Philippine government positions and requirements
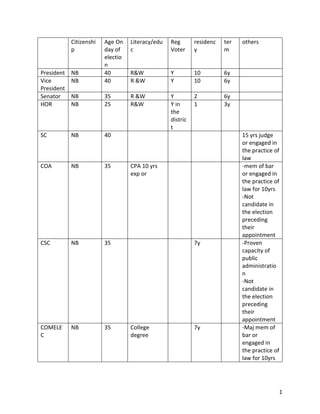
- 1. 1 Citizenshi p Age On day of electio n Literacy/edu c Reg Voter residenc y ter m others President NB 40 R&W Y 10 6y Vice President NB 40 R &W Y 10 6y Senator NB 35 R &W Y 2 6y HOR NB 25 R&W Y in the distric t 1 3y SC NB 40 15 yrs judge or engaged in the practice of law COA NB 35 CPA 10 yrs exp or -mem of bar or engaged in the practice of law for 10yrs -Not candidate in the election preceding their appointment CSC NB 35 7y -Proven capacity of public administratio n -Not candidate in the election preceding their appointment COMELE C NB 35 College degree 7y -Maj mem of bar or engaged in the practice of law for 10yrs
- 2. 2 -Not candidate in the election preceding their appointment OMB NB 40 Member of Bar -Recognized probity and independence - Not candidate in the election preceding their appointment Judge citizen Member of BAr Section 1 - Judicial power is the duty of the court to settle actual controversies involving rights which are legally demandable and enforceable and to determine whether there is a grave abuse of discretion amounting to lack or excess of jurisdiction on the part any branch or instrumentality of the government. Requisites: 1. Actual case or controversy - ripeness 2. Legal standing 3. Issue of constitutionality must be raised at the earliest possible time 4. Issue of constitutionality must be the very lis mota of the case Section 5- Powers of the SC 1. Exercise original jurisdiction over all cases involving ambassadors, public ministers and consuls and over petitions for certiorari, prohibition, mandamus, quo warranto and habeas corpus. 2. Review, revise, reverse, modify or affirm on appeal or certiorari, as the law of the Rules of Court may provide, final judgments and orders of lower courts in: a. All cases in which the constitutionality or validity of any treaty, international or executive agreement, law, presidential decrees, proclamation, order, instruction, ordinance or regulation is in question. b. All cases involving the legality of any tax, impost, assessment or toll or any penalty imposed thereto. c. All cases in which the jurisdiction of any lower court is in issue.
- 3. 3 d. All criminal cases in which the penalty imposed is reclusion perpetua or higher. e. All cases in which only error or question of law is involved. 3. Assign temporarily judges of lower courts to other stations as public interest may require. Such temporary assignment shall not exceed 6 months without the consent of the judge concerned. 4. Order a change of venue or place of trial to avoid a miscarriage of justice. 5. Promulgate rules concerning the protection and enforcement of constitutional rights, pleading, practice and procedure in all courts, the admission to the practice of law, the Integrated Bar and legal assistance to the underprivileged. Such rules shall provide for a simplified and inexpensive procedure for the speedy disposition of cases, shall be uniform for all court of the same grade and shall not diminish, increase or modify substantive rights. Rules of procedure of special courts and quasi judicial bodies shall remain effective unless disapproved by the Supreme Court 6. appoint all officials and employees of the Judiciary in accordance with the Civil Service law Section 6 – The SC shall have administrative supervision overall courts and the personnel thereof. Separation of Powers – the 3 branches of Government, Executive, Legislative and Judicial department cannot encroach on the powers allocated to each branch Legislative- to enact laws Executive – to execute laws Judicial – to apply/interpret laws A law subjecting COMELEC rules to approval by a Congressional oversight committee is invalid; constitutes legislative veto; contradicts the independence of COMELEC; pre- empts judiciary in its exercise of the power of review The requirement that the implementing rules of a law be subjected to approval of Congress as a condition of its effectivity violates separation of powers, principle of bicameralism and the rule on presentment; from the moment the law becomes effective any provision of law which empowers Congress to play role in its implementation violates sep of power, therefore unconsti. Sovereignty is permanent, exclusive, comprehensive, absolute, indivisible, inalienable and imprescriptible Legal (power to issue final commands) vs political (power behind the legal sovereign) Internal (control its domestic affairs) external (relationship with other states) Rt to self determination -rt of States to freely determine their political status and pursue their economic, social and cultural development
