Uranium speciation, uptake and toxicity in Atlantic salmon
•
0 likes•84 views
This study investigated the speciation, uptake, and toxicity of uranium in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). 800 juvenile salmon were exposed to varying concentrations of depleted uranium over 96 hours. Uranium was found to be predominantly present as low molecular mass species less than 10 kDa. Uranium accumulated in the fish gills in a concentration-dependent manner, influenced by water pH and uranium species. Higher uranium levels in gills were correlated with increased uranium in the liver, causing ion regulation issues and stress as reflected by reduced blood plasma chloride and increased blood glucose. Mortality increased above 0.34 micromoles of uranium per gram of gill dry weight. The LC50 value ranged from
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Determination of acute toxicity and the effects of sub-acute concentrations o...

Determination of acute toxicity and the effects of sub-acute concentrations o...Nanomedicine Journal (NMJ)
Abstract
Objective(s):
Copper oxidenanoparticles have different industrial applications so it is inevitable that nanoparticulate products finally find their way into aquatic ecosystems. Nevertheless there is little information available about their effects on some of edible fish. The present study aims to determine the acute toxicity and evaluate the effect of two sub-acute concentrations (50 and 70% 96 h LC50) of CuO-NPs on some hematological and biochemical parameters of R. rutilus.
Materials and Methods:
225 healthy specimen of R. rutilus (mean weight 5.52±1.2 g; mean length 6.20±0.2 cm) were transported to the laboratory. In order to prepare the stock solution, CuO-NPs was dispersed in pure water with ultrasonication (50-60 kHz) for 15 min every day before dosing. At first, R. rutilus was exposed to CuO-NPs to determine the lethal concentration (LC50) value. Following acute test, fish were treated with sub-acute concentrations of CuO-NPs (50 and 70% 96 h-LC50 at) with one control group (no CuO-NPs) for a week to determine the changes in the level of some plasma hematological and biochemical parameters.
Results:
The 96 h-LC50 values of CuO-NPs was 2.19±0.003 mg/l. R. rutilus exhibited significantly lower RBC count, Hb and Hct values and a significant increase in the WBC numbers, MCH, MCHC and MCV indices (p<0.05).><0.05).
Conclusion:
These alterations indicate R. rutilus sensitivity to CuO-NPs and changes in blood parameters would be a useful tool for measurement early exposure to CuO nanoparticles.Toxicological Effect of Effluents from Indomie Plc on Some Biochemical Parame...

IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB)
Volume 1, Issue 3
Biochemical Alternation In Fresh Water Fishe Labeo Rohita Exposed To The Sodi...

Fishes are regarded as an important high grade protein containing food staple of Indian people.
Ever increasing water pollution level, especially sodium fluoride (NaF), in inland freshwater reservoir has
made significant biochemical changes in the life cycle of fishes. In view of this, the investigations on effects of
acute and chronic sodium fluoride toxicity to fish Labeo rohita have been carried out. The changes in glycogen,
protein and lipid content of selected tissues like muscle, liver, gill and kidney were examined. The study
revealed a highest loss of glycogen, protein and lipid percentage in all tissues as compared to control.
Water Worries -- Nitrogen From Septic Tanks, Fertilizer, Poor Sewage Treatmen...

Water Worries -- Nitrogen From Septic Tanks, Fertilizer, Poor Sewage Treatmen...Save The Great South Bay
Prof Christopher Gobler of Stony Brook University, a global expert on algal blooms and their causes, presents his overview of Long Island's nitrogen pollution problem and how that is triggering destructive algal blooms throughout our bays. The main culprit? 500,000 septic tanks.combined toxicity and bioconcentration of fluoride and arsenic in african (3)

