Liquid biopsy
- 1. LIQUID BIOPSY Dr Shashank Agrawal
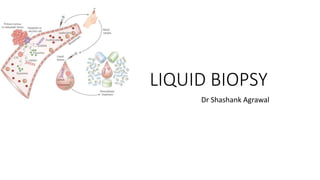
- 2. Introduction • Large amount of molecular data derived from Human Genome Project and advances in Pharmacogenomics has led to paradigm shift in oncology from “One size fits all” to more precise medicine and has led to development of “Personalised Medicine”. • In view of limitations of traditional biopsies- Invasiveness, complications and sometimes impossible, also there cross-sectional behaviour (as tumours and metastasis is dynamic a/c environment and medications and there heterogenicity), a new field analysing cancer derived components in circulation and other body fluids attracts minds in oncology.
- 3. • Apoptotic or necrotic cancer cells release circulating cell-free DNA fragments, designated as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), as well as exosomes (EXOs), namely membrane-encapsulated subcellular structures containing proteins and nucleic acids released by the tumor cells. • Primary tumor and metastatic sites are also able to exfoliate vital cells that, once entered the bloodstream, are circulating tumor cells (CTCs). • Isolation of these tumor-derived components from peripheral blood and other potential fluids and their genomic or proteomic assessment represent a new diagnostic tool that has been called ‘liquid biopsy’.
- 4. Approach to liquid biopsy • Cancer at any stage can shed tumor cells as well as fragments of cancer-causing DNA into the blood system and may give good indication of mutations in the tumor at the time of sampling. • The more advanced the cancer, the more likely tumor cells and cancer-causing DNA can be found in the blood.
- 6. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) • CTCs represent intact, viable non-hematological cells with malignant features that can be isolated from blood. • 1869, Ashworth described CTCs in cancer patients and its presence in blood stream was demonstrated by Engell in 1955. • CTCs are released into the bloodstream during metastatic spread of the cancer through blood and are present as single cells or clusters.
- 7. CTC (cont.…) • Even in patients with metastatic cancer, they occur on average at a frequency of 1 in 100 million cells and are mixed with approximately 10 million leukocytes and 5 billion erythrocytes per 1 ml blood. • And, due to apoptosis of CTCs, which begins soon after separation from the tumor of origin, they are extremely fragile. • Next generation sequencing (NGS) has revealed CTCs carry mutation signatures that resemble the signatures of their primary tumors including driver and druggable mutations like APC, KRAS, TP53, ERBB3, FBXW7 and ERBB2.
- 8. Cell free DNA (cfDNA) • Small DNA fragments found circulating in plasma or serum, as well as other bodily fluids. • The presence of cfDNA in blood plasma was discovered in 1948 by Mandel and Metais. • Plasma cfDNA usually are fragments of about 170– 500 bp, thought to originate mostly from apoptotic cells. • The total amount of ctDNA might be <0.01% of the total cfDNA concentration. • A major breakthrough came with the advancement of NGS technologies for mutation detections which allowed for the sequencing of DNA and RNA much more quickly and cheaply than the previously used Sanger sequencing.
- 9. • Patients with distant metastases have a significantly higher level of cfDNA compared to patients without metastases. Total mutation– specific cfDNA decreases during treatment but the levels increase later on in patients with recurrence. • Initial studies, such as those performed by Diaz et al., suggest that when both cfDNA and CTCs are present, cfDNA fragments outnumbered CTCs by 50 to 1. • In addition, a direct comparison of mutation detection on cfDNA vs CTCs showed a higher abundance of the mutation on the cfDNA from the same patient.
- 10. • An advantage of cfDNA is that they are relatively stable and can be analyzed from bio-banked biofluids, such as frozen plasma. • The most commonly used vacutainers for blood collection for isolation of cfDNA are proprietary Streck Cell-Free DNA BCT and CellSave tubes and standard K2EDTA tubes. • Studies comparing the optimal conditions for blood collection and storage temperature for cfDNA have found similar abundance and stability for up to 6 h in all tube types with no effect on the yield.
