccine are very rare, estimated at about 1 in a million doses, and would happen within a few minutes to a few hours after the vaccination. As with any medicine, there is a very remote chance of a vaccine causing a serious injury or death. The safety of vaccines is always being monitored. For more information, visit: www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/ What should I look for? Look for anything that concerns you, such as signs of a severe allergic reaction, very high fever, or unusual behavior. Signs of a severe allergic reaction can include hives, swelling of the face and throat, difficulty breathing, a fast heartbeat, dizziness, and weakness. These would usually start a few minutes to a few hours after the vaccination. What should I do? If you think it is a severe allergic reaction or other emergency that can’t wait, call 9-1-1 or get the person to the nearest hospital. Otherwise, call your doctor. Afterward, the reaction should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS website at www.vaers.hhs.gov, or by calling 1-800-822-7967. VAERS does not give medical advice. • Ask your healthcare provider. He or she can give you the vaccine package insert or suggest other sources of information. • Call your local or state health department. • Contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) -- Call 1-800-232-4636 (1-800-CDC-INFO) -- Visit CDC’s website at www.cdc.gov/vaccines
- 9. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Standards for Adult Immunization Practice1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. 1. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/adults/for-practice/standards/index.html. Accessed January 17, 2018. 1. ASSESS immunization status of all your patients at every clinical encounter. • Stay informed. Get the latest CDC recommendations for immunization of adults. • Implement protocols and policies. Ensure that patients’ vaccine needs are routinely reviewed and patients get reminders about vaccines they need. 2. Strongly RECOMMEND vaccines that patients need. • Share tailored reasons why vaccination is right for the patient. • Highlight positive experiences with vaccination. • Address patient questions and concerns. • Remind patients that vaccines protect them and their loved ones against a number of common and serious diseases. • Explain the potential costs of getting sick. 3. ADMINISTER needed vaccines or REFER your patients to a vaccination provider. • Offer the vaccines you stock. • Refer patients to providers in the area that offer vaccines that you don’t stock. 4. DOCUMENT vaccines received by your patients. • Participate in your state’s immunization registry. Help your office, your patients, and your patients’ other providers know which vaccines your patients have had. • Follow up. Confirm that patients received recommended vaccines that you referred them to get from other immunization providers.
- 10. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Adult Pneumococcal Vaccination Guide for HCPs1,2 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. Two types of pneumococcal vaccine are recommended for use in US adults: a 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). Recommendations for their use vary by age and risk factors. Every adult aged 65 years and older should receive both PCV13 and PPSV23. The table below will aid in determining which adults aged 19 to 64 years need pneumococcal vaccination. Details on sequence and timing of doses for adults in both age groups can be found on page 2 of this practice aid. Additional information and clinical guidance regarding the use of PCV13 and PPSV23 can be found at: cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd-vac/pneumo/ Indications for PCV13 and PPSV23 Administration for Adults Aged 19 to 64 Years by Risk Group Risk Group Underlying Medical Conditions PCV13 PPSV23 Recommended Recommended Revaccination 5 Years After First Dose Immunocompromised personsa Congenital or acquired immunodeficiencyb ü ü ü HIV ü ü ü Chronic renal failure ü ü ü Nephrotic syndrome ü ü ü Leukemia ü ü ü Lymphoma ü ü ü Hodgkin disease ü ü ü Generalized malignancy ü ü ü Iatrogenic immunosuppressionc ü ü ü Solid organ transplant ü ü ü Multiple myeloma ü ü ü Persons with functional or anatomic aspleniaa Sickle cell disease/other hemoglobinopathy ü ü ü Congenital or acquired asplenia ü ü ü Immunocompetent personsa Cerebrospinal fluid leak ü ü Cochlear implant ü ü Immunocompetent persons Chronic heart diseased ü Chronic lung diseasee ü Diabetes mellitus ü Alcoholism ü Chronic liver disease, cirrhosis ü Cigarette smoking ü a See Figure 1 for timing of these doses. b Includes B- (humoral) or T-lymphocyte deficiency, complement deficiencies (particularly C1, C2, C3, and C4 deficiencies), and phagocytic disorders (excluding chronic granulomatous disease). c Diseases requiring treatment with immunosuppressive drugs, including long-term systemic corticosteroids and radiation therapy. d Including congestive heart failure and cardiomyopathies, excluding hypertension. e Including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, and asthma.
