The document discusses NuGram's approach to dynamic grammars. Key points:
- Dynamic grammars allow grammar content to come from external sources like databases or web services, since the content is not fully known in advance.
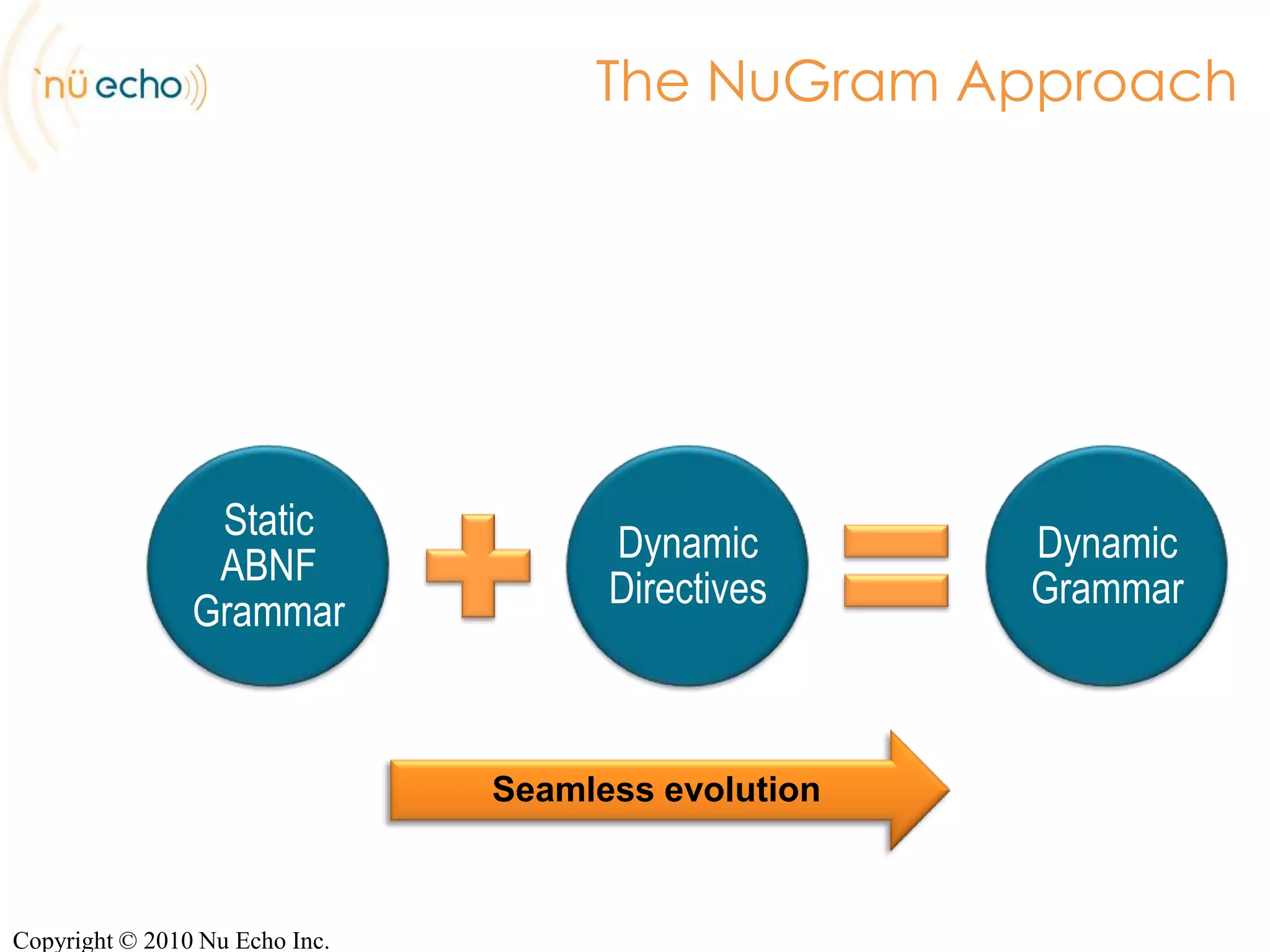
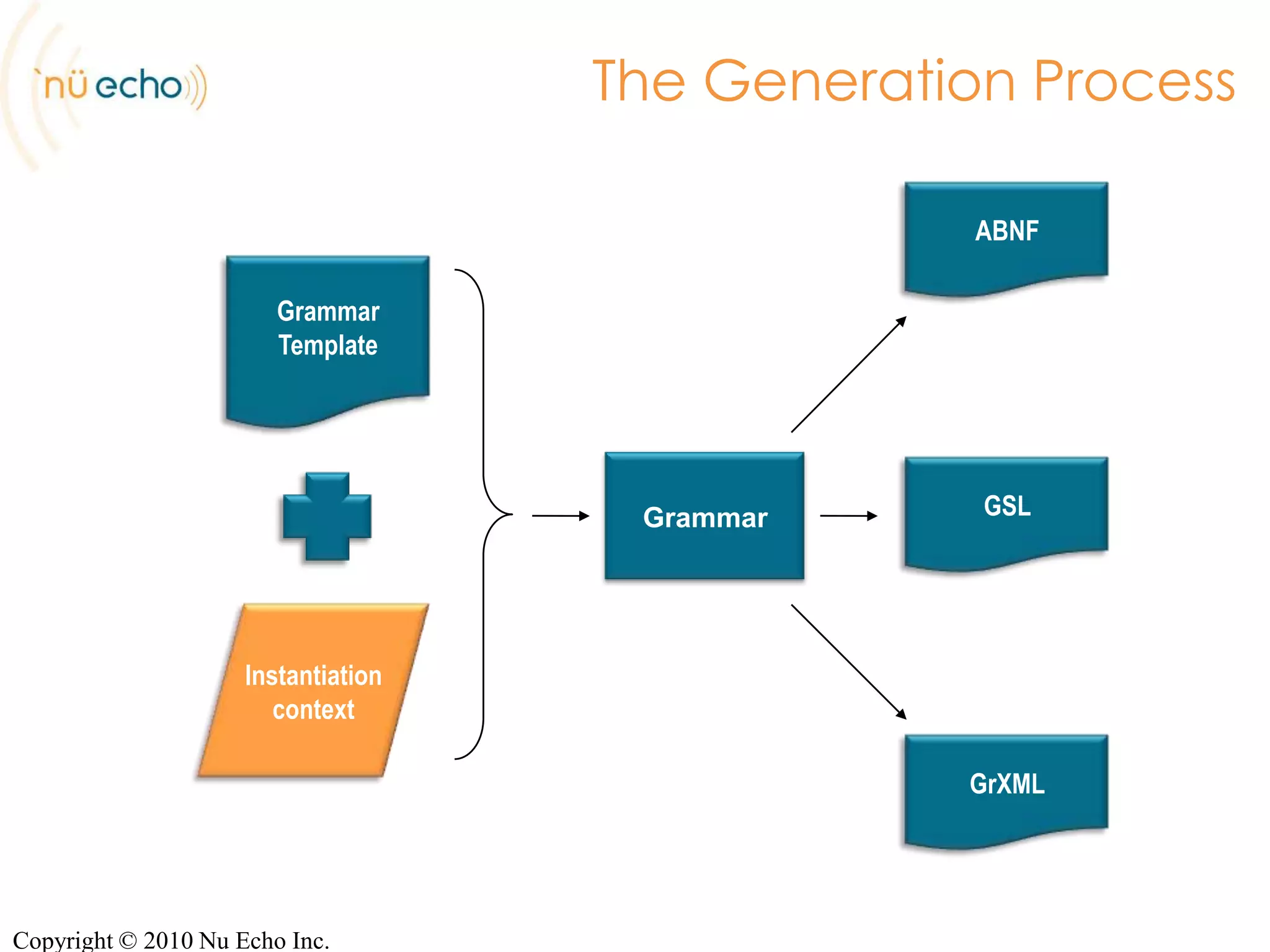
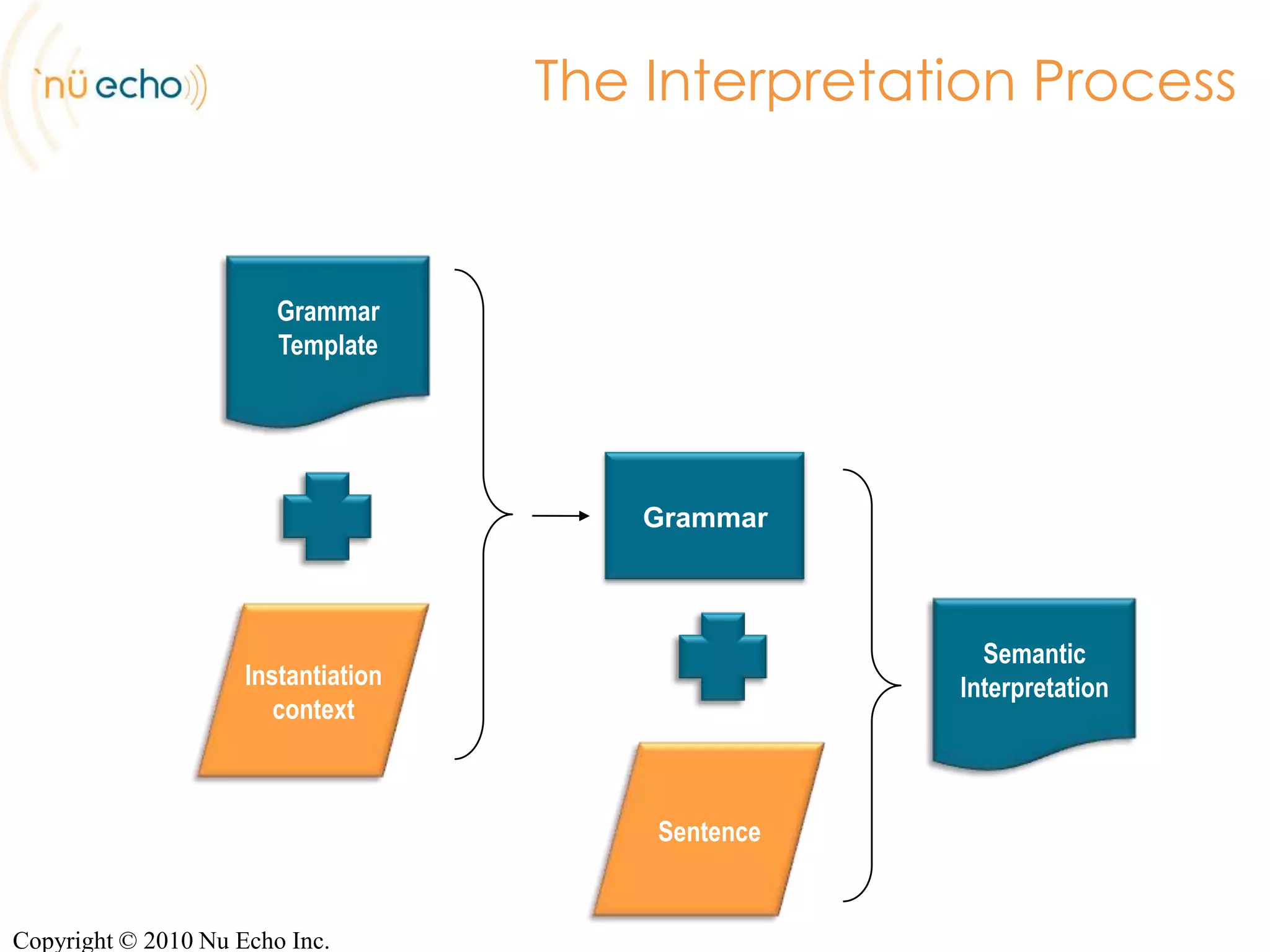
- NuGram's approach includes a server that can generate grammars from templates populated by dynamic context, and outputs formats like ABNF, GrXML, and GSL.
