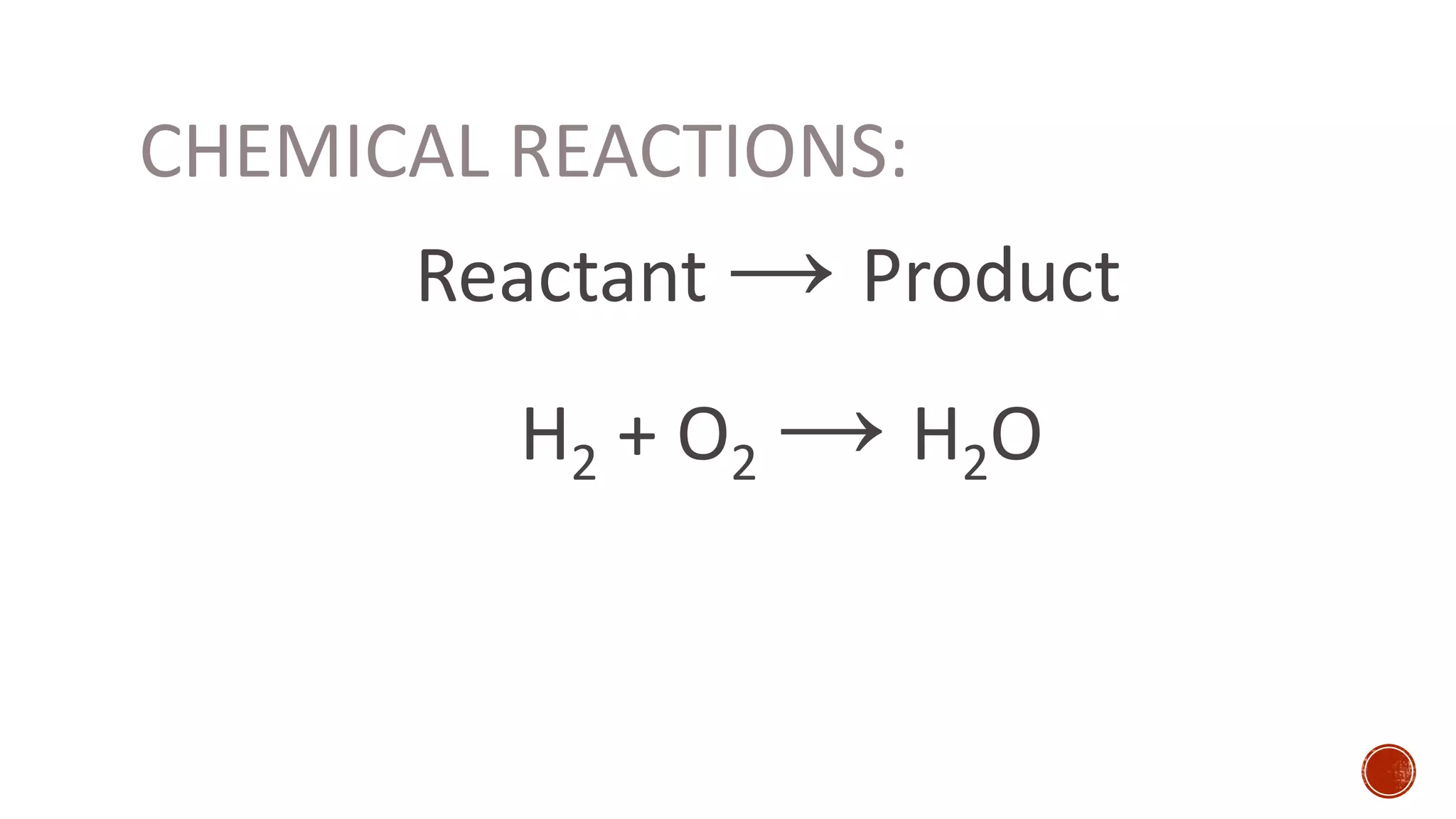
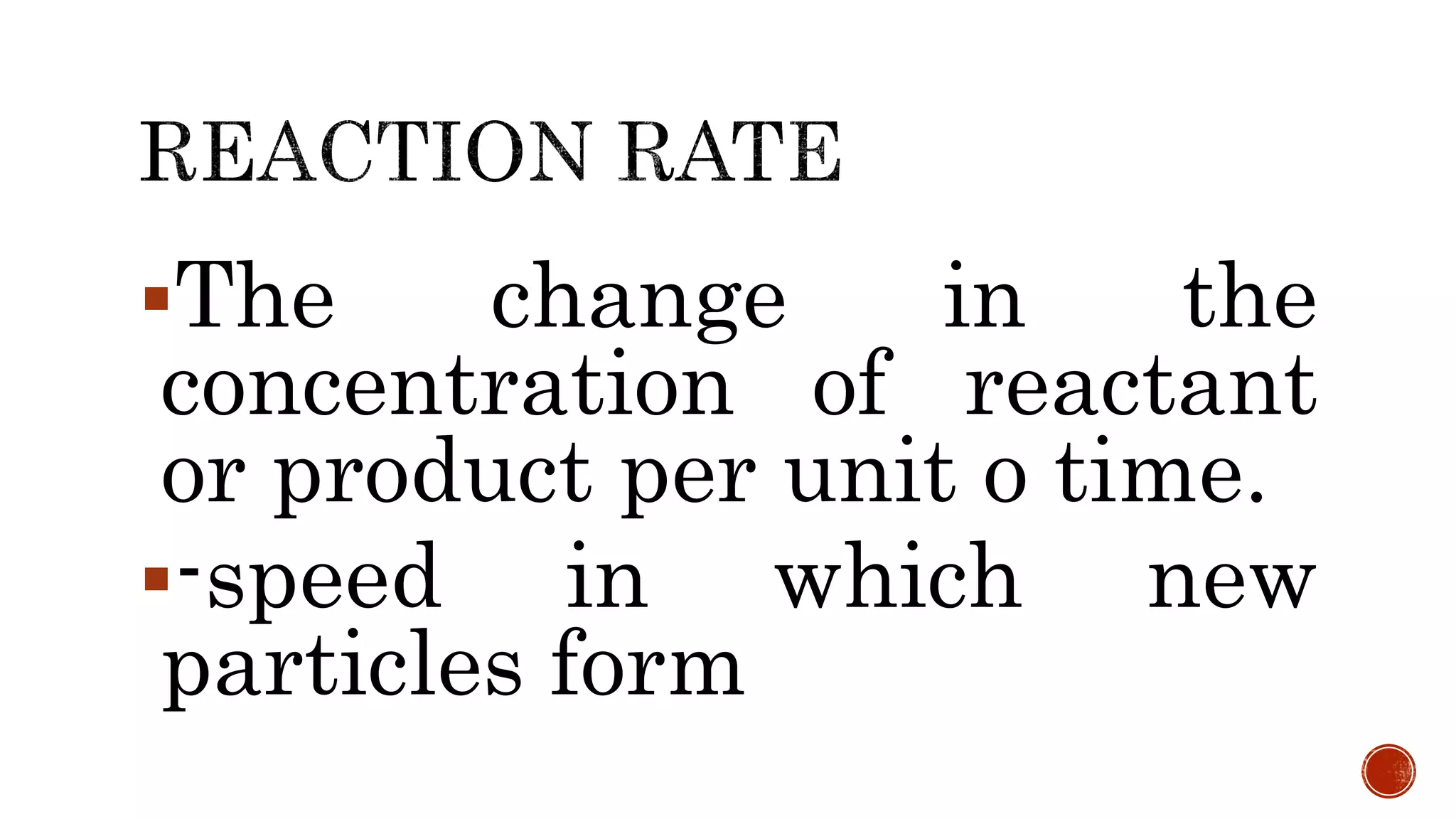
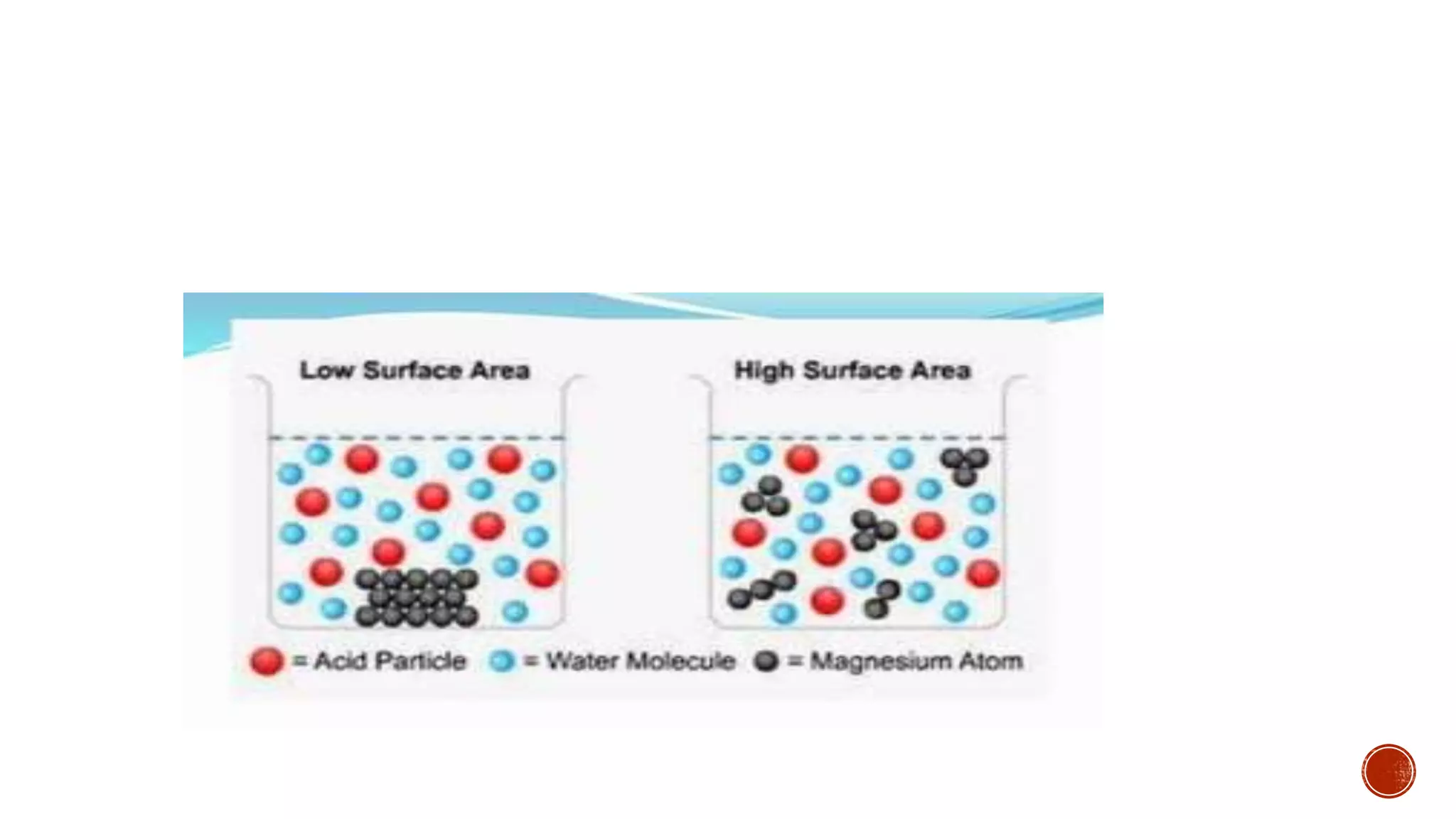