- 11. Exosomes and circulating RNA • Tumor cells actively release several species of cfRNAs, into the blood including non-coding RNAs (e.g., microRNAs or miRNA, small nucleolar RNAs, PIWI interacting RNAs, and long non-coding RNAs). • Such species are enriched in exosomes and strongly resist RNases. • High levels of exosomes are found in several bodily fluids from cancer patients and because of their resistant nature, exosomes and miRNA can be isolated from biofluid samples and stored for many years in the freezer. • Their composition seems to reflect that of the parental cells and therefore provide a novel type of biomarker for various patient scenarios. • Like cfDNA, circulating miRNA seems to give a better picture of variations present in the tumor than CTC.
- 12. • Recent studies have shown that plasma miRNA levels significantly correlate with larger tumor size, chemoresistance, and recurrence of tumors. • A study of plasma miR-224 levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma found that plasma levels could accurately predict presence of small tumors which were less than 18 mm preoperatively. • Similarly, the overexpression of miR-21 and its detection in plasma contributed to chemo-resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. • Level trends of miRNA in plasma co-relates with disease activity as well as treatment response.
- 13. Isolation and Analysis • Initial limitations were difficulties in isolation of nucleic acid and differentiating between normal and tumor derived material. • Various new technologies and advances have been introduced for proper assessment of tumor derived materials.
- 14. Current approaches for detection of liquid biopsy components from blood can be divided into three different categories: • Methods targeting specific druggable driver mutations or all possible aberrations in cfDNA, • Methods to isolate and identify CTCs, and • Methods to isolate and identify exosomes,
- 15. Methods to isolate and identify CTC CTCs in blood can be enriched using marker-dependent techniques: CTCs can be Positively selected in vitro or in vivo using antibodies to epithelial and/or mesenchymal proteins (such as epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EPCAM) and/or cytokeratins including CK8, CK18, CK19 and mesenchymal vimentin or N-cadherin) or Negatively selected for through depletion of leukocytes using anti-CD45 antibodies (endothelial cells, with markers such as CD146, and hematopoietic stem cells, with markers such as CD34). Positive enrichment of CTCs can also be performed in vitro using assays based on CTC characteristics including size(6 μm to >20 μm), deformability , density and electrical charge.
- 16. • Following enrichment, the isolated CTCs can be identified using immunocytological, molecular or functional assays. • With immunocytological platforms, CTCs are identified by membrane and/or intra-cytoplasmic staining with antibodies to epithelial, mesenchymal, tissue-specific or tumor-associated markers. Most common being CellSearch platform for Cytokeratin staining. • AdnaTest EMT-2 (Qiagen) test is an immuno-magnetic bead enrichment step targeting the surface proteins EpCAM, HER2 and EGFR. • Molecular and functional characterization need single CTC isolation- Done using DEPArray platform.
- 17. • Molecular technologies enable the identification of CTCs using RNA-based assays, such as quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR), RNA sequencing or in situ RNA hybridization. • Functional assays can be used to detect viable CTCs on the basis of their biological activities, for example, the fluoro- Epithelial ImmunoSPOT (EPISPOT) assay for certain proteins secreted or shed by CTCs and the related EPISPOT in a drop (EPIDROP) technology that enables the detection of single CTCs in microdroplets. • The molecular characteristics of CTCs can be further explored at the DNA , RNA and protein level, and the functional properties of CTCs can be investigated in vivo by injecting the cells into immunodeficient mice to form patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models.
- 22. Methods of cfDNA analysis
- 23. BEAMing, beads–emulsion–amplification–magnetics; biPAP, bidirectional pyrophosphorolysis-activated polymerization; CAPP-Seq, cancer personalized profiling by deep sequencing; ddPCR , droplet digital PCR; NGS, next-generation sequencing. Druggable, Resistant, New mutations etc
- 24. Commercial Kits • “SiRe” panel to identify 568 clinically relevant mutations in six genes (EGFR, KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, cKIT and PDGFRα) involved in NSCLC, gastro-intestinal stromal tumor, metastatic colorectal carcinoma and melanoma. • Guardant360 platform has been designed to identify tumor-related genomic alterations via complete exon sequencing in 73 different genes in cfDNA from blood. • FoundationACT Liquid Biopsy Assay sequences the exons of 315 cancer-associated genes and introns from 28 genes involved in rearrangements.
