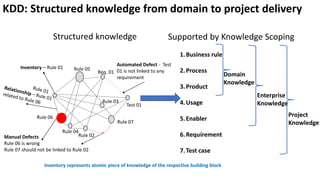
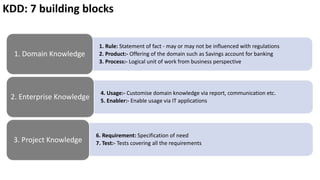
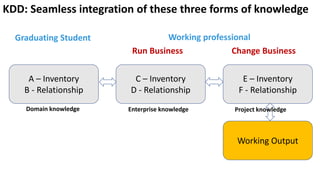
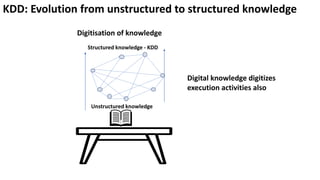
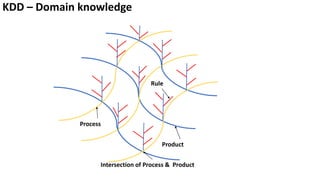
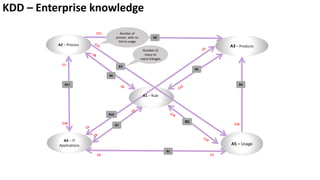
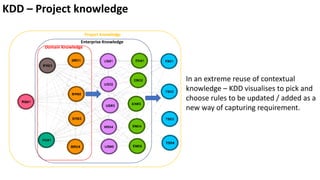
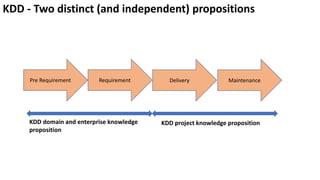
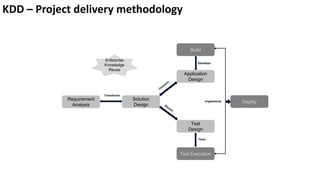
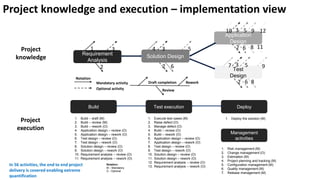
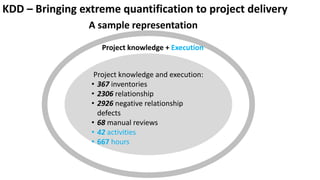
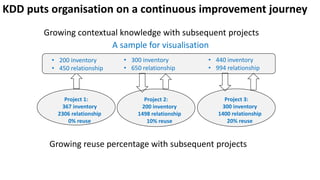
The document presents a new framework called Knowledge Driven Development (KDD) designed to improve digital knowledge management by integrating domain, enterprise, and project knowledge. KDD addresses challenges in traditional methodologies such as waterfall and agile by promoting reusability of knowledge and reducing dependencies on experts, thus enhancing efficiency in project delivery. It emphasizes structured knowledge and outlines components that facilitate the digitization and management of knowledge to drive continuous improvement in organizations.