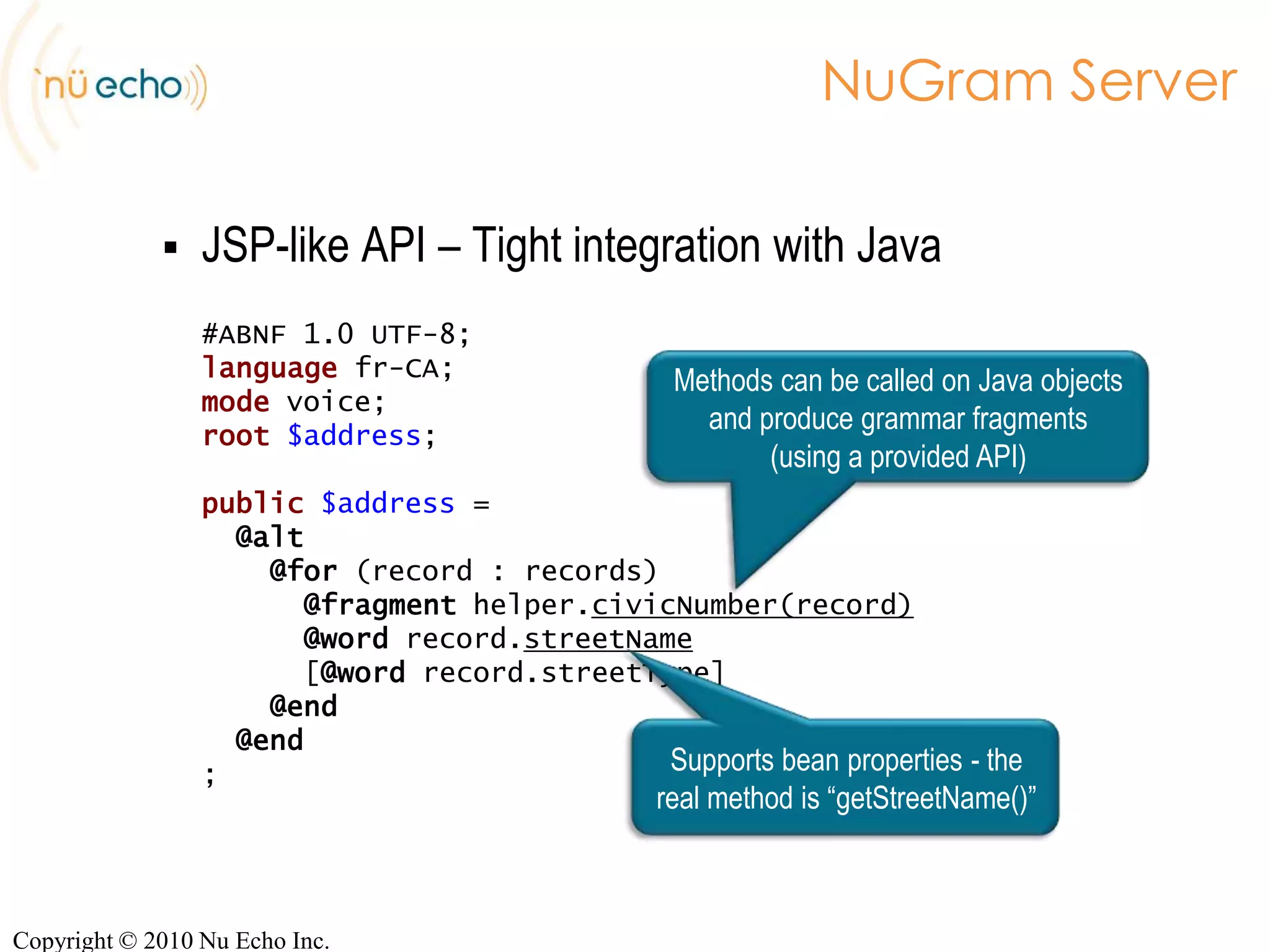
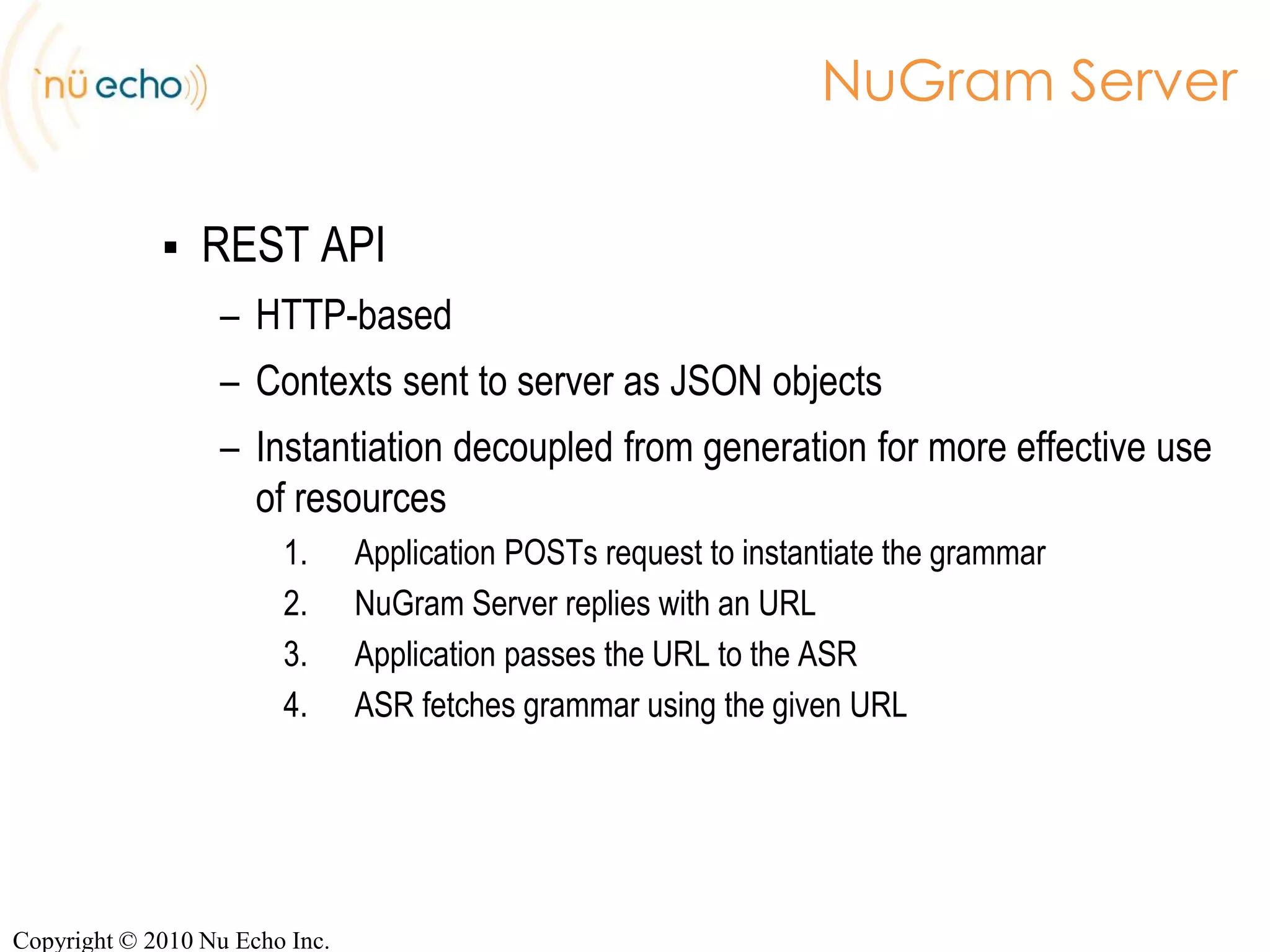
- The server provides JSP-like and REST APIs to integrate dynamic grammar generation into applications using Java or HTTP.





![Start with an ABNF grammar#ABNF 1.0 ISO-8859-1;languageen-US;root$name;public$name= [$pre_filler] $employeeName[$post_filler];$employeeName= [dominique] boucher;Copyright © 2010 Nu Echo Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nugram-server-100507082859-phpapp02/75/The-NuGram-approach-to-dynamic-grammars-10-2048.jpg)
![Add dynamic directives#ABNF 1.0 ISO-8859-1;language@string callerLanguage;root$name;public$name= [$pre_filler] $employeeName[$post_filler];$employeeName = [@word employee.firstname] @word employee.lastname;Copyright © 2010 Nu Echo Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nugram-server-100507082859-phpapp02/75/The-NuGram-approach-to-dynamic-grammars-11-2048.jpg)
