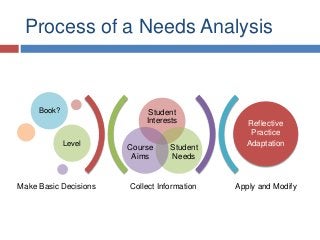
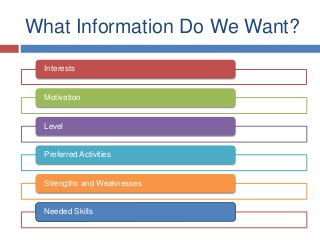
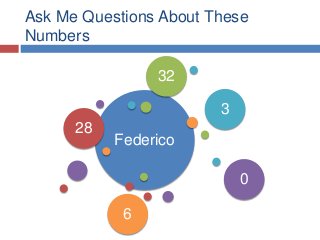
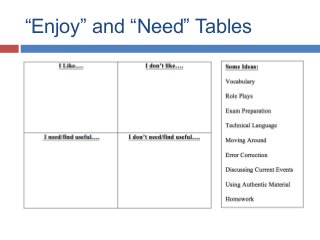
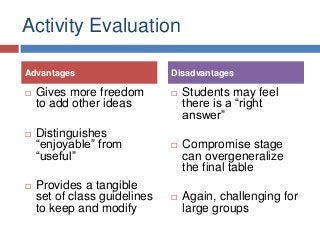
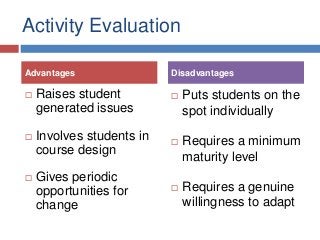
Slides from my presentation/workshop on needs analyses for the language classroom. Full details of this talk are available at http://fedefl.blogspot.com/2014/06/the-necessity-of-needs-analyses.html
Summaries of other professional development talks are available on the main blog feed at http://fedefl.blogspot.com