- 26. mRNA and Exosomes • Isolation of Exosomes and mRNA based on specific centrifugation techniques and electron microscope. • miRNeasy mini and microKits (Qiagen) seems to the most popular kits for isolation of exosome-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs
- 27. Comparison
- 28. • To date, liquid biopsy is not a routine test in clinical practice, but its potential applications are rapidly growing: from diagnostic genomic profiling to the monitoring of radicality in surgical outcomes, from evaluating either response or resistance to systemic treatments, to quantifying minimal residual disease.
- 30. Esophageal Cancer (EC) Screening • Data suggests about 93% have no prior screening and 40% presents with advanced ds. • CTC is a sensitive and minimally invasive alternative tech to endoscopy. • A small study of CTC-based liquid biopsy differentiated squamous cell EC patients from healthy controls with 86.3% sensitivity and 90.3% specificity. • ctDNA is less sensitive, as it is detectable in only 58% of patients without metastatic disease, however, sensitivity increases with late disease stage. Staging • PET-CT and endoscopic ultrasound • 50% individuals at curative intent procedure present with hematogenous spread at 5 years. • CTC corresponds with higher stages but also been detected in N0 ds. • ctDNA helps in prognostication by defining tumor biology. E.g. in SCC, MSH2 hypermethylation promoter was associated with inferior DFS. • Overall LB helps in stratifying high risk individuals for refining need of neoadjuent/adjuent therapies.
- 31. Response to Therapy/Surveillance • Management is multimodal. • Studies have shown post RT CTC positivity is associated with poor outcome. • 13-39% patients have discordant mutation b/w primary and CTC affecting personalised care. • The Personalized Antibodies for GastroEsophageal Adenocarcinoma (PANGEA) trial highlighted the significance of tumor heterogeneity and the potential of ctDNA-based liquid biopsy to guide precision therapy. • Another group demonstrated that acquired MET amplifications detected in ctDNA can serve as markers of resistance to trastuzumab and novel HER- kinase inhibitors in adenocarcinoma.
- 32. Gastric Cancer (GC) • Both CTC (epithelial, intermediate and mesenchymal on EMT) and ctDNA have been seen in GC. • No screening protocols for average risk individuals at present. • ctDNA and miRNA are promising and more sensitive then CTC. • But due to overall low sensitivity can’t be considered replacement of endoscopy. • CancerSeek is the platform available for evaluating ctDNA.
- 33. Staging • A study of 44 patients demonstrated that the CTC count at diagnosis is predictive of advanced stage, peritoneal dissemination, presence of metastases, and poor survival. • Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis of 16 studies demonstrated that quantitative ctDNA level correlated with the above outcomes . • HER2 amplification or overexpression. • A prospective study of 88 patients demonstrated discordance in HER2 amplification status between primary tumors and CTCs in patients with metastatic GC. • So LB can be used to tailor the treatment accordingly.
- 34. Response to Therapy/Surveillance • Trastuzumab resistance in metastatic HER2-positive disease can be monitored with serial liquid biopsies. • A similar example of this is illustrated in a study that trialed a pan- HER kinase inhibitor (afatinib) and found that resistance to this drug was correlated with tumor cells that were lacking EGFR amplification or with MET amplification. • CTC levels in post-treatment patients can be a prognostic marker.
- 35. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) • In patients with PDAC, both CTCs and ctDNA have been identified in peripheral blood. • Enrichment is challenging in PDAC due to small numbers of CTC in peripheral blood and pilot studies demonstrated that 7.5 mL whole blood is required for adequate sensitivity; in addition, cell size-based isolation (ISET) was more sensitive than the Cellsearch system. • Following enrichment, CTCs are analyzed using immunocytochemistry, FISH, and whole genome sequencing. • A study of 34 patients demonstrated that PDAC patients released ctDNA into the circulation at a rate that was orders of magnitude higher than healthy controls and genomic and epigenetic mutations were detectable in 5 mL of whole blood. • The optimal technique for enrichment and analysis of both CTCs and ctDNA in PDAC is a topic of ongoing laboratory investigation.