Laboratory experiments were performed to examine the combined toxic effects of two important aquatic contaminants viz., arsenic and fluoride on African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Additionally, the bio concentration factors (BCFs) of the two contaminants in tissues and blood of catfish were also determined. The LC50 for sodium fluoride and arsenic trioxide were determined to be 619.3 mg L-1, 30.3 mg L-1, respectively. Erratic swimming movements with hyperactivity, loss of equilibrium, augmented air gulping and decreased food consumption were observed in the experimental groups. In co-exposure groups of arsenic and fluoride, the concentration of fluoride in fish tissues increased with increasing water fluoride concentration in the test aquaria with significant differences (P<0.01)><0.05)>0.05) among the exposure groups. Arsenic was observed to exceedingly bioaccumulate and biomagnify in the tissues. Perhaps due to the complex formation of arsenic and fluoride the bio concentration of arsenic in tissues was observed to decrease with increasing water fluoride concentration and vice-versa. The study concludes that fluoride may interfere with the bio-concentration of arsenic.
New Spectrophotometric Determination of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumaratein Bulk ...

Two new, selective and sensitive visible spectrophotometric methods (method A and B) have been developed for the estimation of Tenofovir disoproxil fumaratein bulk and in pharmaceutical preparations. Method ‘A’ is based on the reaction with wool fast blue, in the presence of buffer at PH 1.5 to form a colored species with a λmax 590nm. Method B is based on the reaction with tropaeoline -00 dye under acidic condition with a λ max 410nm. Beer’s law is obeyed in the concentration range of 50 to 250µg/ml for both the methods. The methods were extended to pharmaceutical formulations and there was no interference form any common pharmaceutical excepients and diluents. The result of analysis has been validated statistically and by recovery studies.
Recommended
Determination of acute toxicity and the effects of sub-acute concentrations o...

Determination of acute toxicity and the effects of sub-acute concentrations o...Nanomedicine Journal (NMJ)
Abstract
Objective(s):
Copper oxidenanoparticles have different industrial applications so it is inevitable that nanoparticulate products finally find their way into aquatic ecosystems. Nevertheless there is little information available about their effects on some of edible fish. The present study aims to determine the acute toxicity and evaluate the effect of two sub-acute concentrations (50 and 70% 96 h LC50) of CuO-NPs on some hematological and biochemical parameters of R. rutilus.
Materials and Methods:
225 healthy specimen of R. rutilus (mean weight 5.52±1.2 g; mean length 6.20±0.2 cm) were transported to the laboratory. In order to prepare the stock solution, CuO-NPs was dispersed in pure water with ultrasonication (50-60 kHz) for 15 min every day before dosing. At first, R. rutilus was exposed to CuO-NPs to determine the lethal concentration (LC50) value. Following acute test, fish were treated with sub-acute concentrations of CuO-NPs (50 and 70% 96 h-LC50 at) with one control group (no CuO-NPs) for a week to determine the changes in the level of some plasma hematological and biochemical parameters.
Results:
The 96 h-LC50 values of CuO-NPs was 2.19±0.003 mg/l. R. rutilus exhibited significantly lower RBC count, Hb and Hct values and a significant increase in the WBC numbers, MCH, MCHC and MCV indices (p<0.05).><0.05).
Conclusion:
These alterations indicate R. rutilus sensitivity to CuO-NPs and changes in blood parameters would be a useful tool for measurement early exposure to CuO nanoparticles.Toxicological Effect of Effluents from Indomie Plc on Some Biochemical Parame...

IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB)
Volume 1, Issue 3
Biochemical Alternation In Fresh Water Fishe Labeo Rohita Exposed To The Sodi...

Fishes are regarded as an important high grade protein containing food staple of Indian people.
Ever increasing water pollution level, especially sodium fluoride (NaF), in inland freshwater reservoir has
made significant biochemical changes in the life cycle of fishes. In view of this, the investigations on effects of
acute and chronic sodium fluoride toxicity to fish Labeo rohita have been carried out. The changes in glycogen,
protein and lipid content of selected tissues like muscle, liver, gill and kidney were examined. The study
revealed a highest loss of glycogen, protein and lipid percentage in all tissues as compared to control.
Water Worries -- Nitrogen From Septic Tanks, Fertilizer, Poor Sewage Treatmen...

