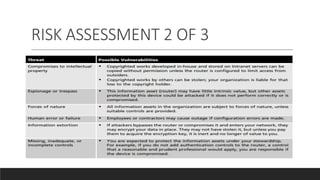
A database containing sensitive information on ongoing criminal investigations is hacked and confidential case details are leaked online. The incident response plan would provide guidelines on immediate actions to contain the breach, secure remaining systems, notify relevant stakeholders, and initiate forensic analysis to identify the source of the attack.



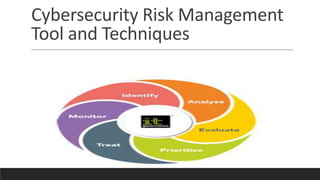

































![Plans that make
mitigation effective
What should the administrator do first?
Who should he or she contact?
The IR plan supplies the answers. In the event of a serious virus or
worm outbreak, the IR plan can be used to assess the likelihood of
imminent damage and to inform key decision-makers [1]. makers
in the various communities of interest (IT, information security,
organization management, and users)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cybersecurityriskmanagementtoolsandtechniques1-230709083313-f35f4dab/85/Cybersecurity-Risk-Management-Tools-and-Techniques-1-pptx-48-320.jpg)