The document proposes two frameworks for developing mashups:
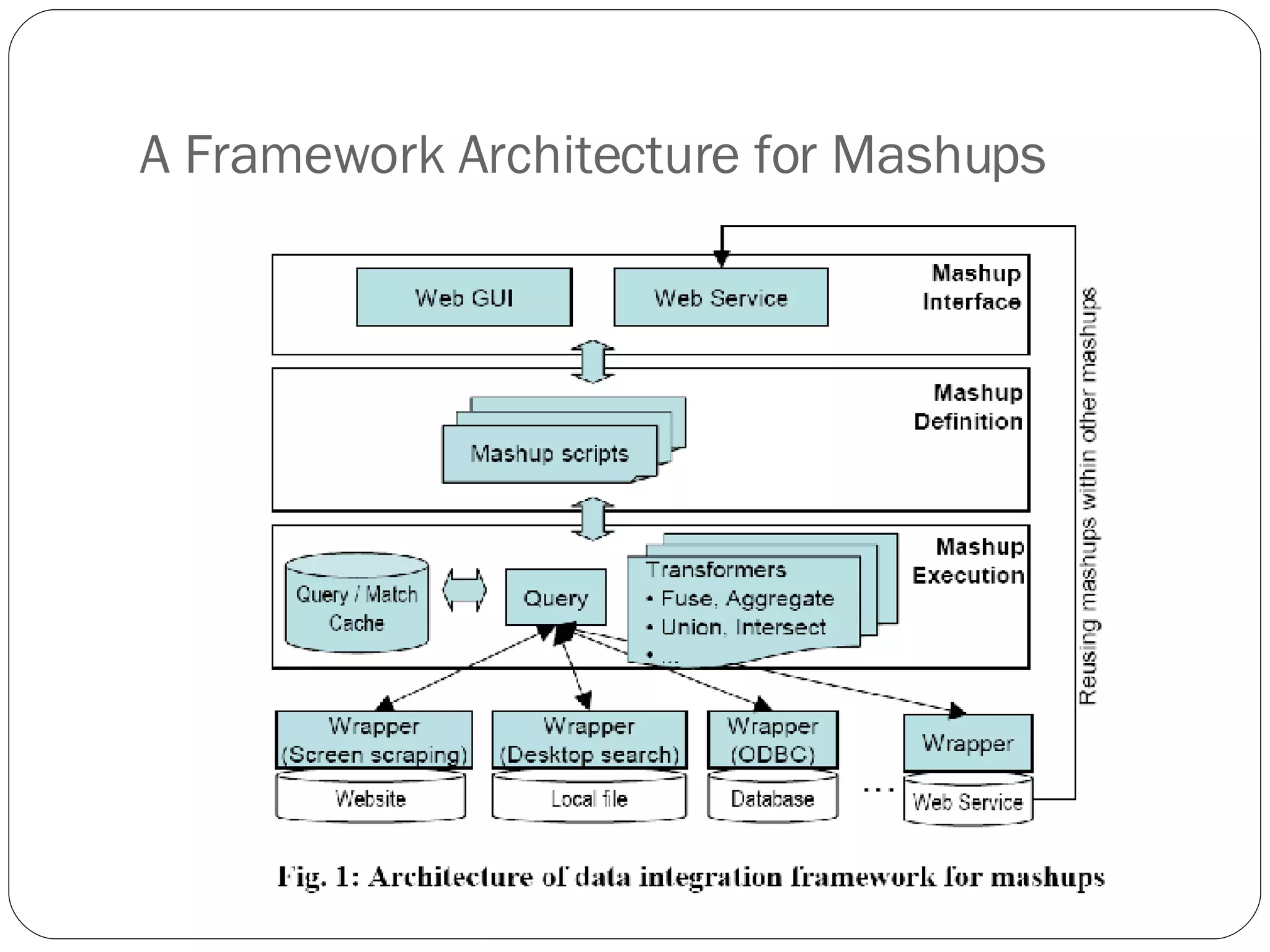