Water Worries -- Nitrogen From Septic Tanks, Fertilizer, Poor Sewage Treatmen...Save The Great South Bay
Prof Christopher Gobler of Stony Brook University, a global expert on algal blooms and their causes, presents his overview of Long Island's nitrogen pollution problem and how that is triggering destructive algal blooms throughout our bays. The main culprit? 500,000 septic tanks.combined toxicity and bioconcentration of fluoride and arsenic in african (3)

Laboratory experiments were performed to examine the combined toxic effects of two important aquatic contaminants viz., arsenic and fluoride on African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Additionally, the bio concentration factors (BCFs) of the two contaminants in tissues and blood of catfish were also determined. The LC50 for sodium fluoride and arsenic trioxide were determined to be 619.3 mg L-1, 30.3 mg L-1, respectively. Erratic swimming movements with hyperactivity, loss of equilibrium, augmented air gulping and decreased food consumption were observed in the experimental groups. In co-exposure groups of arsenic and fluoride, the concentration of fluoride in fish tissues increased with increasing water fluoride concentration in the test aquaria with significant differences (P<0.01)><0.05)>0.05) among the exposure groups. Arsenic was observed to exceedingly bioaccumulate and biomagnify in the tissues. Perhaps due to the complex formation of arsenic and fluoride the bio concentration of arsenic in tissues was observed to decrease with increasing water fluoride concentration and vice-versa. The study concludes that fluoride may interfere with the bio-concentration of arsenic.
New Spectrophotometric Determination of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumaratein Bulk ...

Two new, selective and sensitive visible spectrophotometric methods (method A and B) have been developed for the estimation of Tenofovir disoproxil fumaratein bulk and in pharmaceutical preparations. Method ‘A’ is based on the reaction with wool fast blue, in the presence of buffer at PH 1.5 to form a colored species with a λmax 590nm. Method B is based on the reaction with tropaeoline -00 dye under acidic condition with a λ max 410nm. Beer’s law is obeyed in the concentration range of 50 to 250µg/ml for both the methods. The methods were extended to pharmaceutical formulations and there was no interference form any common pharmaceutical excepients and diluents. The result of analysis has been validated statistically and by recovery studies.
A study on length weight relationships (lwr) and growth responses of major ca...

The International Institute for Science, Technology and Education (IISTE). All Rights Reserved.
Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, Malaysia

Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, MalaysiaUnited International Journal for Research & Technology
Wan Marlin Rohalin, Nadzifah Yaakub and Najwa Mohd Fazdil. “Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, Malaysia” United International Journal for Research & Technology (UIJRT) 1.1 (2019): 44-48.Levels of PAHs and Potentially Toxic Metals in Three Species of Fresh and Smo...

