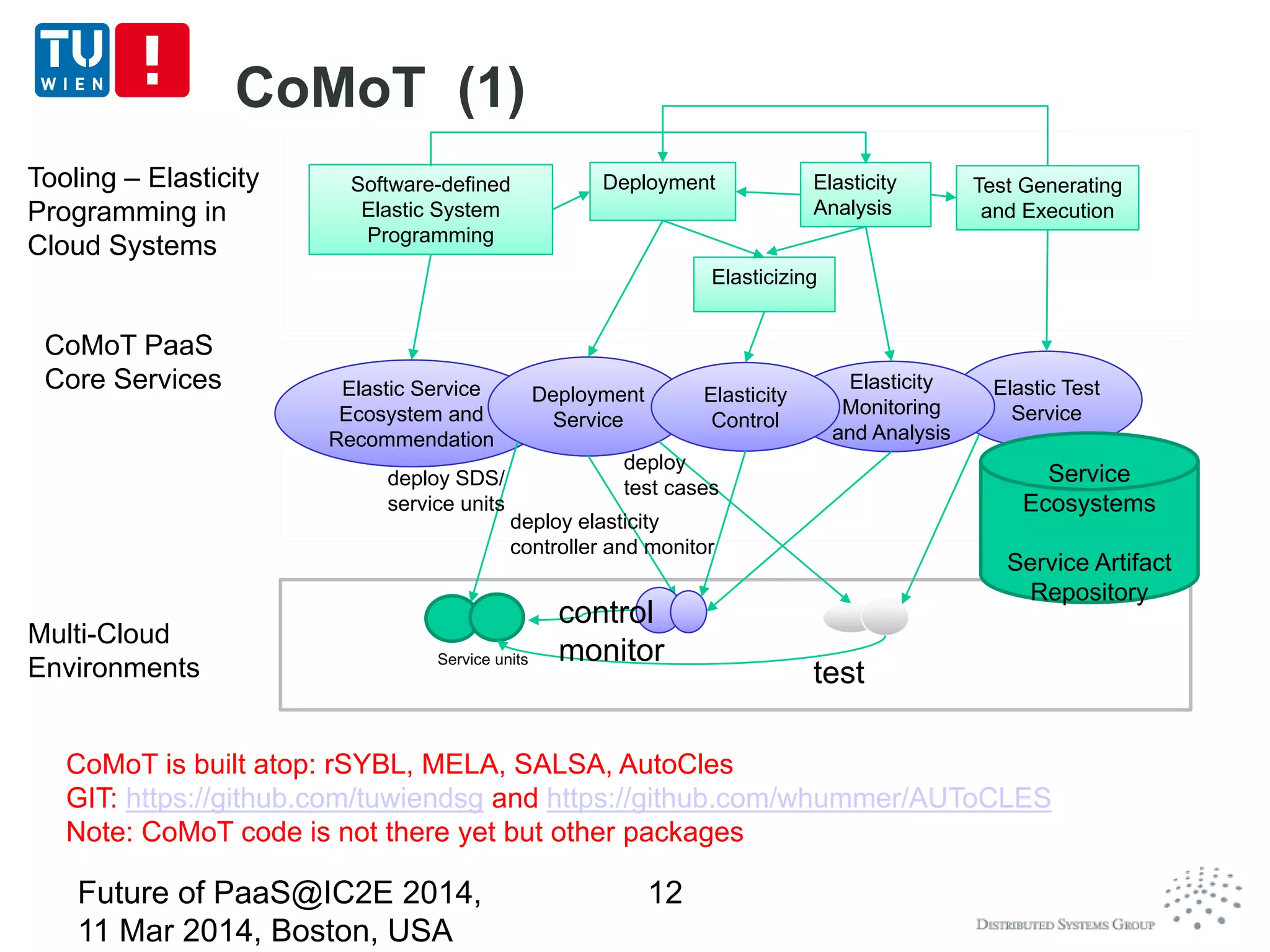
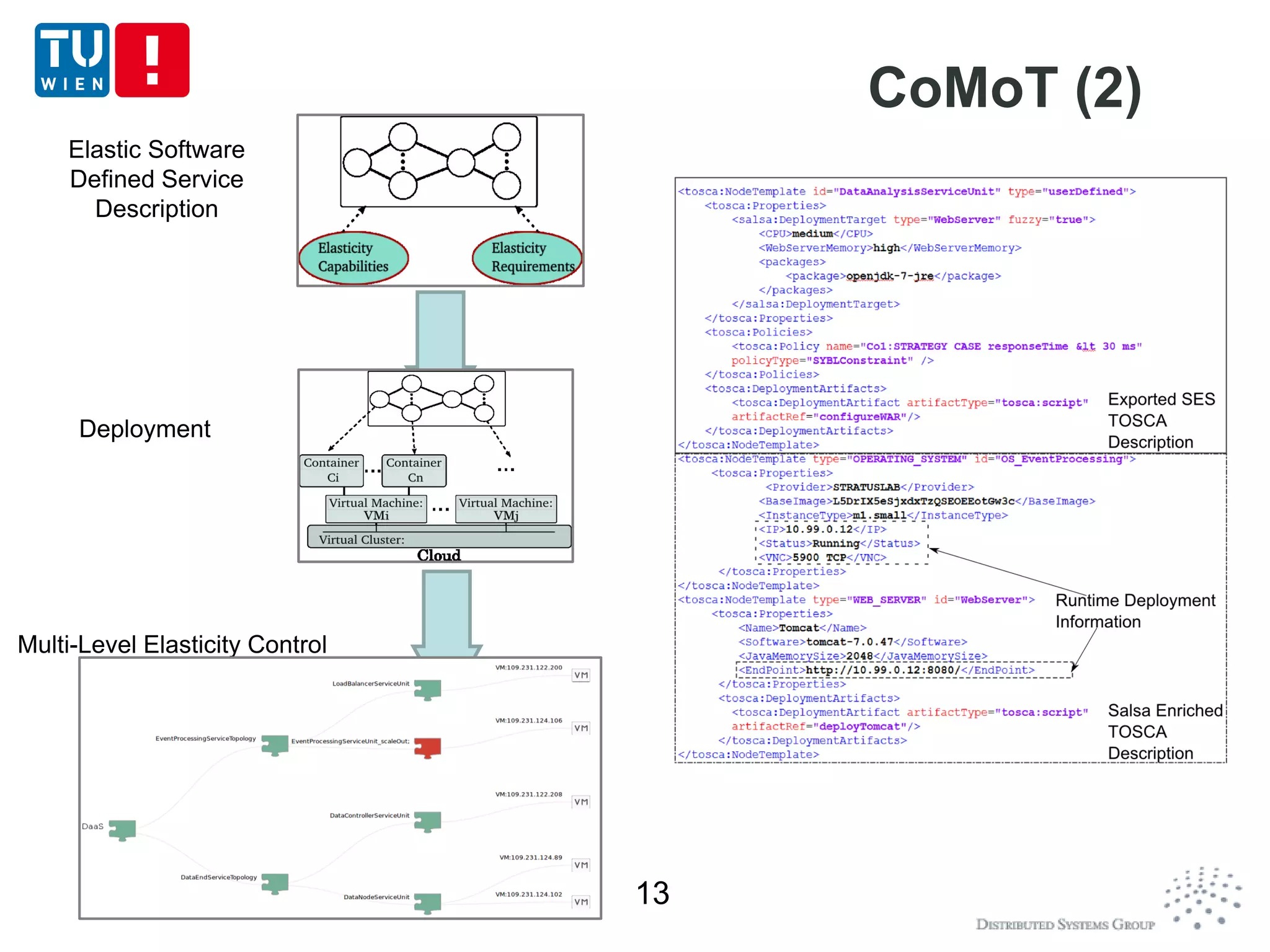
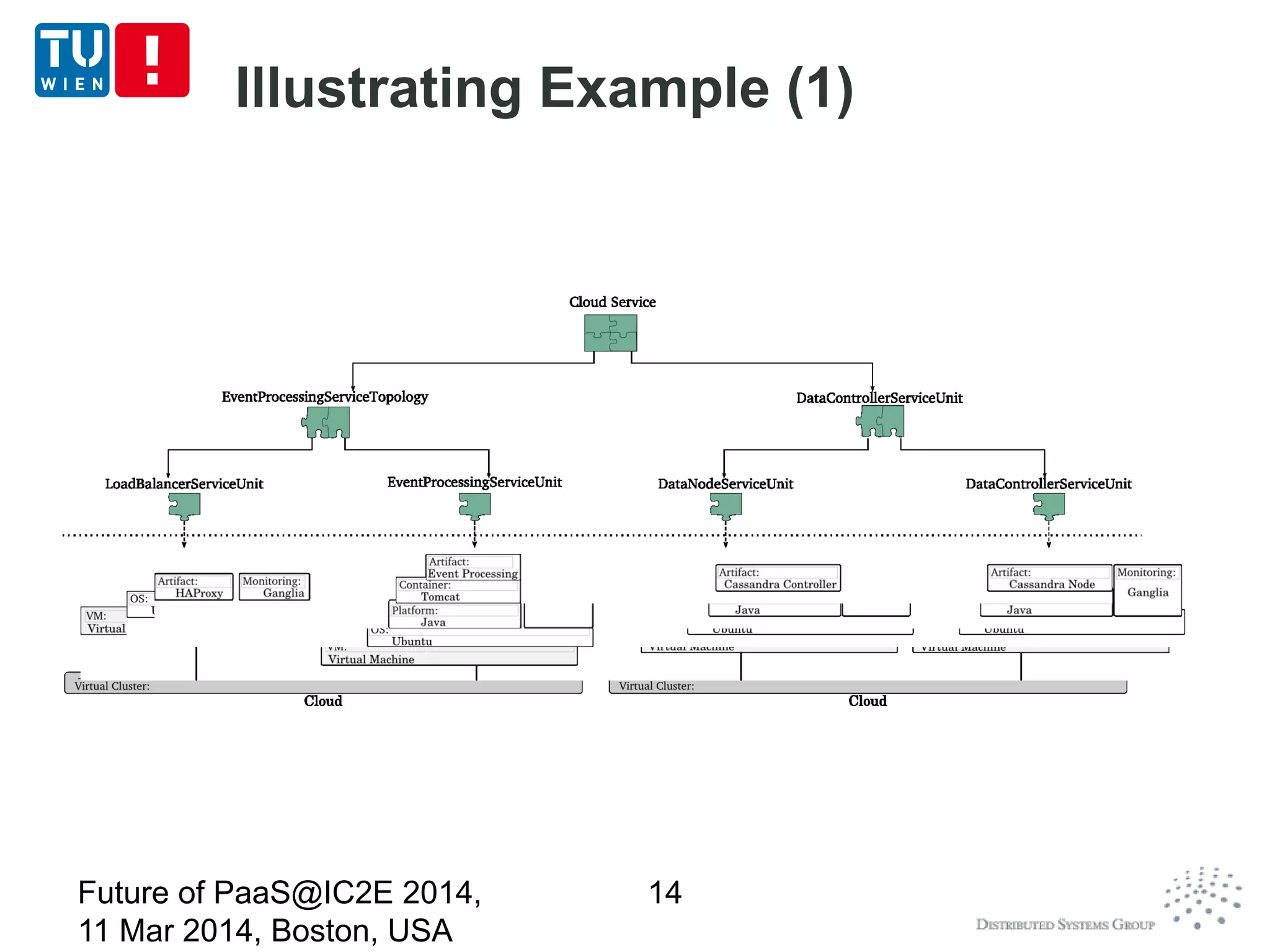
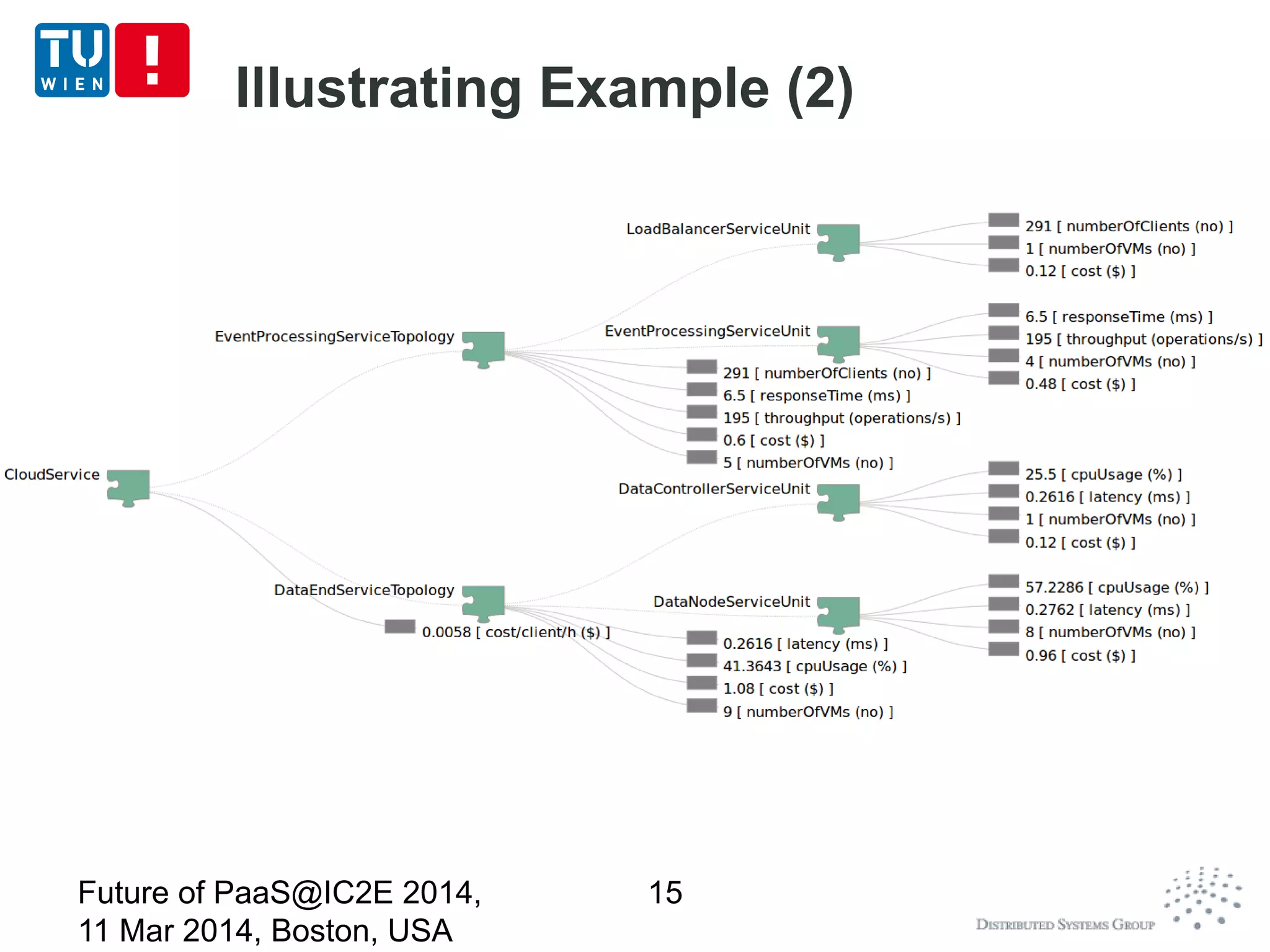
