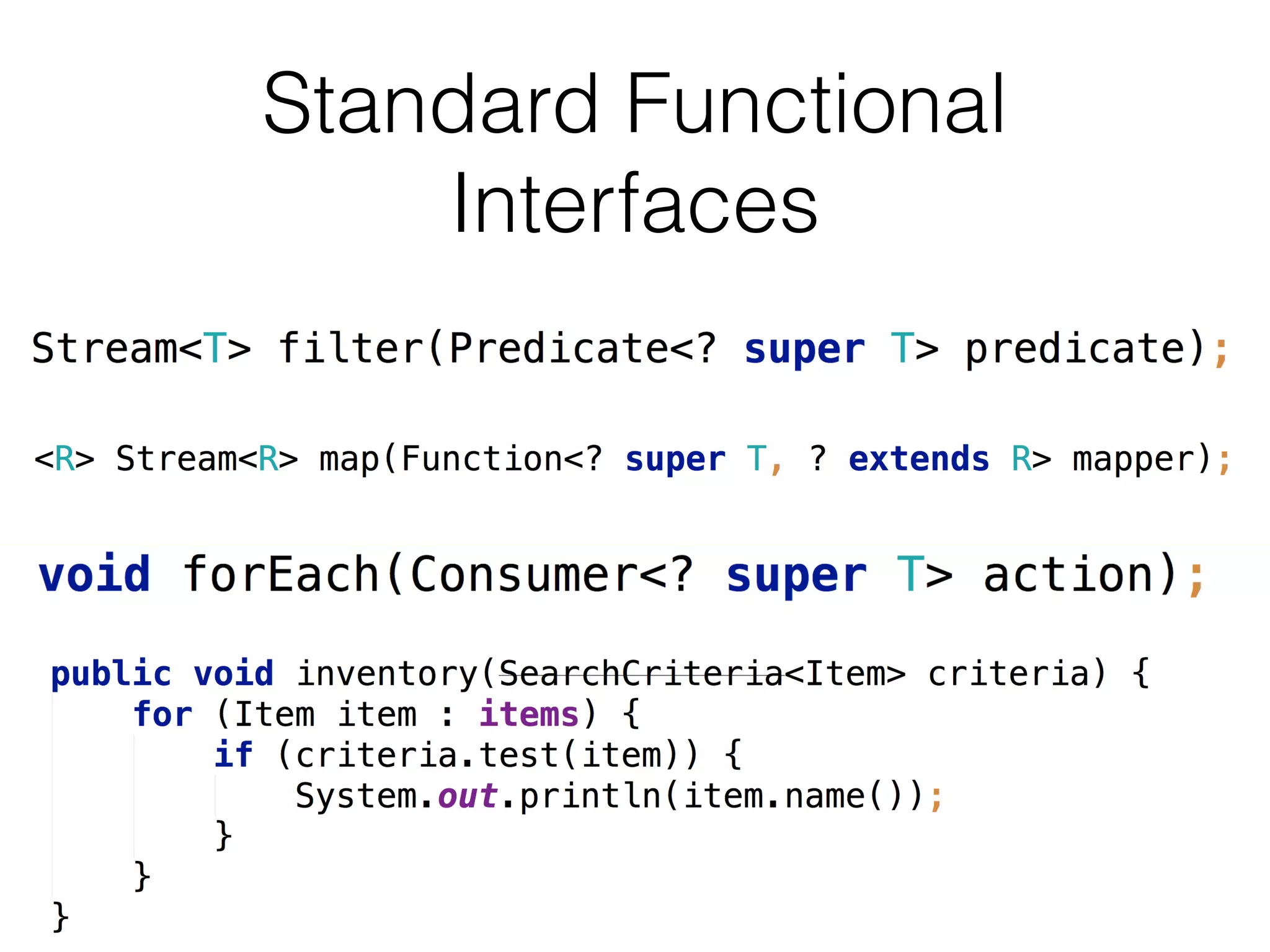
The document discusses functional programming in Java, highlighting its evolution from Java 6 to Java 8. It details tasks related to inventory management, demonstrating the benefits of using functional programming techniques such as lambdas and method references. The author emphasizes the modular, side-effect free nature of functional programming, while also cautioning against excessive use of certain libraries that can lead to verbose and confusing code.