- 11. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Adult Pneumococcal Vaccination Guide for HCPs1,2 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. C1: complement component 1; C2: complement component 2; C3: complement component 3; C4: complement component 4; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; HCPs: healthcare providers; PCV13: 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PPSV23: 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. 1. http://www.adultvaccination.org/professional-resources/pneumo/adult-pneumo-guide-hcp.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. 2. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/vacc-specific/ pneumo.html. Accessed January 3, 2018. People aged 19 to 64 years with chronic heart, lung or liver disease, diabetes, alcoholism, cirrhosis, or who are cigarette smokers need one dose of PPSV23. The charts below provide details on timing of PCV13 and PPSV23 doses for all others. Figure 1. PCV13 and PPSV23 Timing for US Adults Aged 19 to 64 Years With Immunocompromising Conditions, Functional Asplenia, CSF Leaks, or Cochlear Implantsa Pneumococcal Vaccine-Naïve Persons Persons Previously Vaccinated With PPSV23 a See Table on page 1 for details on which adults aged 19 to 64 years need pneumococcal vaccination. b This dose not indicated for adults with CSF leaks or cochlear implants. Figure 2. PCV13 and PPSV23 Timing for US Adults Aged 65 Years or Older Pneumococcal Vaccine-Naïve Persons Persons Who Previously Received PPSV23 at ≥65 Years Persons Who Previously Received PPSV23 Before Age 65 Years Because They Have a Risk Factor Pneumococcal vaccines given at intervals <1 year do not need to be repeated. Additional Facts About Pneumococcal Vaccination • Mild side effects include redness or pain at the injection site. In rare cases fever, muscle aches, or more severe injection-site reactions may develop. • Vaccination can be administered any time of year, and one pneumococcal vaccine can be given at the same time as influenza vaccine. Note: Medicare will reimburse for two pneumococcal vaccines as long as they are given at least 11 months apart. ≥8 weeks ≥5 years and PPSV23 at 65 years or older PCV13 PPSV23 PPSV23b ≥5 years ≥1 year ≥8 weeks and PPSV23 at 65 years or older PCV13 PPSV23 PPSV23b ≥1 year ≥1 year ≥5 years PPSV23 at age ≤65 years PPSV23PCV13 at age ≥65 years PPSV23 at age ≥65 years ≥1 year PCV13 PCV13 at age ≥65 years ≥1 year PPSV23
- 12. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Adult Vaccination Reminder Email1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. 1. http://www.adultvaccination.org/professional-resources/adult/reminder-email.docx. Accessed January 4, 2018. Suggested Subject Line: Adults Need Vaccines Too Dear [PATIENT NAME], Vaccines aren’t only for kids; adults need them too. Vaccine-preventable diseases kill more US adults each year than HIV/AIDS, breast cancer, or traffic accidents. We encourage all of our adult patients to get their vaccines. There are good reasons to make sure you are vaccinated: • Seasonal influenza vaccine for all adults, every year – The flu is not just a runny nose and a case of the sniffles. People of all ages can die from influenza. Even an average case can put you in bed for weeks. • Tdap vaccine (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis) for all adults who have never received it – This vaccine helps prevent pertussis, or whooping cough, which can make adults very sick but can be fatal if you pass it on to a baby. You can help protect infants in your family and our community by getting this vaccine. Pregnant women should receive a Tdap vaccine with every pregnancy. [OPTIONAL: There has been an increase of whooping cough cases in our community this year, making this vaccine extremely important.] • Pneumococcal vaccine for adults age 65 and older, younger adults with certain health conditions, and cigarette smokers – Pneumococcal disease causes pneumonia, bloodstream infection, and meningitis. In the United States, it kills tens of thousands each year, including 18,000 adults age 65 years and older. • Shingles vaccine for all adults age 60 and older – About one million people in the United States get shingles every year. Shingles pain may last for weeks, months, or even years. • Hepatitis B vaccine for adults at risk and those with certain health conditions, including all adults age 19 through 59 years with diabetes – There is no treatment for hepatitis B virus. It is a silent disease that many people don’t know they have until they develop complications like liver cancer or cirrhosis. In the United States, an estimated 2.2 million people are chronically infected with the hepatitis B virus. • HPV vaccine for women through age 26; all men through age 21 and some men through age 26 with certain health conditions or lifestyle factors, if not previously immunized – HPV causes cervical, vulvar, and vaginal cancers in females; penile cancer in males; and anal, throat, and other oral cancers in both sexes. If you are not sure about your vaccination history and status, please call us today. We want all of our patients to be protected. For more information, visit adultvaccination.org. Sincerely, [INSERT NAME] [INSERT OFFICE CONTACT INFORMATION]
- 13. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Immunization Assessment Tool: Risk for Pneumococcal Disease1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. HCPs: healthcare providers. 1. http://www.adultvaccination.org/professional-resources/pneumo/assessment-tool-inoffice.pdf. Accessed January 3, 2018. Pneumococcal disease is a very serious infection that causes pneumonia, meningitis, and bloodstream infection. There are vaccines that greatly reduce your chance of getting it. To determine whether you may need pneumococcal vaccination, please check all that apply below. Even if you already had one vaccination, you may need another. Check all that apply ü Yes Are you 65 years or older? Do you have any of these diseases or medical conditions? Alcoholism Asthma Blood disorder (eg, anemia, leukemia, sickle cell anemia, etc) Cancer Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks Cochlear implants Diabetes Heart disease HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiency Kidney disease Liver disease Lung disease Solid organ transplant Spleen damaged, inactive, or surgically absent Do you smoke cigarettes? Do you live or work at a long-term residential facility such as a nursing home? Have you ever received a pneumococcal vaccination or a “pneumonia shot” in the past? If you checked any of the boxes above, your doctor may recommend that you be vaccinated against pneumococcal disease. All adults should also receive an annual influenza vaccine to reduce risk of both flu and pneumococcal disease. Any adult who has never received a Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis or “whooping cough”) vaccine should get one. If you are age 60 or older, have other chronic health conditions, or are age 26 or younger, you may need additional vaccinations. For more information, visit adultvaccination.org. Note for healthcare professionals: For more information, please refer to the Adult Pneumococcal Vaccination Guide for HCPs or visit cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd-vac/pneumo.
