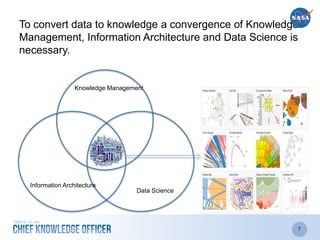
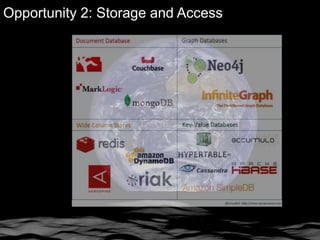
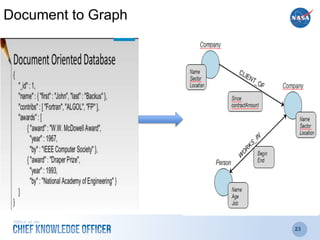
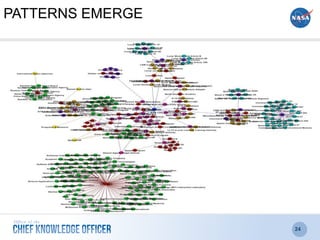
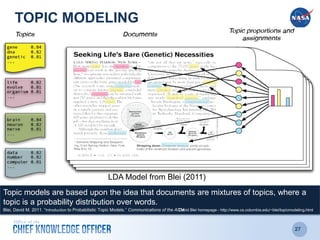
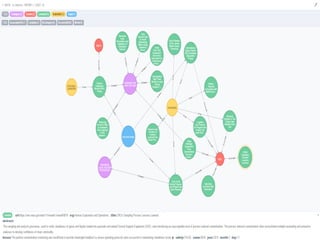
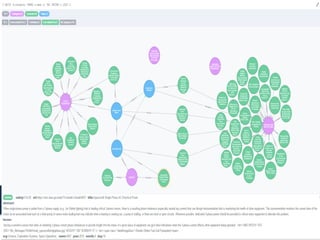
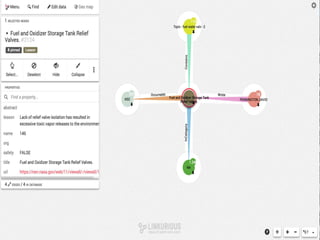
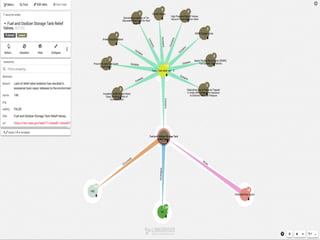
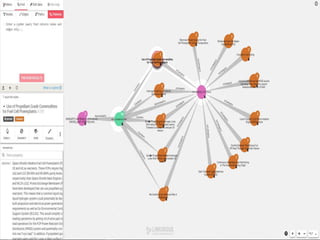
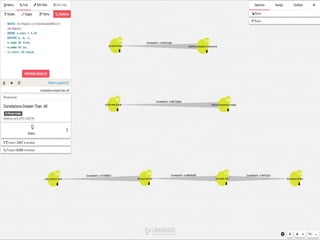
The document discusses the significance of knowledge architecture, which integrates knowledge management, information architecture, and data science to optimize organizational data into actionable knowledge. It highlights the challenges faced by NASA in managing vast amounts of data and identifies areas for improvement, including search, storage, and data-driven visualization. The opportunities presented aim to enhance decision-making and reduce inefficiencies in knowledge work.