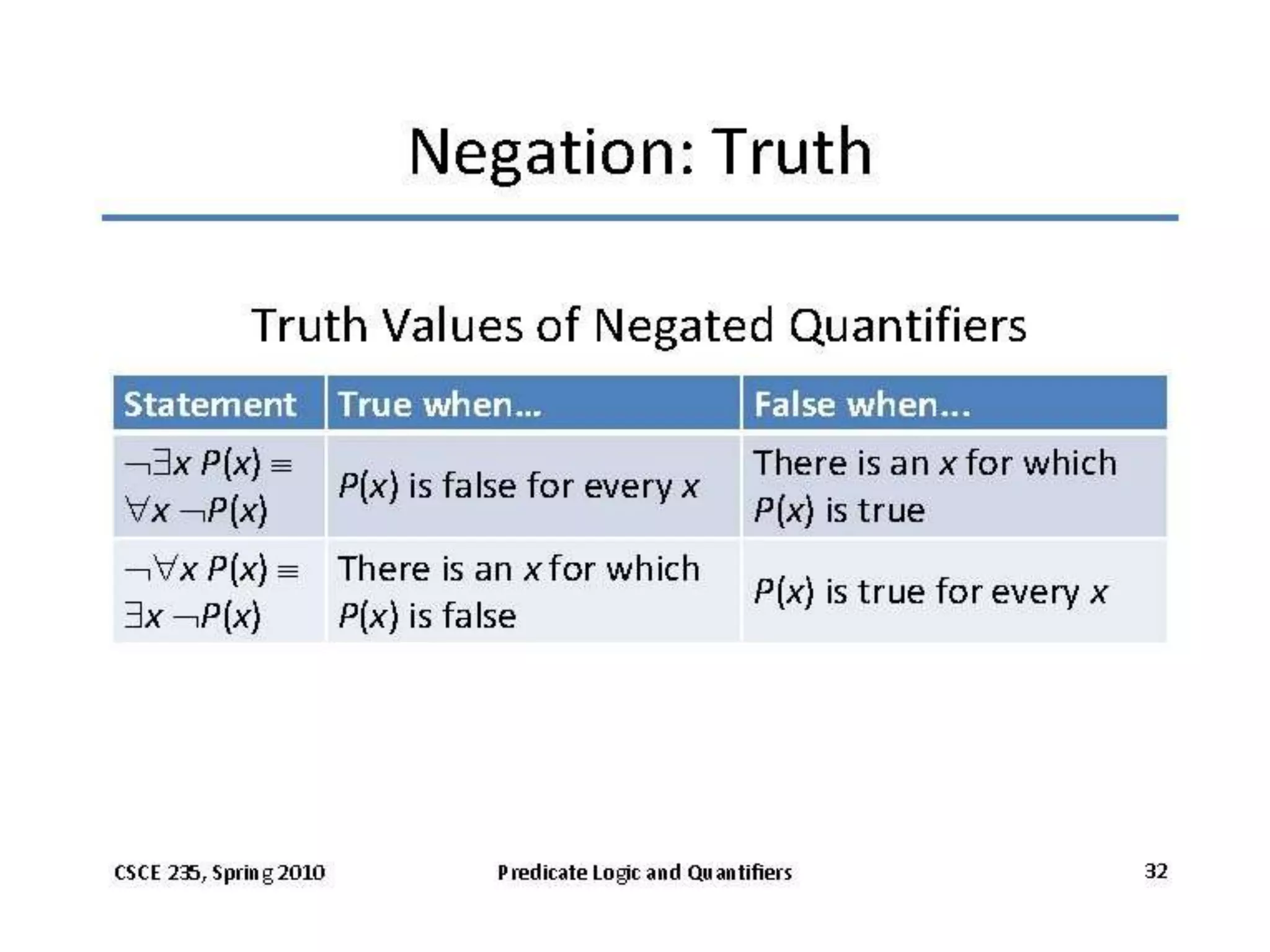
Predicate logic uses predicates to describe properties or relations among objects. Predicates are represented by propositional functions like P(x) which denotes "x is a student". Predicates are quantified using quantifiers like the existential quantifier ∃ and universal quantifier ∀. The existential quantifier denotes there exists an object with a certain property, while the universal quantifier denotes a property is true for all objects. When quantified propositions are negated, an existentially quantified proposition becomes universally quantified, and vice versa, according to De Morgan's laws.