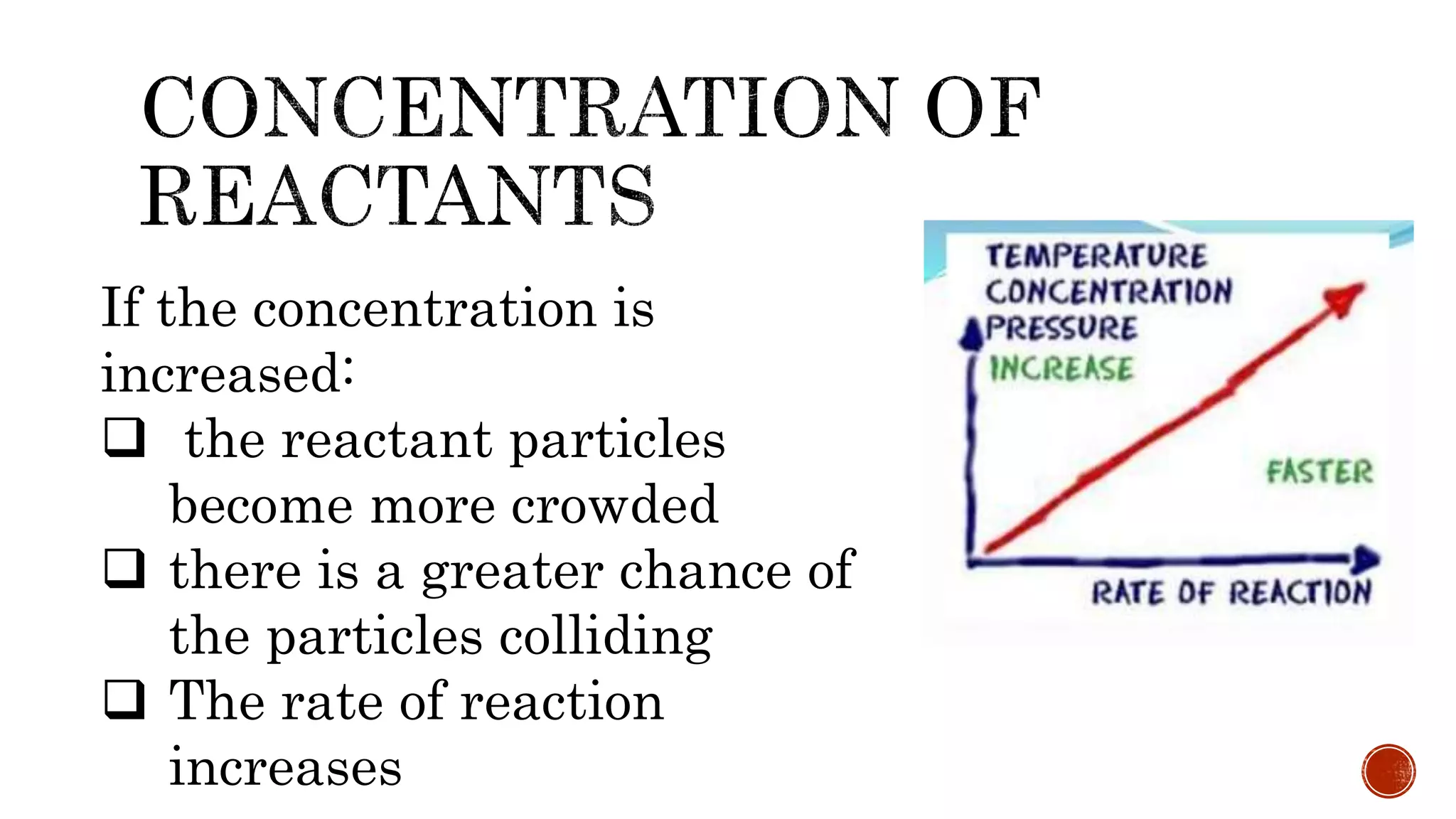
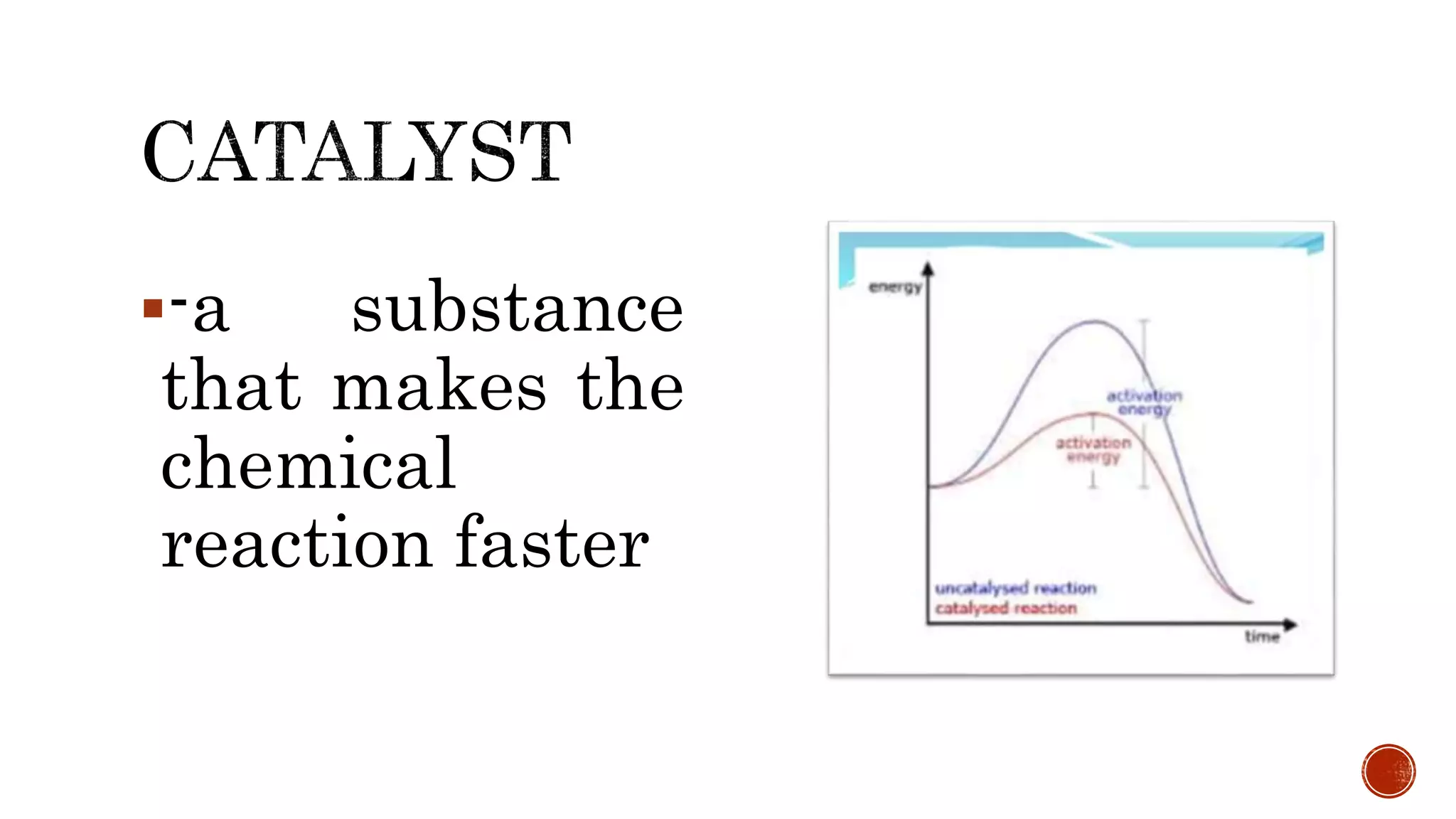
The document discusses chemical reactions and factors that affect reaction rates. It states the collision theory, which says that reaction rates increase with more frequent collisions between reactant particles that have sufficient kinetic energy. The document defines reaction rate and explains how increasing temperature, concentration, and surface area, or using a catalyst, can increase reaction rates by enhancing collisions between reactants.