Three samples of fish, Scomber japonica (titus), Sardinellaeba (sardine) and Merlucciuspolli (fresh stock fish) were collected from Ojo main market in Lagos. Two low molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (naphthalene and anthracene) were determined using high performance liquid chromatography, (HPLC), after extraction with n-hexane by ultrasonication and clean up using SPE cartridges. Heavy metals were determined in the samples using atomic absorption spectrometer, (Perkin Elmer, Analyst 200) after digestion with aqua regia. The fat content was determined gravimetrically. The unsmoked samples had naphthalene range from 0.0788±0.0078 μg/g in Merlucciuspolli to 0.3845±0.0199 μg/g in Scomber japonica. Anthracene levels ranged from 0.4798± 0.0072 μg/g in unsmoked samples of Merlucciuspolli to 1.2254±0.0071 μg/g in Scomber japonica. The low fat containing specie (Merlucciuspolli) accumulated PAHs over the smoking periods, while a decrease was observed in the high fat containing species (Scomber japonica and Sardinellaeba). The highest concentration of Pb (8.65 μg/g), Cu (9.53 μg/g), Fe (201.80 μg/g) and Zn (122.15 μg/g) in the unsmoked fishes were found in unsmoked Scomber japonica while the highest concentration of Cr (13.68 μg/g) and Ni (5.88 μg/g) in the fishes were found in the unsmoked Merlucciuspolli. Cadmium was not detected in all the samples. The low fat containing specie showed increase in heavy metals over the smoking periods, while the high fat containing species also accumulated these heavy metals at 1 hour smoking period, but a decrease was noted over the 2 hours and 3 hours smoking periods. Smoking has effect on the level of these toxicants, as PAHs and heavy metals tend to accumulate on smoking. Smoking appeared to influence toxicants levels the fishes. Levels of the PAHs were higher than the regulatory permissible limits of the World Health Organization. Levels of the toxic metals were within the WHO set permissible limits except for Pb (in unsmoked Scomber japonica), Fe (in Sardinellaeba smoked for 1 and 2 hours, and in Merlucciuspolli smoked for 2 and 3 hours) and Cr (in all the samples).
Heavy Metals in organs and endoparasites of Oreochromisniloticus, Sediment an...

IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) multidisciplinary peer-reviewed Journal with reputable academics and experts as board member. IOSR-JESTFT is designed for the prompt publication of peer-reviewed articles in all areas of subject. The journal articles will be accessed freely online.
Protective Effect of Garlic Extract (Allium sativum L.) on the Liver Tissue o...

Protective Effect of Garlic Extract (Allium sativum L.) on the Liver Tissue o...BRNSS Publication Hub
Arsenic in its inorganic form is toxic and can cause severe health effects including cancers. In several
in vitro experiments, arsenic exposure has shown multiple effects at the molecular level. However, the
proper understanding of the role of arsenic in the cause of these diseases is still limited. In this work, we
demonstrated the toxicity effect of sodium arsenite in the liver tissues of freshwater fish Channa punctatus
and observed the histopathological as well as surface ultrastructural changes on it. A simultaneous study
was performed to observe the protective effect of garlic extract (Allium sativum L.) on the liver tissue of
arsenic-induced C. punctatus. The liver tissue of the control group showed a normal histoarchitecture.
The arsenic-exposed liver tissue revealed hepatic lesions in the form of cloudy swelling of hepatocytes,
vacuolar degeneration, karyolysis, dilation of sinusoids, and nuclear hypertrophy. Lesser hepatic
alternation was observed in the liver tissue of arsenic-exposed C. punctatus concurrently treated with
garlic extract. The protective effect of garlic was shown in the normalization of hepatocytes in the
arsenic-induced liver tissue.Oral toxic exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on serum biochemical ch...

Oral toxic exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on serum biochemical ch...Nanomedicine Journal (NMJ)
Abstract
Objective(s):
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used in commercial food additives and cosmetics worldwide. Uptake of these nanoparticulate into humans by different routes and may exhibit potential side effects, lags behind the rapid development of nanotechnology. Thus, the present study designed to evaluate the toxic effect of mixed rutile and anatase TiO2 NPs on serum biochemical changes in rats.
Materials and Methods:
In this study, adult male Wistar rats were randomly allotted into the experimental and control groups (n=6), which were orally administered with 50 and 100 mg/kg body weight of TiO2 NPs. Toxic effects were assessed by the changes of serum biochemical parameters such as glucose, total protein, albumin, globulin, cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein, alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen, uric acid and creatinine. All the serum biochemical markers were experimented in rats, after 14-days of post exposure.
Results:
Changes of the serum specific parameters indicated that liver and kidney were significantly affected in both experimental groups. The changes between the levels of total protein, glucose, aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase and alkaline phosphatase indicate that TiO2 NPs induces liver damage. Significant increase in the blood urea nitrogen and uric acid indicates the renal damage in the TiO2 NPs treated rats.
Conclusion:
The data shows that the oral administration of TiO2 NPs (<100nm) may lead to hepatic and renal toxicity in experimental rats.Ecotoxicology cadmium poster RIVM

Poster on the risk of Cadmium to Dutch aquatic ecosystem as presented at the Novembre 2015 RIVM seminar on ecotoxicology
More Related Content
Similar to Uranium speciation, uptake and toxicity in Atlantic salmon
A study on length weight relationships (lwr) and growth responses of major ca...