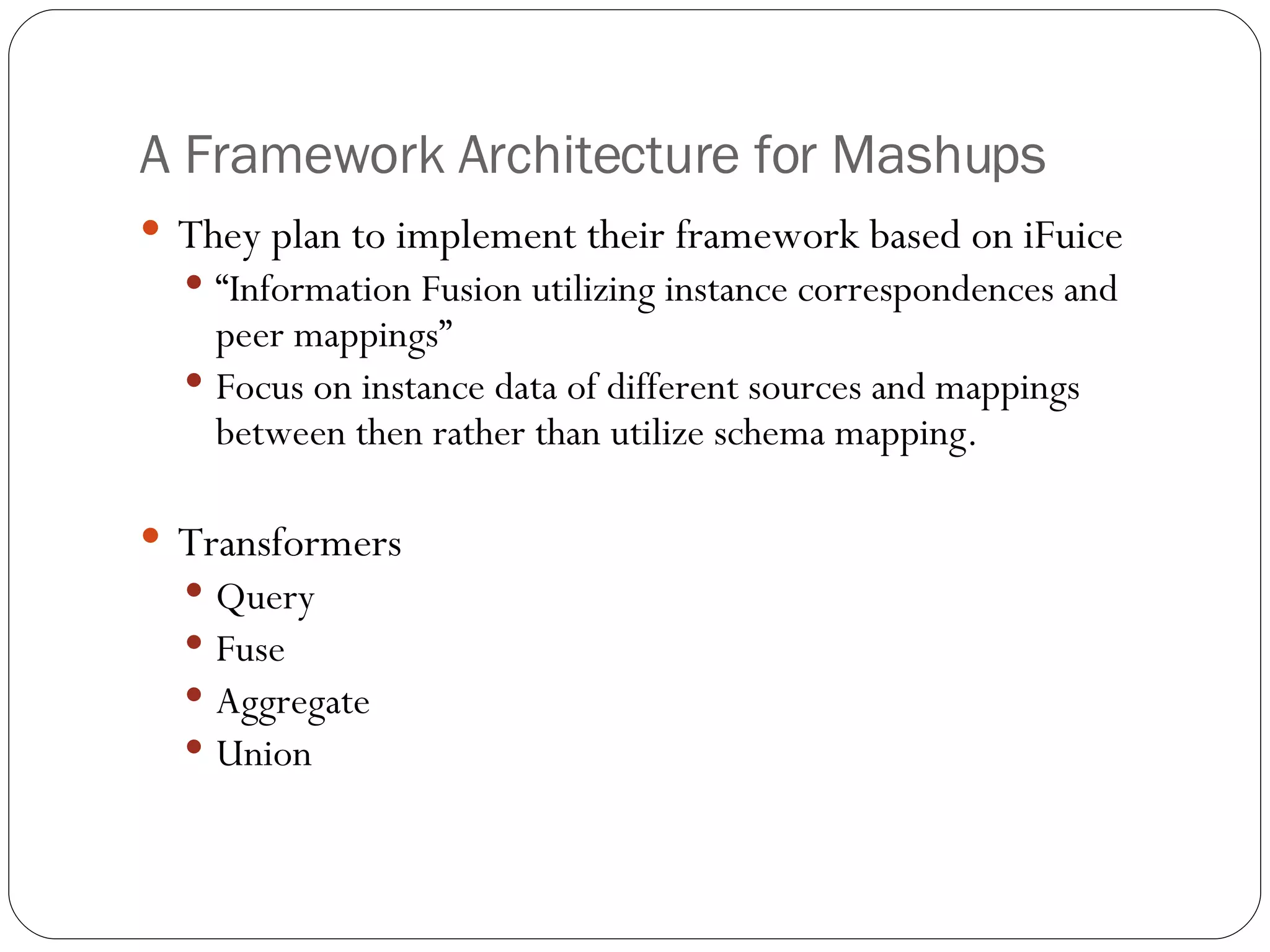
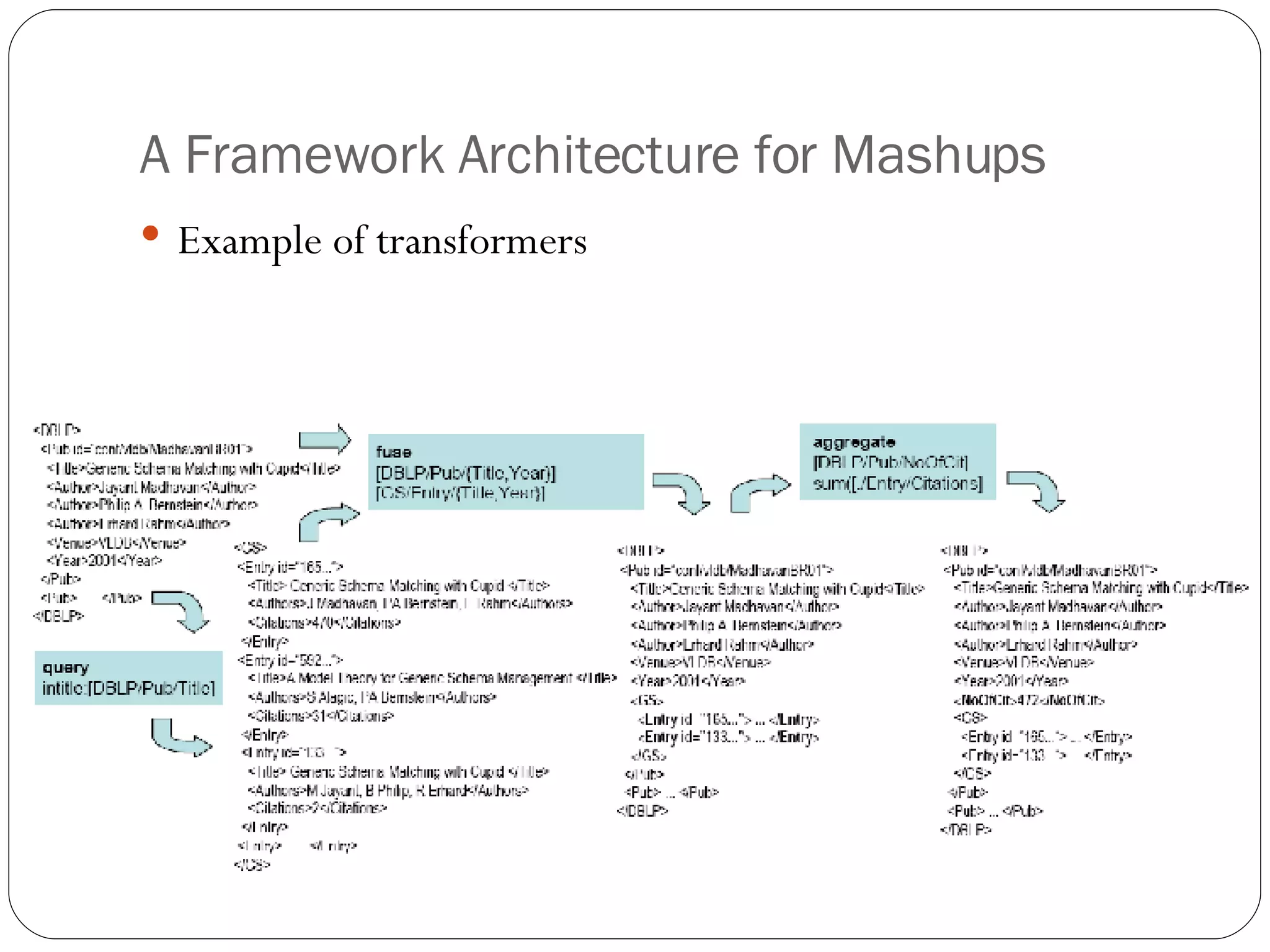
1. A framework architecture that supports dynamic data integration mashups through a script-based definition and multiple query strategies to access external data sources.
