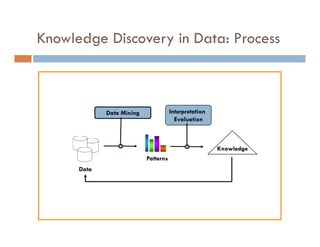
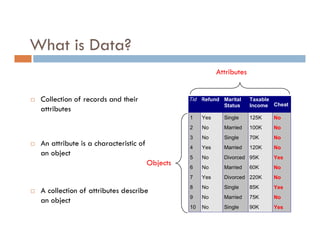
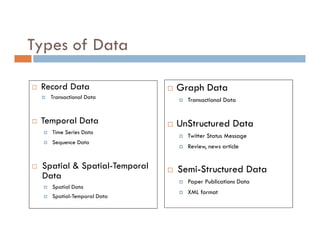
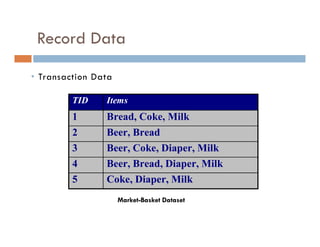
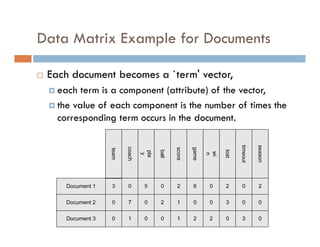
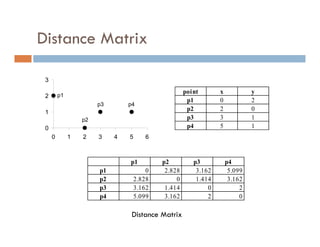
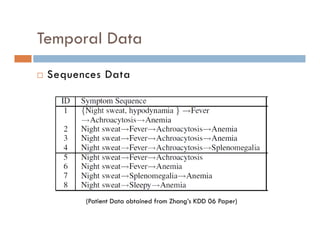
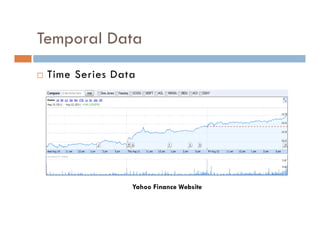
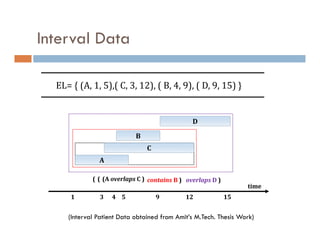
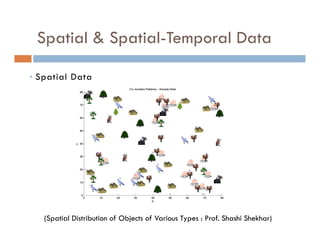
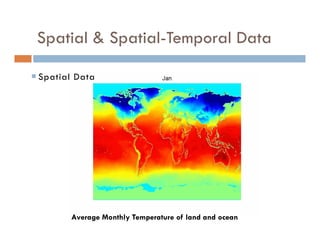
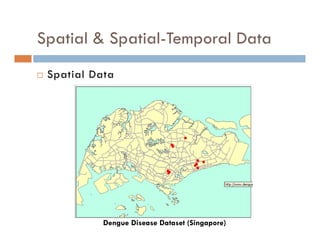
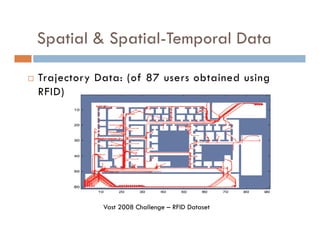
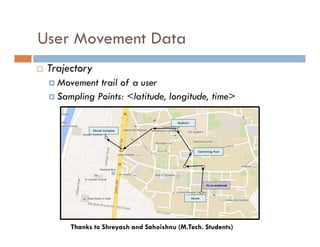
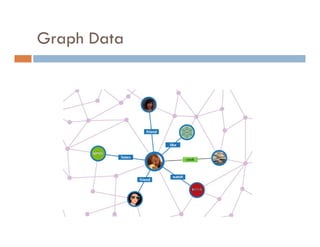
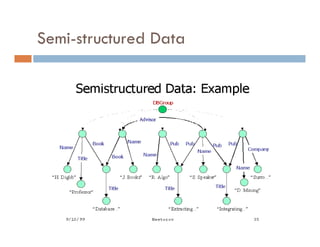
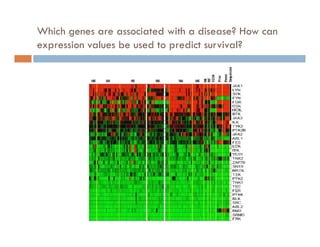
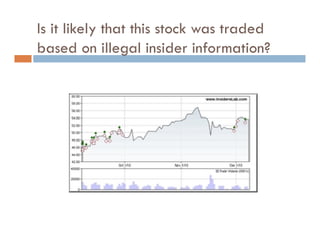
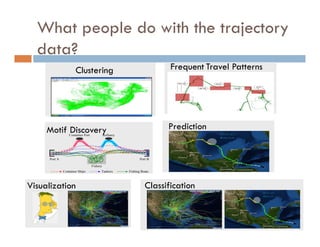
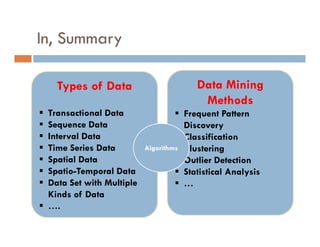