The International Institute for Science, Technology and Education (IISTE). All Rights Reserved.
Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, Malaysia

Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, MalaysiaUnited International Journal for Research & Technology
Wan Marlin Rohalin, Nadzifah Yaakub and Najwa Mohd Fazdil. “Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, Malaysia” United International Journal for Research & Technology (UIJRT) 1.1 (2019): 44-48.Levels of PAHs and Potentially Toxic Metals in Three Species of Fresh and Smo...

Three samples of fish, Scomber japonica (titus), Sardinellaeba (sardine) and Merlucciuspolli (fresh stock fish) were collected from Ojo main market in Lagos. Two low molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (naphthalene and anthracene) were determined using high performance liquid chromatography, (HPLC), after extraction with n-hexane by ultrasonication and clean up using SPE cartridges. Heavy metals were determined in the samples using atomic absorption spectrometer, (Perkin Elmer, Analyst 200) after digestion with aqua regia. The fat content was determined gravimetrically. The unsmoked samples had naphthalene range from 0.0788±0.0078 μg/g in Merlucciuspolli to 0.3845±0.0199 μg/g in Scomber japonica. Anthracene levels ranged from 0.4798± 0.0072 μg/g in unsmoked samples of Merlucciuspolli to 1.2254±0.0071 μg/g in Scomber japonica. The low fat containing specie (Merlucciuspolli) accumulated PAHs over the smoking periods, while a decrease was observed in the high fat containing species (Scomber japonica and Sardinellaeba). The highest concentration of Pb (8.65 μg/g), Cu (9.53 μg/g), Fe (201.80 μg/g) and Zn (122.15 μg/g) in the unsmoked fishes were found in unsmoked Scomber japonica while the highest concentration of Cr (13.68 μg/g) and Ni (5.88 μg/g) in the fishes were found in the unsmoked Merlucciuspolli. Cadmium was not detected in all the samples. The low fat containing specie showed increase in heavy metals over the smoking periods, while the high fat containing species also accumulated these heavy metals at 1 hour smoking period, but a decrease was noted over the 2 hours and 3 hours smoking periods. Smoking has effect on the level of these toxicants, as PAHs and heavy metals tend to accumulate on smoking. Smoking appeared to influence toxicants levels the fishes. Levels of the PAHs were higher than the regulatory permissible limits of the World Health Organization. Levels of the toxic metals were within the WHO set permissible limits except for Pb (in unsmoked Scomber japonica), Fe (in Sardinellaeba smoked for 1 and 2 hours, and in Merlucciuspolli smoked for 2 and 3 hours) and Cr (in all the samples).
Heavy Metals in organs and endoparasites of Oreochromisniloticus, Sediment an...

IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) multidisciplinary peer-reviewed Journal with reputable academics and experts as board member. IOSR-JESTFT is designed for the prompt publication of peer-reviewed articles in all areas of subject. The journal articles will be accessed freely online.
Protective Effect of Garlic Extract (Allium sativum L.) on the Liver Tissue o...