- 4. 4 Internal pursue their economic, social and cultural development within the framework of an existing state External establishment of a sovereign and independent state State Immunity – a State cannot be sued without its consent Xpn: 1. Can give consent Expressly: through a law Implied: when the state enters into a contract with a private person (state has descended to a level of an individual Make a distinction between jure imperii (in their sovereign capacity/public acts) and jure gestionis (private acts) When the state sues, opens itself to a counterclaim Suability does not mean liability. As a rule, public funds may not be disbursed absent an appropriation of law or other specific statutory authority. Money claims against the government should be brought before the COA. Only when COA rejects can it be elevated to the courts thru certiorari. 3 powers of the government: Police power – power of the state to regulate, prohibit reqts: lawful purpose/subject – interest of the public as distinguished from those of a particular class; lawful means- means employed must be reasonably necessary to obtain the objective sought Taxation – power to raise revenues inorder to defray the expenses of the government Eminent Domain- taking of private property for public purpose upon payment of just compensation Reqt for LGU; 1. ordinance 2. for public purpose 3. payment of just compensation 4. valid and definite offer to the owner previously made and the owner rejects phases: 1. Determination of public purpose 2. Determination of just compensation ( exclusively a judicial function) Police power Taxation Eminent domain Liberty and property Property property Govt Govt Govt/private Property taken is destroyed bec it is noxious Property taken is for public purpose Property taken is for public purpose Compensation is the intangible altruistic feeling that he has contributed to the general welfare Protection and improvements for the taxes paid Full and fair equivalent of the property taken
- 5. 5 Bill of Rights No person shall deprived of his life, liberty or property without due process of law nor shall any person de denied the equal protection of the laws. Substantial due process Procedural due process – right to be heard Requisites of valid classification 1. rest on substantial distinction 2. it must be germane to the purpose of law 3. must apply to all members of the same class 4. apply to both present and future conditions no law shall be passed abridging the freedom of speech, of expression, or of the press or the right of the people to peaceably assemble and petition the government for redress of grievances. Freedom from prior restraint Freedom from subsequent punishment Heckler’s veto – when an acting party’s rt to freedom of speech is curtailed or restricted by the govt inorder to prevent a reacting party’s behaviour. Clear and present danger rule – whether the words are used in circumstances AND OF Such nature as to create a clear and present danger that will bring about the substantive evils that Congress has rt to prevent Content based restriction – if restriction is based on the subject matter or content of the speech – subject to strict scrutiny test Content neutral – merely concerned with the incidents of speech such as the time, place or manner and under well defined standards. – intermediate review Facial challenges Overbreadth Doctrine – when a statute restrains even constitutionally protected rights Void for Vagueness- it lacks comprehensible standards that men of ordinary intelligence would guess as to its meaning or differ as to its application autolimitation – a State, by entering into a treaty, Team buhay - Political speech Expropriation – forcible taking of private property for public purpose upon payment of just compensation – when govt takes over a prop even without initiating an expropriation case The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers and effects against unreasonable searches and seizures of whatever nature and for any purpose shall be inviolable and no search warrant or warrant of arrest shall issue except upon probable cause to be determined personally by the judge after examination under oath or
- 6. 6 affirmation of the complainant and the witnesses he may produce, and particularly describing the place to be searched and the persons or things to be seized. Bantay bayan, barangay based volunteer orgs in charge of peace and order, port police and port personnel – agents of the govt that have a color of state related function 4 instances when probable cause is required 1. during prelim investigation for purposes of filing info in court 2. by the judge for purposes of issuing warrant of arrest 3. by the judge for purposes of issuing search warrant 4. by the police officer when making a hot pursuit arrest Prelim inquiry Prelim Investigation By the judge by the prosec Purpose of issuing warrant of arrest Purpose of determining whether the offender should be held for trial Judicial in nature Executive function Determination of the existence of facts and circumstances that would lead a reasonably discreet and prudent person to believe that an offense has been committed by the person sought to be arrested Ascertaining existence of facts sufficient to engender a well founded belief that a crime has been committed and the respondent has been guilty thereof. Reqts for valid warrant of arrest/search warrant 1. based on probable cause 2. personally determined by the judge 3. particulary describing the place to be searched or the persons or things to be seized Reqts in flagrante: 1. The person to be arrested must execute an overt act indicating that he has just committed a crime, is committing or is attempting to commit a crime 2. The he executed the overt act in the presence or with in the view of the arresting officer Reqts hot pursuit: 1. That a crime has just been committed 2. The arresting officer has personal knowledge of facts and circumstances indicating that the person arrested has committed the crime Search warrant Specific offense With particularity – a description of a place to be searched is sufficient if the officer with the warrant can ascertain and identify with reasonable effort the place intended and distinguish it from other places in the community.
