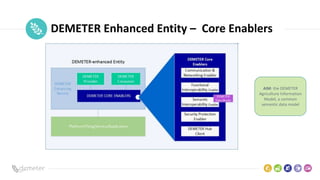
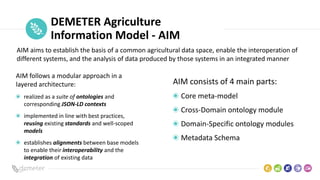
The document discusses the Demeter project, which aims to enhance interoperability in agriculture through a common Agriculture Information Model (AIM). It highlights the challenges of data integration in agtech due to varying formats and lack of standards, while defining a structured approach for achieving semantic interoperability among different data systems. The presentation includes details on the architecture, layers, and components of AIM, emphasizing the evolution and ongoing updates of this data-driven innovation initiative.