Protective Effect of Garlic Extract (Allium sativum L.) on the Liver Tissue o...BRNSS Publication Hub
Arsenic in its inorganic form is toxic and can cause severe health effects including cancers. In several
in vitro experiments, arsenic exposure has shown multiple effects at the molecular level. However, the
proper understanding of the role of arsenic in the cause of these diseases is still limited. In this work, we
demonstrated the toxicity effect of sodium arsenite in the liver tissues of freshwater fish Channa punctatus
and observed the histopathological as well as surface ultrastructural changes on it. A simultaneous study
was performed to observe the protective effect of garlic extract (Allium sativum L.) on the liver tissue of
arsenic-induced C. punctatus. The liver tissue of the control group showed a normal histoarchitecture.
The arsenic-exposed liver tissue revealed hepatic lesions in the form of cloudy swelling of hepatocytes,
vacuolar degeneration, karyolysis, dilation of sinusoids, and nuclear hypertrophy. Lesser hepatic
alternation was observed in the liver tissue of arsenic-exposed C. punctatus concurrently treated with
garlic extract. The protective effect of garlic was shown in the normalization of hepatocytes in the
arsenic-induced liver tissue.Oral toxic exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on serum biochemical ch...

Oral toxic exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on serum biochemical ch...Nanomedicine Journal (NMJ)
Abstract
Objective(s):
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used in commercial food additives and cosmetics worldwide. Uptake of these nanoparticulate into humans by different routes and may exhibit potential side effects, lags behind the rapid development of nanotechnology. Thus, the present study designed to evaluate the toxic effect of mixed rutile and anatase TiO2 NPs on serum biochemical changes in rats.
Materials and Methods:
In this study, adult male Wistar rats were randomly allotted into the experimental and control groups (n=6), which were orally administered with 50 and 100 mg/kg body weight of TiO2 NPs. Toxic effects were assessed by the changes of serum biochemical parameters such as glucose, total protein, albumin, globulin, cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein, alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen, uric acid and creatinine. All the serum biochemical markers were experimented in rats, after 14-days of post exposure.
Results:
Changes of the serum specific parameters indicated that liver and kidney were significantly affected in both experimental groups. The changes between the levels of total protein, glucose, aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase and alkaline phosphatase indicate that TiO2 NPs induces liver damage. Significant increase in the blood urea nitrogen and uric acid indicates the renal damage in the TiO2 NPs treated rats.
Conclusion:
The data shows that the oral administration of TiO2 NPs (<100nm) may lead to hepatic and renal toxicity in experimental rats.Ecotoxicology cadmium poster RIVM

Poster on the risk of Cadmium to Dutch aquatic ecosystem as presented at the Novembre 2015 RIVM seminar on ecotoxicology
Similar to Uranium speciation, uptake and toxicity in Atlantic salmon (20)
A study on length weight relationships (lwr) and growth responses of major ca...

A study on length weight relationships (lwr) and growth responses of major ca...
Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, Malaysia

Level of Zinc and Lead in Freshwater Fishes in Balok River, Pahang, Malaysia
Levels of PAHs and Potentially Toxic Metals in Three Species of Fresh and Smo...

Levels of PAHs and Potentially Toxic Metals in Three Species of Fresh and Smo...
SAGB2013 Dr Ed Pope/Dr Frances Hopkins (UK Ocean Acidification Consortium)

SAGB2013 Dr Ed Pope/Dr Frances Hopkins (UK Ocean Acidification Consortium)
Heavy Metals in organs and endoparasites of Oreochromisniloticus, Sediment an...

Heavy Metals in organs and endoparasites of Oreochromisniloticus, Sediment an...
Protective Effect of Garlic Extract (Allium sativum L.) on the Liver Tissue o...

Protective Effect of Garlic Extract (Allium sativum L.) on the Liver Tissue o...
Oral toxic exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on serum biochemical ch...

