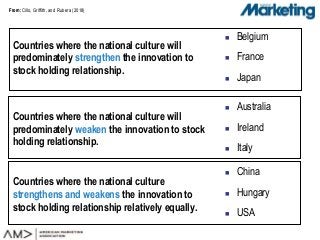
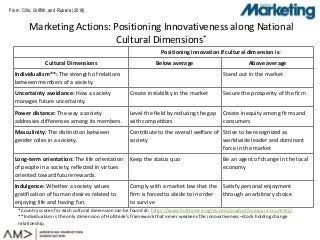
The marketing-finance interface literature has investigated the direct link between innovativeness and stock returns. Moving a step further, we investigate two unanswered questions: How and under what conditions is innovativeness associated with stock returns? Answering these questions is important for managers who have to defend innovation investments to board members and time the introductions of new products. We investigate large individual investors and their national culture in the food and beverage industry. Combining multiple datasets, we first investigate the relationship between innovativeness and large individual investor's stock holding decisions (i.e., to sell, hold onto or buy a firm's stocks). The results indicate that national culture moderates this relationship. At the firm level, we show that large investors' stock holding partially mediates the innovativeness-stock returns relationship and that the culture of a firm's large investors moderates this mediated relationship. Hence, we unveil a special segment of investors, large individual investors, which influence the extent to which firms benefit from innovativeness in the stock market, at least in the food and beverage industry.