- 36. Screening • Unmet Need • It takes 15 years from single mutation to metastatic PDAC. • CTC is in all stage but low specificity. • Four principal mutations have been identified in ctDNA as most commonly found in PDAC: KRAS, CDKN2A, SMAD4, and TP53. • A study combining the detection of ctDNA KRAS mutations with CA 19-9 levels differentiated PDAC (47 patients) from chronic pancreatitis (31 patients) with a sensitivity of up to 98% and a specificity of 77% • Need further validation.
- 37. Staging • A meta-analysis of 16 studies regarding the use of CTCs and disseminated tumor cells (CTCs in bone marrow) as prognostic indicators demonstrated that detection of CTCs in peripheral blood and CTCs in bone marrow is associated with both progression-free and overall survival. • As for the role of ctDNA, a meta-analysis of 18 studies including 1243 patients determined that the presence of ctDNA with KRAS or ERBB2 mutations in peripheral blood significantly impacted overall and progression-free survival. • Furthermore, specific mutations, hypermethylation, and a high absolute quantity of ctDNA were associated with inferior survival.
- 38. Response to Therapy/Surveillance • CTC positivity, which dropped from 80.5% of patients to 29.3% after a cycle of fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in 41 patients with advanced PDAC. • Berger et al. demonstrated that in 20 therapy naive patients with ctDNA- positive (KRAS or TP53 mutations) metastatic PDAC who underwent chemotherapy, detectable mutations significantly decreased during treatment and the resulting levels correlated with progression-free survival. • One study demonstrated that specific CTC phenotypes (high expression of CD44, CD133, and aldehyde dehydrogenase) are predictive of recurrence. • Higher post-treatment levels of overall plasma ctDNA were found to correlate with both recurrence and metastases. • Furthermore, one study showed that ctDNA detected recurrences 6.5 months earlier than CT imaging among 77 patients.
- 39. Colorectal Cancer • The role of liquid biopsy in colorectal cancer (CRC) is evolving rapidly. • CTCs, ctDNA, and exosomal DNA have been isolated from the blood of patients with CRC. • Location of the blood-draw impacts the sensitivity of liquid biopsy in CRC, as blood from the portal system is enriched with tumor material compared to peripheral venous blood. • Detection limits reach as low as 3 CTCs per 2ml whole blood. • CTCs in CRC patients frequently have a genotype distinct from tissue tumor cells, as demonstrated by the up- or down-regulation of hundreds of genes involved in metabolism, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and cell survival. • The half-life of ctDNA in CRC is roughly 2.5 h, allowing for a relatively rapid determination of response to therapy. • Both variant alleles and epigenetic markers (CpG island methylation) are relevant in the detection and interpretation of ctDNA in CRC.
- 40. Screening • CRC is unique among gastrointestinal malignancies in that a relatively mature screening program exists for average-risk patients. • Colonoscopic screening is effective yet invasive, associated with poor compliance from patients, and is labor- and resource-intensive. • Less invasive means of screening, such as fecal immunochemical tests and DNA tests (e.g., Cologuard), have been developed and deployed clinically in recent years. • No liquid biopsy-based assays were recommended for CRC screening in the 2018 Guideline Updates from the American Cancer Society, however, as trial data are collected and as technology improves, such tests may have a greater role in CRC screening in the future. • Various platforms like CancerSEEK for ctDNA and FirstSight CTC based assays, are under rapid evolution to increase sensitivity.