Oral toxic exposure of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on serum biochemical ch...
Uranium speciation, uptake and toxicity in Atlantic salmon
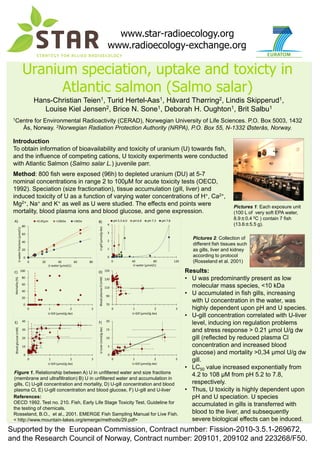
- 1. www.star-radioecology.org Supported by the European Commission, contract number: Fission-2010-3.5.1-269672, and the Research Council of Norway, contract numbers: 209101 and 209102. www.radioecology-exchange.org Uranium speciation, uptake and toxicty in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) Hans-Christian Teien1, Turid Hertel-Aas1, Håvard Thørring2, Lindis Skipperud1, Louise Kiel Jensen2, Brice N. Sone1, Deborah H. Oughton1, Brit Salbu1 1Centre for Environmental Radioactivity (CERAD), Norwegian University of Life Sciences. P.O. Box 5003, 1432 Ås, Norway. 2Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority (NRPA), P.O. Box 55, N-1332 Østerås, Norway. Introduction To obtain information of bioavailability and toxicity of uranium (U) towards fish, and the influence of competing cations, U toxicity experiments were conducted with Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) juvenile parr. Method: 800 fish were exposed (96h) to depleted uranium (DU) at 5-7 nominal concentrations in range 2 to 100µM for acute toxicity tests (OECD, 1992). Speciation (size fractionation), tissue accumulation (gill, liver) and induced toxicity of U as a function of varying water concentrations of H+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ as well as U were studied. The effects end points were mortality, blood plasma ions and blood glucose, and gene expression. Pictures 1: Each exposure unit (100 L of very soft EPA water, 8.9±0.4 0C ) contain 7 fish (13.6±5.5 g). Pictures 2: Collection of different fish tissues such as gills, liver and kidney according to protocol (Rosseland et al. 2001) Figure 1. Relationship between A) U in unfiltered water and size fractions (membrane and ultrafiltration) B) U in unfiltered water and accumulation in gills, C) U-gill concentration and mortality, D) U-gill concentration and blood plasma Cl, E) U-gill concentration and blood glucose, F) U-gill and U-liver Results: • U was predominantly present as low molecular mass species, <10 kDa • U accumulated in fish gills, increasing with U concentration in the water, was highly dependent upon pH and U species. • U-gill concentration correlated with U-liver level, inducing ion regulation problems and stress response > 0.21 µmol U/g dw gill (reflected by reduced plasma Cl concentration and increased blood glucose) and mortality >0,34 µmol U/g dw gill. • LC50 value increased exponentially from 4.2 to 108 µM from pH 5.2 to 7.8, respectively. • Thus, U toxicity is highly dependent upon pH and U speciation. U species accumulated in gills is transferred with blood to the liver, and subsequently severe biological effects can be induced. 0 5 10 15 20 0 1 2 3 U-Liver(nmol/gdw) U-Gill (µmol/g dw) F) 0 20 40 60 80 0 20 40 60 80 U-waterfractions(µmol/L) U-water (µmol/L) A) <0.45µm <10kDa <3kDa 0 1 2 3 4 0 40 80 120 U-gill(µmol/gdw) U-water (µmol/L) B) pH 5.5-6.0 pH 6.8 pH 7.3 pH 7.8 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 1 2 3 Mortality(%) U-Gill (µmol/g dw) C) 70 90 110 130 150 0 1 2 3 BloodplasmaCl(mM) U-Gill (µmol/g dw) D) 0 10 20 30 40 0 1 2 3 Bloodglucose(mM) U-Gill (µmol/g dw) E) References: OECD 1992. Test no. 210. Fish, Early Life Stage Toxicity Test. Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Rosseland, B.O., et al., 2001. EMERGE Fish Sampling Manual for Live Fish. < http://www.mountain-lakes.org/emerge/methods/29.pdf> Supported by the European Commission, Contract number: Fission-2010-3.5.1-269672, and the Research Council of Norway, Contract number: 209101, 209102 and 223268/F50.