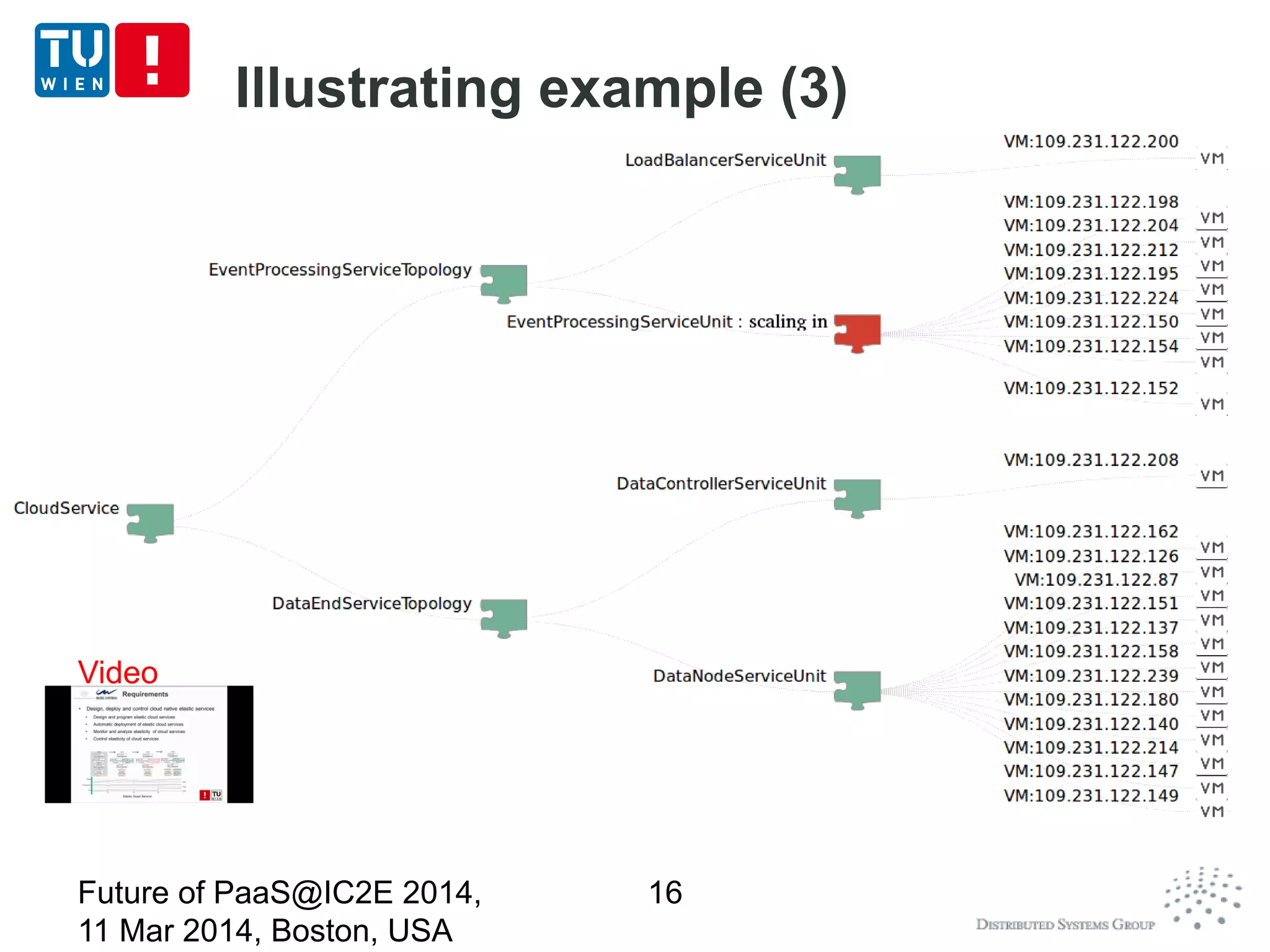
CoMoT is a platform-as-a-service that provides tools for programming, deploying, controlling, monitoring, and testing elasticity in cloud systems. It introduces concepts of elastic objects and fundamental building blocks for engineering multi-dimensional elasticity. CoMoT's tools include programming elastic services using enriched OCCI and TOSCA, deploying and controlling elasticity based on requirements, monitoring elasticity using metrics, and testing elastic properties. The platform aims to provide native support for elasticity across all phases of cloud service engineering.