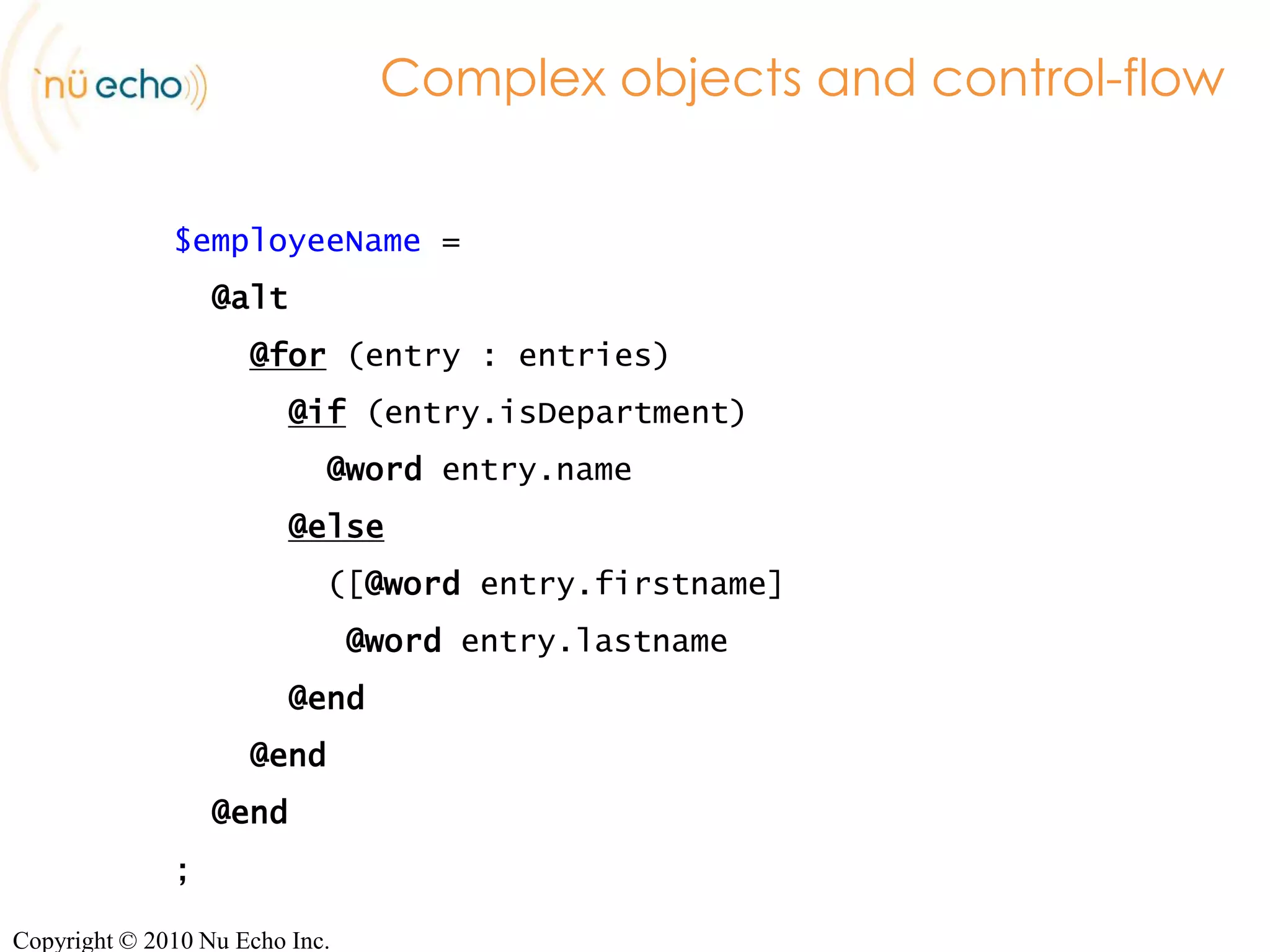
![Complex objects and control-flow$employeeName = @alt@for(entry : entries)@if(entry.isDepartment)@word entry.name@else ([@word entry.firstname]@word entry.lastname@end@end@end;Copyright © 2010 Nu Echo Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nugram-server-100507082859-phpapp02/75/The-NuGram-approach-to-dynamic-grammars-12-2048.jpg)
![NuGram ServerJava Context Initializers for full controlpublicclassCanadianAddressContextInitializerimplementsContextInitializer{public Map getContext(Map httpParameters,GrammarFragmentFactory factory,CacheControl control) {Map context = new HashMap();// 1. Extract the HTTP parameterString[] postalCode = httpParameters.get(“code”); // 2. Look in the postal code databasePostalCodeRecord[] records = findRecords(postalCode);// 3. Populate the instantiation contextcontext.add(“records”, records);context.add(“helper”, new AddressHelper(factory));return context; }Copyright © 2010 Nu Echo Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nugram-server-100507082859-phpapp02/75/The-NuGram-approach-to-dynamic-grammars-15-2048.jpg)
![NuGram ServerJSP-like API – Tight integration with Java #ABNF 1.0 UTF-8;languagefr-CA;mode voice;root$address;public$address = @alt@for (record : records)@fragmenthelper.civicNumber(record)@wordrecord.streetName [@wordrecord.streetType]@end@end;Methods can be called on Java objects and produce grammar fragments (using a provided API)Supports bean properties - the real method is “getStreetName()”Copyright © 2010 Nu Echo Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nugram-server-100507082859-phpapp02/75/The-NuGram-approach-to-dynamic-grammars-16-2048.jpg)