- 41. Staging • Doubtful role of adjuent CT in stage 2. • A meta-analysis of 11 studies demonstrated that ctDNA positivity at the time of diagnosis is associated with inferior overall survival in colon cancer, however, the strength of this association varies with timing and technique. • Exosomal mircoRNA-21 positivity was correlated with poor disease-free and overall survival in stage II and III colon cancer. • Post-resection positivity of ctDNA have proven role in deciding CT in stage 2. • Ill defined role of CRS/HIPEC unless patient is symptomatic. • A pilot study of 14 patients suggested that postoperative CTC-positive patients with suspicion of peritoneal disease would benefit from CRS/HIPEC in terms of overall survival.
- 42. Response to Therapy/Surveillance • Liquid biopsy has demonstrated promise in detecting minimal residual disease or recurrence during the surveillance of colon cancer. • Standard post-treatment surveillance requires the use of non-specific serum markers (CEA), endoscopy, and an abdominopelvic CT scan. • A well-designed study of 230 patients determined that ctDNA with either a KRAS, TP53, or APC mutation was sufficient evidence of residual disease after curative-intent therapy. • Supporting this, a recent prospective study of 125 stage I–III colon cancer patients reported that, following definitive treatment, patients with persistent ctDNA during surveillance had a 40 times higher risk of recurrence that those with negative ctDNA .
- 43. • Most patients with CRC are treated with 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Targeted agents such as panitumumab and cetuximab are routinely added to these regimens if the tumor is RAS wild-type. • However, most patients develop resistance to these agents. • One well-designed study demonstrated that ctDNA-based liquid biopsy was extremely sensitive (>85%) for primary resistance to HER2 inhibitors . • A randomized controlled trial of 254 patients used ctDNA to identify a subgroup of patients with anti-EGFR resistance that benefited from alternative targeted therapy.
- 44. • Response to systemic therapy could also be monitored with CTC-based liquid biopsy and persistent positivity following adjuvant mFOLFOX in stage III colon cancer patients was a poor prognostic factor. • Advances in regional therapy for rectal cancer in particular have made distant recurrences the primary cause of mortality. • A well-designed cohort study with 159 patients demonstrated that the presence of ctDNA after resection is indicative of residual disease and a high probability of recurrence. In these patients, treatment with adjuvant systemic chemotherapy significantly improved OS . • Another study of 130 patients with stage I–III CRC suggested that serial ctDNA analysis with ultradeep sequencing could predict recurrence as early as 30 days after resection, which is much sooner than the capabilities of current radiographic, endoscopic, and CEA-based surveillance.
- 45. LIMITATIONS • Technically demanding. • Rapid EMT • Benign and premalignant conditions of various cancers express alterations in BRAF, RAS, EGFR, HER2, FGFR3, PIK3CA, TP53, CDKN2A,and NF1/2 genes as compared to malignant tissues. • Blood processing delays, storage, temperature, agitation of the sample and shipment are also a major source of variability between samples.
- 46. Summary • As a screening tool, liquid biopsy has the potential to save the cost and morbidity of invasive endoscopic screening procedures in diseases such as CRC and improve early detection of diseases such as pancreatic adenocarcinoma. • It appears ctDNA-based liquid biopsy is generally more sensitive for the early detection of gastrointestinal cancers than CTC-based assays. • While surgical techniques and outcomes continue to improve, procedures such as esophagectomy, gastrectomy, and pancreaticoduodenectomy still come with a high risk of morbidity and mortality. • The ability to accurately stage patients with micrometastatic disease could save patients, who would not benefit from upfront resection, the morbidity inherent to such operations. • Presence of CTCs may be an indicator of unresectability in certain gastrointestinal tumors, whereas the presence of ctDNA in determining resectability is less clear.
- 47. • Regarding the selection of systemic therapy regimens, ctDNA is generally more predictive of response to therapy and more useful in identifying actionable mutations for targeted therapy. • Improvements in surveillance would benefit thousands of patients each year with locally advanced disease who may be candidates for systemic or extensive regional therapy, including cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC). • LB is a example of benefit derived from academic and industrial sector. • One promising example is the Circulating Cell-free Genome Atlas study—a collaboration between GRAIL, Inc. and major academic institutions.
- 49. Thank You