![Deploying, Control, Monitoring and
Testing
Runtime deployment
Complex services at multiple software stacks (IaaS,
PaaS and application)
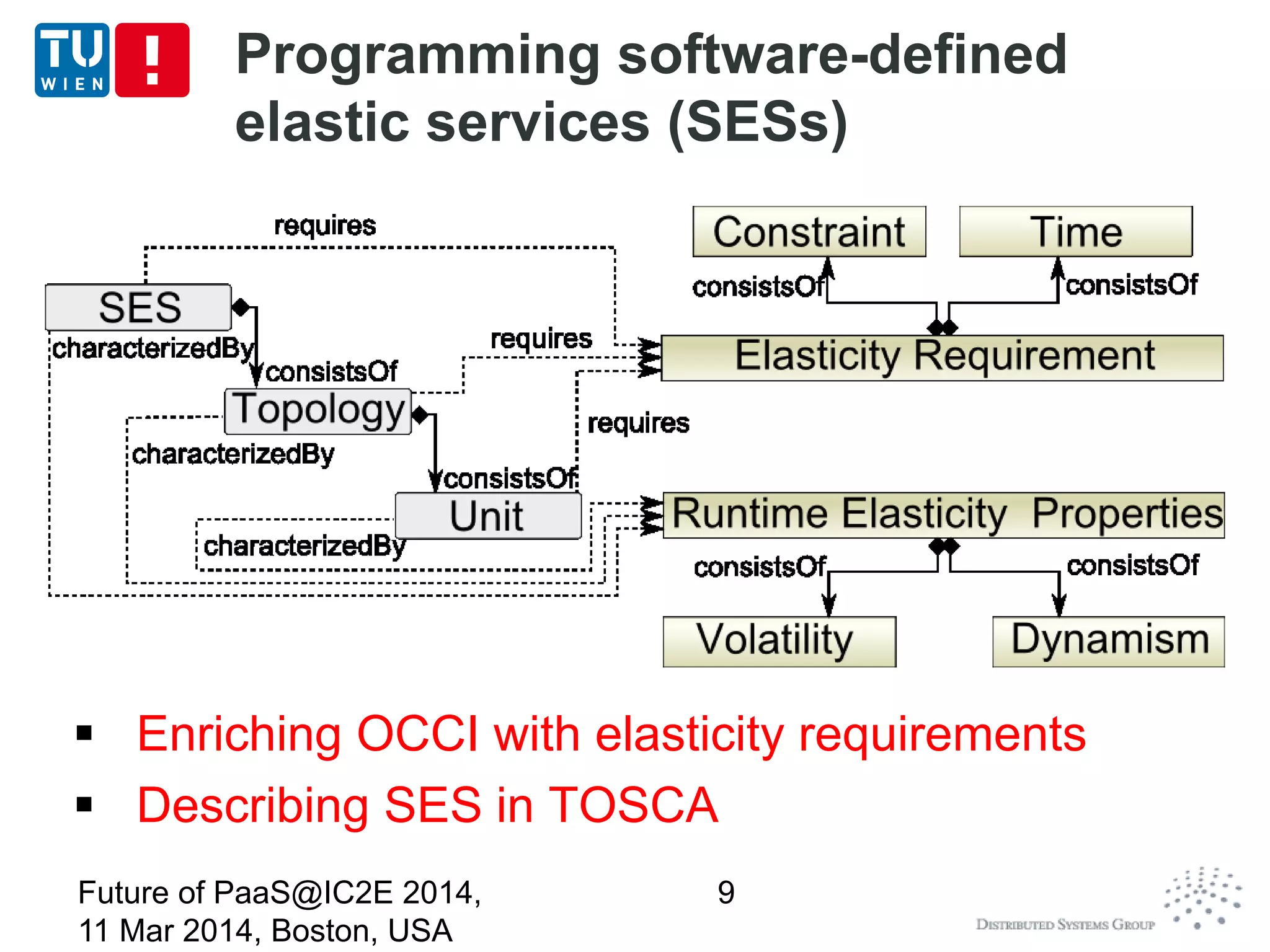
Using and enriching TOSCA for describing
deployment topology
Different interactions between deploying and control
and monitoring components
Control elasticity
Using a high-level specification for specifying
elasticity requirements, constraints and strategies
Based on SYBL/rSYBL ([CCGrid 2013])
Future of PaaS@IC2E 2014,
11 Mar 2014, Boston, USA
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/truong-comot-ic2e-2014-140311121247-phpapp02/75/CoMoT-A-Platform-as-a-Service-for-Elasticity-in-the-Cloud-10-2048.jpg)
![Deploying, Control, Monitoring and
Testing
Elasticity monitoring and analysis
Utilize low-level metrics to build „Elasticity Space“
and analyze the elasticity based on such spaces
(based on MELA – [CloudCom 2013])
Monitoring/analysis at multiple levels level (single
unit, topology/group, and the whole service
Testing elasticity
Using clouds to test cloud applications as well as to
test elasticity properties of cloud applications
[ASE2013, IC2014]
Future of PaaS@IC2E 2014,
11 Mar 2014, Boston, USA
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/truong-comot-ic2e-2014-140311121247-phpapp02/75/CoMoT-A-Platform-as-a-Service-for-Elasticity-in-the-Cloud-11-2048.jpg)