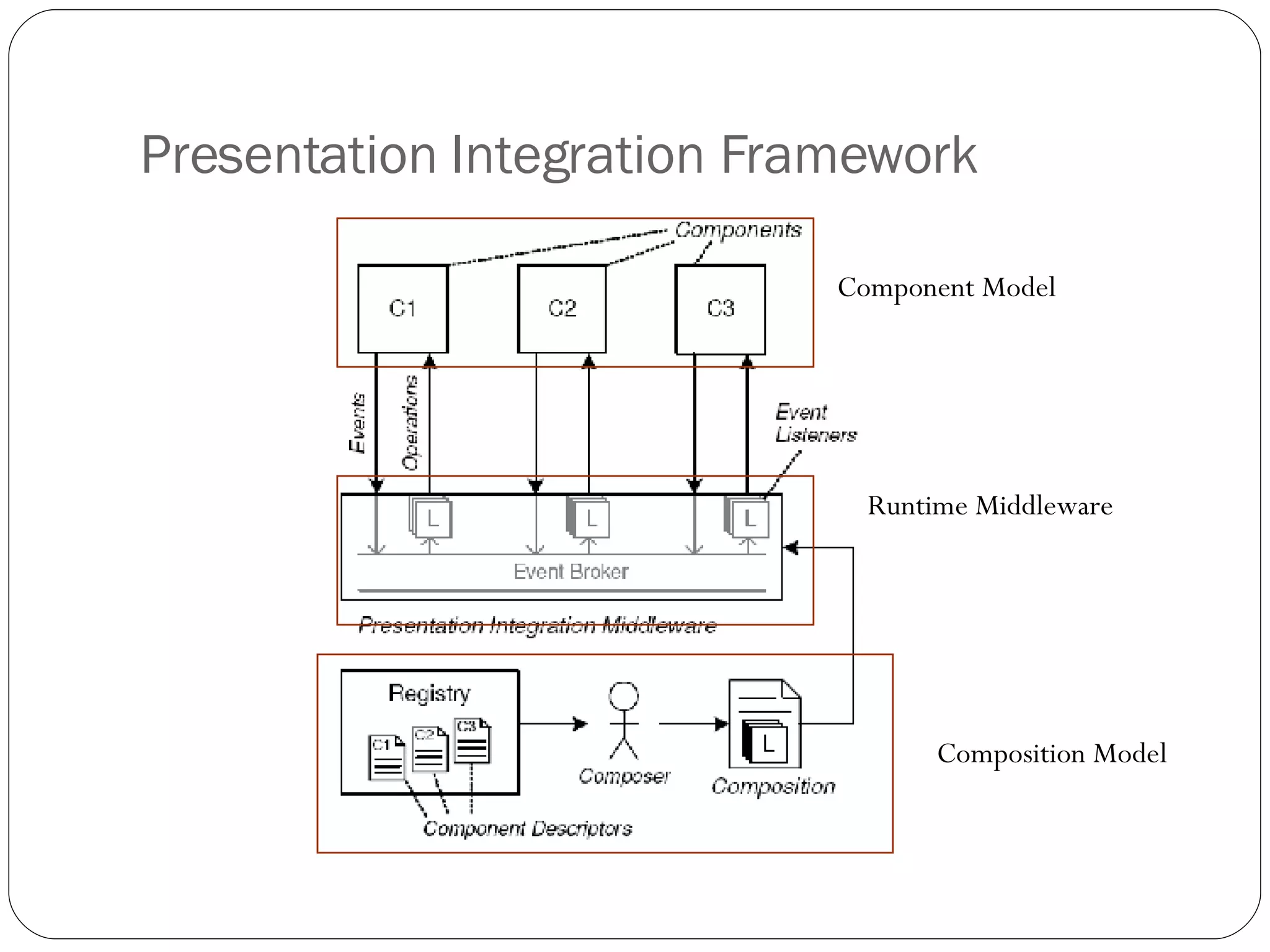
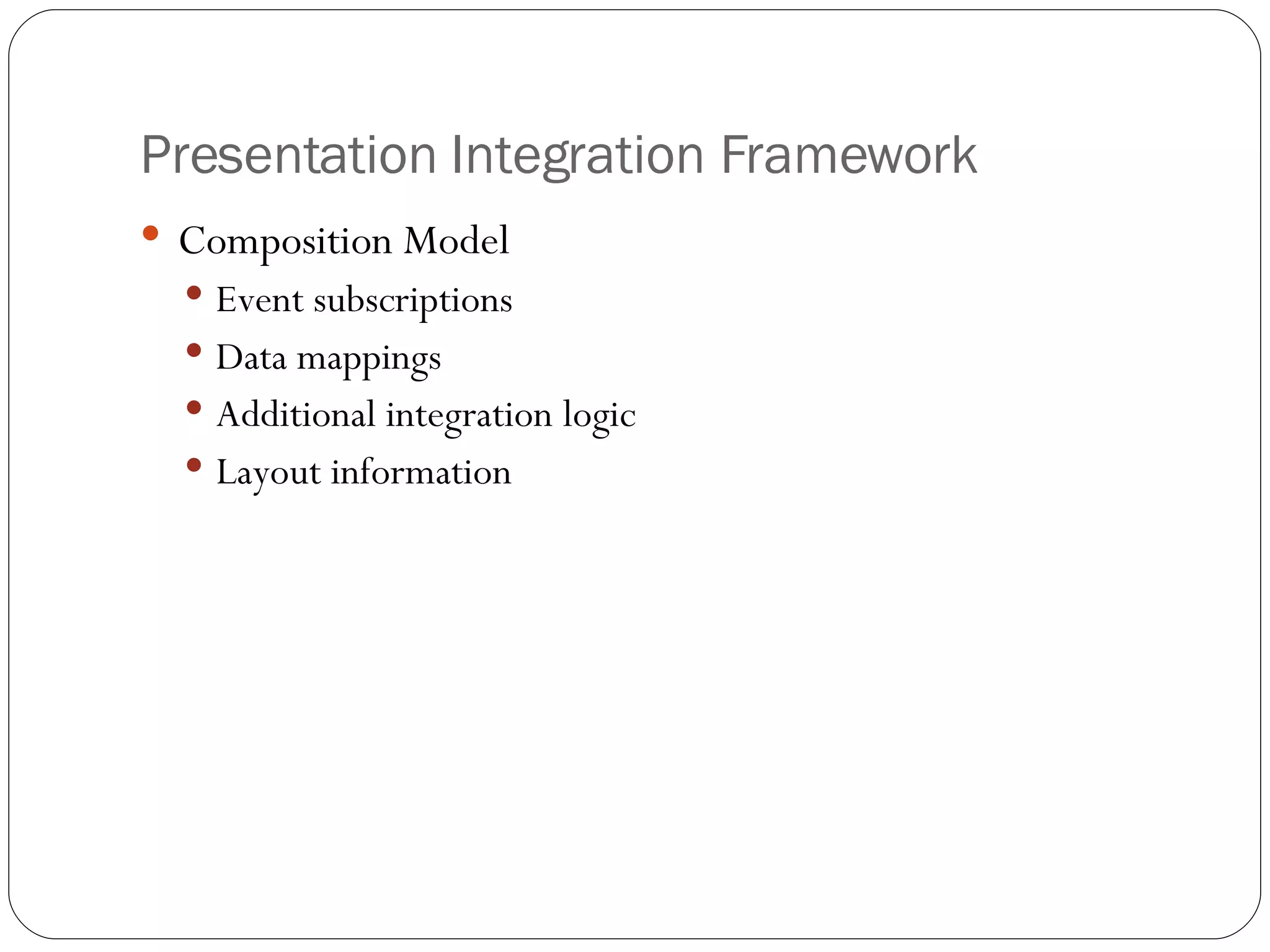
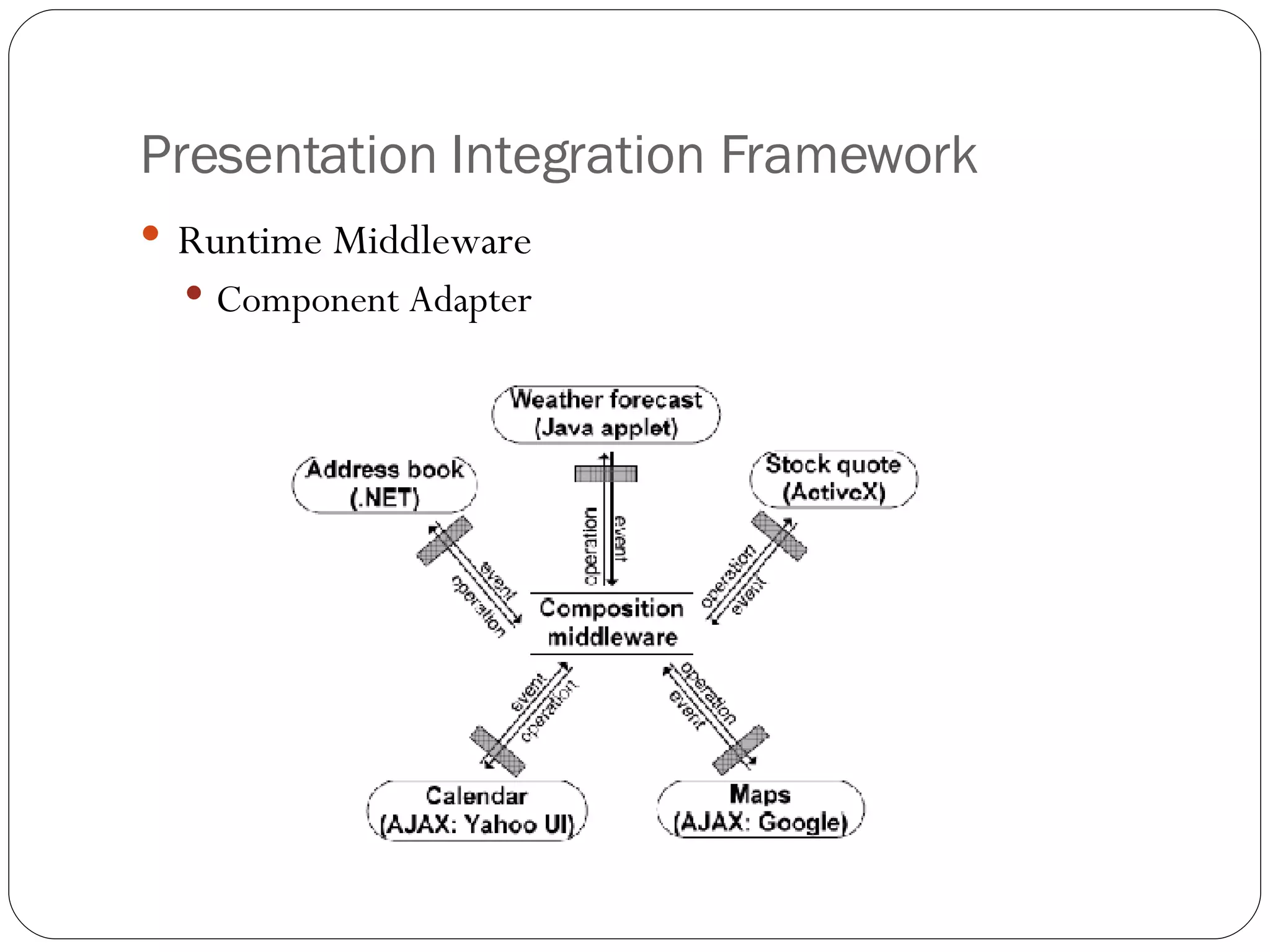
2. A presentation integration framework that facilitates creating composite applications from reusable components using a composition language (XPIL) and middleware for event automation and component invocation. It was implemented in ASP.NET with adapters for Flickr.NET and AJAX components.