- 14. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Patient Education: Pneumococcal Infographic1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. 1. www.adultvaccination.org/pneumococcal-infographic. Accessed January 4, 2018. What do they all have in common? They are all at increased risk for an infection called pneumococcal disease. Getting vaccinated is the safest, most effective way to protect yourself. Nearly one million people get pneumococcal pneumonia in the United States every year and 5% to 7% of them die. Everyone 65 years and older and all adults with certain health conditions are at risk. Learn more at adultvaccination.org/pneumococcal • Pneumococcal disease can cause pneumonia, meningitis, or bloodstream infection (sepsis), which can lead to severe complications, hospitalizations, or death Ask your healthcare provider about pneumococcal vaccination today. Medicare and most private insurers cover the cost of vaccination for those who need it. PharmacyMedical office Miguel, age 55 Diabetes Diane, age 50 Heart disease Bill, age 28 Smoker David, age 30 Asthma Lily, age 65 Patricia, age 41 Lymphoma Carl, age 37 HIV Pneumococcal meningitis and bloodstream infection are less common, but more deadly. One in every four to five people over the age of 65 who get it will die.
- 15. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Addressing Common Questions about Pneumococcal Vaccination for Adults1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. What diseases do these vaccines protect against? There are two vaccines that protect against pneumococcal disease, which is caused by infection with a common bacterium called Streptococcus pneumoniae. • PCV13 (pneumococcal conjugate vaccine) protects against 13 of the approximately 90 types of pneumococcal bacteria that can cause the most serious types of pneumococcal disease, including pneumonia, meningitis, and bacteremia. • PPSV23 (pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine) protects against 23 types of pneumococcal bacteria. This vaccine helps prevent invasive infections like meningitis and bacteremia. How common is pneumococcal disease? Each year in the United States, pneumococcal disease kills thousands of adults, including 18,000 adults 65 years or older. Thousands more end up in the hospital because of pneumococcal disease. How does pneumococcal disease spread? Pneumococcal bacteria can spread from person to person by direct contact with respiratory secretions, like saliva or mucus. People can carry the bacteria in their nose and throat, and can spread the bacteria without feeling sick. Who is at risk for pneumococcal disease? • People 65 years and older • People with certain health conditions, such as chronic lung disease or diabetes • People with conditions that lower the body’s resistance to infection (weakened immune system) • People who smoke cigarettes What could happen if I get this disease? Pneumococcal disease ranges from mild to very dangerous. Pneumococcal disease can spread from the nose and throat to ears or sinuses, causing generally mild infections, or spread to other parts of the body, leading to severe health problems such as lung infections (pneumonia), blood infections (bacteremia), and infection of the covering around the brain and spinal cord (meningitis). These serious illnesses can lead to disabilities like deafness, brain damage, or loss of arms or legs. These illnesses can also be life threatening. • Pneumococcal pneumonia kills about 1 out of 20 people who get it • Pneumococcal bacteremia kills about 1 out of 6 people who get it • Pneumococcal meningitis kills about 1 out of 6 people who get it Adults with chronic conditions are at increased risk of developing complications from pneumococcal disease.