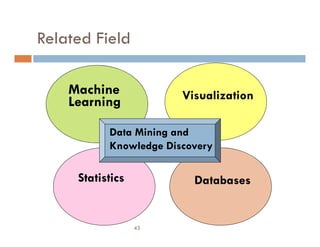
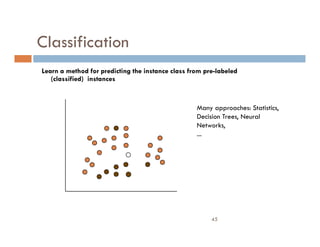
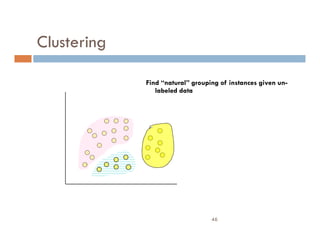
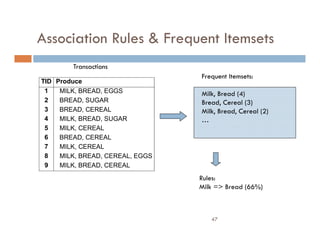
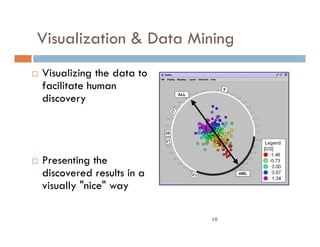
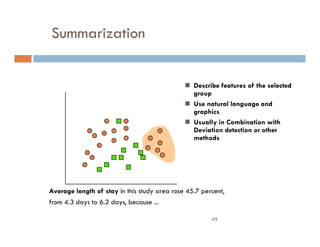
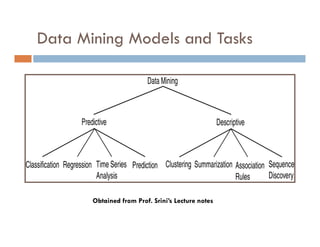
This document provides an introduction and overview of data mining and the data mining process. It discusses different types of data like transactional data, temporal data, spatial data, and unstructured data. It also covers common data mining tasks like classification, clustering, association rule mining and frequent pattern mining. Additionally, it discusses related fields like statistics, machine learning, databases and visualization and how they differ from data mining. Finally, it provides examples of different data mining models and tasks.