- 7. 7 What can be the subj of search warrant: a. Subject of the offense b. Stolen or embezzled and other proceeds or fruits of the offense c. Those used or intended to be used as the means of committing an offense There is Particularity in describing the things when: a. The description is as specific as the circumstances will ordinarily allow b. Description expresses a conclusion of fact- not of law which the police officer may use as a guide in making the search and seizure c. When the things to be descriped are limited to those which has direct connection to the offense for which the warrant is being issued Enforcement of search warrants: 2 witnesses required; occupant thereof, or any member of the family. If unavailable, 2 witnesses of sufficient age and discretion residing in the same locality; mandatory; if not complied with, exclusionary rule applies Valid waiver of rt: clear, unequivocal, specific, intelligently given and unattended by duress or coercion; not subjected to a coercive environment ( surrounded by armed police) 1. Existence of a right 2. Knowledge of the existence of such right 3. Clear intention to relinquish the right Reduced expectancy of privacy – valid custom searches in the airport, bus, malls Reasonable searches – arises from reduced expectation of privacy for which reason Art.III Section 2 finds no application eg. Searches in airports, seaports, bus stations, malls Warrantless search is presumably unreasonable search but by reason of practicality, a search warrant may be dispensed with. Eg. Search incidental to a lawful arrest (lawful arrest must precede the search), search in plain view, consented search, search of a moving vehicle Reqts for plain view search 1. Valid prior intrusion 2. Discovered inadvertently 3. Immediately apparent Reqts for stop and frisk (terry search)- limited protective search of the other clothing of the person arrested Conditions reasonable search of bus in transit 1. Manner of search must be least intrusive 2. Search must not be discriminatory 3. Purpose of the search must be confined to ensure pubic safety 4. Precautionary measures that ensure that evidence is not planted
- 8. 8 Checkpoints – more extensive or intrusive search of the vehicle requires a probable cause on the part of the apprehending officers 1. Simply looks into the vehicle 2. Flash light without opening door 3. Visual search 4. Occupants not subjected to physical or body search 5. Routine check is conducted in a fixed area Legislative Power -PEARL Power to Enact, Amend, Repeal Laws -includes appropriation, taxation and expropriation Bill Joint reso 3 readings on separate days Can be approved on 1,2, 3 days on the same or separate days depending on the rules of procedure adapted Presented to the president for approval or veto Does not need the presidents approval Printed copies must be given to the members 3 days before Printed copies can be given after approval On 3rd reading, no amendment allowed followed immediately by voting No such reqt Process of how a bill becomes a law is permanently fixed by the Consti Procedure for passing a joint reso is adapted separately by each house and may be changed anytime Power to augment – pres, Cj,Sen pres, speaker, chairmen of commissions Law, from savings, to augment (purpose), no cross border Inquiry in aid of legislation; in accordance with published rules; respect the rts of those appearing Question hour – department heads, Emergency powers – congress; law; authorize president; war or national emergency; limited period; resolution needed to withdraw Non -legislative powers Commission on Appointment – Sen pres as ex-officio Chair, 12 Senate, 12 HOR to be chosen based on proportional representation from the political parties and party list reps Who are to be appointed by the pres:
- 9. 9 1. Heads of exec dept (CA) 2. Ambassadors, public ministers, consul, officers of the armed forces with a rank of naval captain (CA) 3. Other offices whose appointments are vested in him by the Consti (CA) – Consti Commissioner and REGULAR members of the JBC (retired Justice of SC, rep from the Private sector, law 4. Appointments Not provided by law 5. Those whom he may be authorized by law to appoint Ad-interim vs regular appointment Ad Interim regular Not in Session In session Made before confirmation Made after the nomination is confirmed by CA Cease to be valid if disapproved by CA Once confirmed, continues until the end of term Privilege from Arrest Congress in session Not more than 6yrs PET Congress- Revoke by majority vote declaration of martial law; voting jointly Senate – Concur treaties, international agreements 2/3 House – initiate impeachment; senate try and hear Amnesty – concurrence of majority; Congress Amendment and revision – Con Ass – ¾ vote; Congress; call for Con Con 2/3 votes; submit to electorate question of calling for COnCOn, majority of all mems Executive Qualified Political agency – dept secretaries are alter ego of the president and their acts are presumed to be those of the Pres unless disapproved or reprobated by him. XPN; The president is required to personally act as provided by the Consti Power to suspend the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus and declaration of martial law- grounds: invasion or rebellion when public safety requires Amnesty pardon Public act; court takes judicial notice Private act of the pres; needs to be pleaded and proved in court Needs concurrence of Congress Does not need concurrence
