Multiple Choice Practice Questions
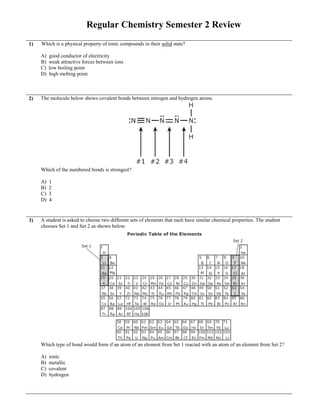
- 1. Regular Chemistry Semester 2 Review 1) Which is a physical property of ionic compounds in their solid state? A) good conductor of electricity B) weak attractive forces between ions C) low boiling point D) high melting point 2) The molecule below shows covalent bonds between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. Which of the numbered bonds is strongest? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 3) A student is asked to choose two different sets of elements that each have similar chemical properties. The student chooses Set 1 and Set 2 as shown below. Which type of bond would form if an atom of an element from Set 1 reacted with an atom of an element from Set 2? A) ionic B) metallic C) covalent D) hydrogen
- 2. 4) Which structural formula shows a polar molecule? 5) Which Lewis structure is correct for a molecule of chlorine gas (Cl 2)? 6) During the combustion of glucose, more energy is released when bonds form in the products than is absorbed to break bonds in the reactants. Which term best describes the energy change for the combustion of glucose? A) ionic B) exothermic C) endothermic D) acidic
- 3. 7) Which type of molecular shape is shown by this molecule? A) trigonal pyramidal B) tetrahedral C) bent D) trigonal planar 8) Which is NOT a diatomic molecule? A) Fluorine B) Nitrogen C) Bromine D) Boron 9) The stronger the chemical bond between two elements is, A) the more energy will be needed to break the bond B) the more energy is stored in the bond C) the shorter the bond D) all of the above 10) What molecular shape does the compound CCl4 have? A) trigonal planar B) tetrahedral C) octahedral D) bent
- 4. 11) The table below compares melting points and bond types of four different substances. Melting Points and Bond Types of Some Substances Substance Melting Point (°C) Bond Type Fe2O3 1566.0 ionic Ni 1453.0 metallic NaCl 801.0 ionic Na 97.8 metallic Which substance has the strongest forces between its particles? A) Fe2O3 B) Ni C) NaCl D) Na 12) A student has two identical solid metal samples at 90°C. She carefully places one of the metal samples into a beaker of water at 10°C and the other into an empty beaker (only air) at 10°C. Why would the metal sample placed into water cool faster than the one placed into air? A) Water has faster-moving molecules than air, enabling more heat transfer by conduction. B) