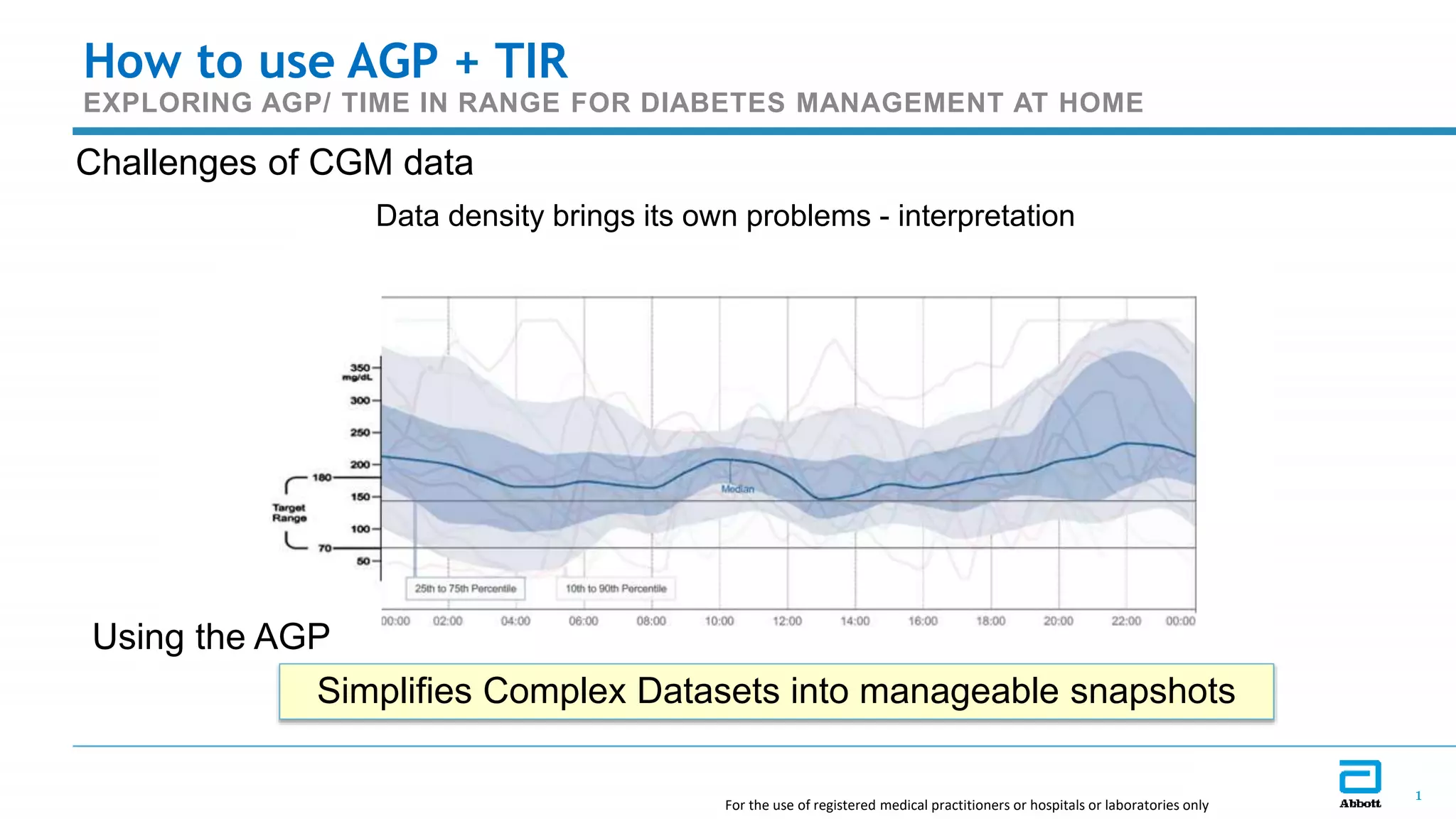
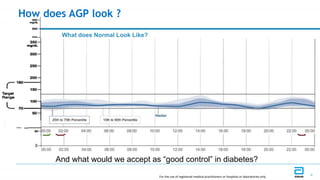
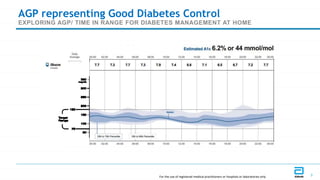
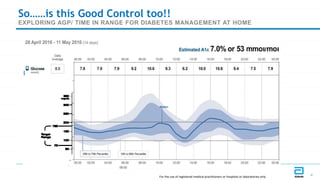
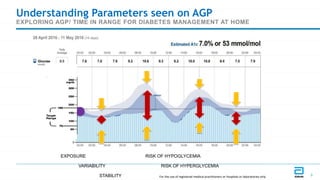
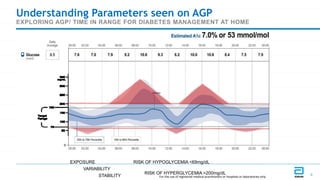
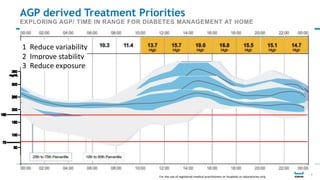
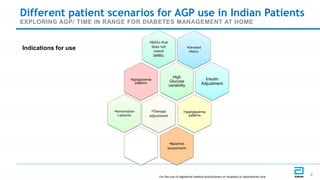
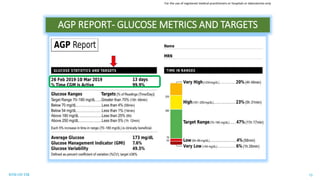
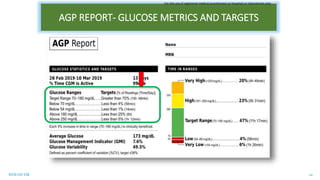
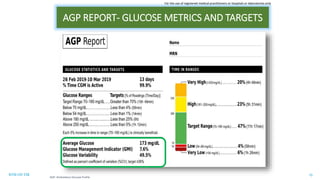
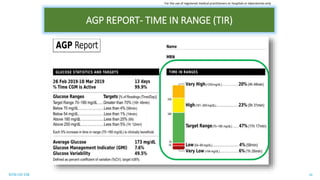
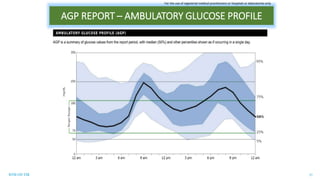
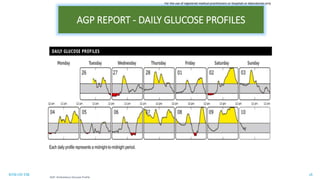
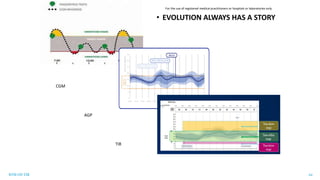
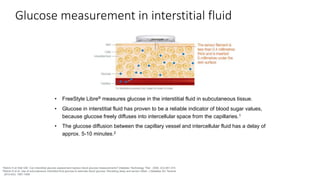
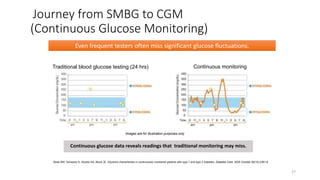
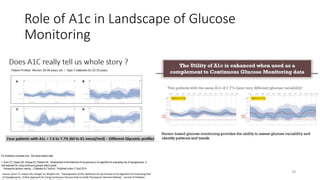
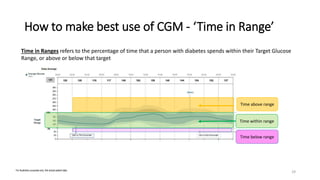
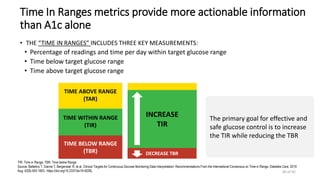
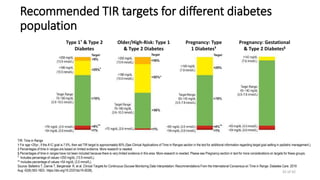
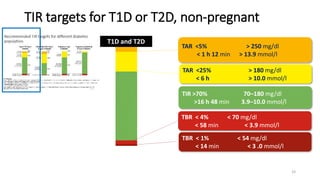
This document discusses the use of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) and Time in Range (TIR) metrics for diabetes management. It provides guidance on interpreting AGP reports, which simplify complex continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data into snapshots like TIR. TIR measures the percentage of time spent within, above, and below target glucose ranges and is a useful measurement that complements A1C. The document recommends increasing TIR and reducing time below range as primary goals for effective glucose control. It also presents different patient scenarios and indicators for using AGP and TIR data in diabetes management.