- 10. 10 Involves political offenses Infractions of the peace of the State May be granted at whatever stage Upon final conviction Class of persons Individual Looks backward, and abolishes the offense itself; obliterates the offense with which he is charged and puts the person released stands before the law as though he had not committed any offense Looks forward and relives the offender from the consequences of the offense of which he has been convicted Cannot be granted in cases of impeachment For violation of election laws, favorable recommendation from the COMELEC Judiciary requisites for a valid judicial review 1. there must be an actual case or controversy 2. raised by the proper party 3. raised at the earliest opportune time 4. the issue of constitutionality must be the very lis mota of the cases Mootness Priniciple – ceased to present a justiciable controversy 1. grave violation of the Consti 2. paramount public interest involved 3. requires formulation of principles to guide the bench, bar or the public 4. capable of repetition yet evading review 3 levels of scrutiny to determine reasonableness of classification 1. rational scrutiny – provide rational basis for the classification 2. immediate scrutiny – challenged classification serves as important state interest and that classification is at least substantially related to serving that interest 3. strict scrutiny – legislative classification which impermissibly interferes with the exercise of consti rights are presumed to be unconsti Operative Fact Doctrine – the law is recognized as unconstitutional but the effects of the unconstitutional law, prior to its declaration of nullity, may be left undisturbed as a matter of equity and fair play. Administrative Jurisdiction over all courts and its personnel. Powers of SC 1. orig juris over public ministers, consuls, ambassadors and (CPMHQ) 2. appellate juris on final judgments and orders of lowers courts in:
- 11. 11 a. constitutionality of TIEL,PPOORI (treaty, intl agree, exec agree, law, pres decree, proc, ordinance, order, regulation, instruction) b. legality if TITA (tax, impost,assessment, toll) c. issues of jurisdiction of lower courts d. penalty imposed is RP or higher e. questions of law review the sufficiency and factual basis of the proclamation of Martial Law or the suspension of the writ of habeas corpus PET - sole judge of all contests relating to election, contests and qualifications of Pres and VP Rule making power Promulgate rules concerning: 1. the protection and enforcement of constitutional rights 2. pleadings, practice and procedure in all courts 3. admission to the practice of law, the Integrated Bar 4. legal assistance to the underprivileged limitations: 1. Provide a simplified and inexpensive procedure for the speedy disposition of cases 2. Uniform for all courts of the same grade 3. Shall not diminish, increase or modify substantial rights Supervision over the JBC – composition: CJ as ex officio chair, SOJ and mem of Congress as ex officio mems, rep of the IBP, retired justice of SC, professor of law, rep of private sector Disqualifications and prohibitions Congress – incompatible office – not hold any other office in the government, during his term without forfeiting his seat Forbidden office- appointed to an office which may have been created or emoluments have been increased during the term for which he as elected Prohibited to appear personally as counsel, interested financially in any contract, not intervene in any matter with the government for his pecuniary benefit President,VP,Cabinet, deputies and assistants shall not hold any other office during his tenure - Not practice their profession, participate in any business, interested financially, strictly avoid conflict of interest - Spouse and relatives 4th degree shall not be appointed as mems of ConComs, Omb,secretaties, deputies…
- 12. 12 Members of the SC shall not be designated to any agency performing quasi judicial or admin functions Members of ConCOms and OMB – hold any other office, engage in the practice of profession, intervene in any contract, financially interested in any contract with the govt Nationalization Priniciple Regalian Doctrine – all lands of public domain are owned by the State and the State is the source of any asserted right to ownership in land. EDU of natural resources – under control and supervision of the State - State may directly undertake or enter into joint venture, co-production, or production- sharing agreements with Filipino Citizens or corp 60% filipino ownership- 25 yrs renewable 25 yrs Large scale exploration, development and utilization of minerals, petroleum and other mineral oils – President may enter into agreements with foreign owned corporations involving technical or financial assistance International Law Sources: Primary: international treaties and conventions, intl customs - general and consistent practice of States recognized and followed by them from legal sense of obligation general principles of law – by virtue of incorporation, form part of the laws of the land even if they do not derive from treaty obligations Subsidiary: decisions of courts and teachings of publicists Relation to Domestic laws Doctrine of transformation – requires that an international law be transformed into a domestic law through a constitutional mechanism such as local legislation. Ie. No treaty or international agreement shall be valid unless concurred by 2/3 votes of the members of the Senate Doctrine of Incorporation - general principles of law, by virtue of incorporation, form part of the laws of the land even if they do not derive from treaty obligations By their nature, treaties and intl agreements have limiting effect on the absolute nature of sovereignty. By their voluntary act, nations surrender a portion or certain aspects of their state power, the usual underlying condition of this partial surrender Is the greater benefits derived from a pact or reciprocal undertaking of one contracting party to grant the same privileges or immunities to others. – sovereignty as auto-limitation