- 16. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Addressing Common Questions about Pneumococcal Vaccination for Adults1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. 1. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/adults/downloads/fs-pneumo-hcp.pdf. Accessed January 4, 2018. Who should get these vaccines? When and how often are they needed? PCV13: Adults should get one dose of this vaccine before starting or continuing doses of PPSV23. It is recommended for • All adults 65 years or older • Adults 19 years or older with certain medical conditions PPSV23: Adults should get one, two, or three doses of this vaccine, depending on their age, health condition, and timing of the first dose. It is recommended for • All adults 65 years or older • Adults 19 years or older with certain health conditions • Adults 19 years or older who smoke cigarettes Who should not get these vaccines? PCV13: Anyone who has ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to a dose of the vaccine, to an earlier pneumococcal vaccine called PCV7 (or Prevnar), or to any vaccine containing diphtheria toxoid (for example, DTaP), should not get PCV13. Anyone with a severe allergy to any component of PCV13 should not get the vaccine. PPSV23: Anyone who has ever had a life- threatening allergic reaction to a dose of the vaccine or with a severe allergy to any component of the vaccine should not get the vaccine. How well do the vaccines work? PCV13: Studies done on PCV13 use in adults showed the vaccine to be 75% effective in preventing invasive pneumococcal disease, like bloodstream infections and meningitis, and 45% effective at preventing non-invasive pneumonia caused by the 13 strains it covers. PPSV23: In adults with healthy immune systems, this vaccine has been shown to be 50%-85% effective in preventing invasive disease caused by the 23 strains it covers. How safe are these vaccines? Pneumococcal vaccines are very safe. They went through years of testing before being licensed by the FDA and continue to be monitored for safety by the FDA and CDC. Is it safe to get if I have certain health conditions or am taking prescription meds? Unless you have had an allergic reaction in the past to the vaccine or have allergies to certain components of the vaccine, it is safe to get. It is safe for people taking prescription medications to get vaccines. What are the potential side effects of these vaccines? PCV13: Adults receiving the vaccine have reported redness, pain, and swelling where the shot was given. Mild fever, fatigue, headache, chills, or muscle pain have also been reported. Life-threatening allergic reactions from this vaccine are very rare. PPSV23: About half of people who get PPSV23 have mild side effects, such as redness or pain where the shot is given. Less than 1% develop a fever, muscle aches, or more severe local reactions. The risk of a vaccine causing serious reaction, or death, is extremely small. Where can I get these vaccines? Pneumococcal vaccines may be available at private doctor offices, public or community health clinics, pharmacies, or other community locations (such as schools/universities, workplaces, religious centers or places of worship). Check with your doctor or pharmacist or use the Adult Vaccine Finder (vaccine.healthmap.org) to help find places that provide pneumococcal vaccines near you. How much do the vaccines cost? Most private health insurance covers pneumococcal vaccines. Check with your insurance provider for details on whether there is any cost to you and for a list of in-network vaccine providers. Medicare Part B covers the cost of both pneumococcal vaccines (when administered at least 12 months apart).
- 17. Access the activity,“RISE: Raising Immunization RateS for Pneumococcal DiseasE in Adults,”at www.peerview.com/KHA40. Six STEPS for Implementing a Team-Based Immunization Program1 PRACTICE AID This Practice Aid has been provided as a quick reference to help learners apply the information to their daily practice and care of patients. PCV13: 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PPSV23: 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. 1. https://www.stepsforward.org/modules/adult-vaccinations. Accessed January 4, 2018. 1. Get your team on board. • Your recommendation is the single most important factor in influencing a person’s decision to get vaccinated; therefore, it is vital that you convey strong support for vaccination not only to your patients but also to your team members. 2. Train your team. • Training for your practice/organization can focus on topics such as – Vaccine fundamentals – Communicating benefits and risks of vaccines – Preparation, administration, and adverse event reporting – Storage and handling – Billing, coding, and documentation (includes standing orders) 3. Prepare your team to address common patient questions. • All team members, from medical assistants to nurses, should feel comfortable telling patients that vaccines are safe, necessary, and effective, remembering that anecdotes resonate stronger than data. – Provide short stories of patients who have had a vaccine-preventable illness and emphasize that the most common side effect of vaccination is a sore arm. 4. Implement a standardized process. • Identify which patients are due for which vaccines for the next day's clinic. – Many electronic medical record (EMR) systems have age- and disease-specific reminders for immunizations that are due, and using these can save a lot of time. • Have front desk staff prepare and hand patients a preprinted vaccine information statement (VIS) when they check in. • Use standing order sets for vaccine administration before the physician component of the appointment and for documentation. – These can standardize and streamline practice and may be particularly useful when dealing with vaccines with complicated schedules (eg, the pneumococcal vaccines PPSV23 and PCV13). • If your patient declines a vaccination, ask why and then provide further counseling and encouragement. • Use standard protocols for managing and reporting adverse events from vaccinations. 5. Document vaccines given, and minimize financial risk. • Minimizing the risk for financial losses starts with reducing wasted vaccines. 6. Recognize and reward the participation of your team. • When starting your immunization program, debrief with your team regularly to identify unexpected challenges and troubleshoot how to overcome them.
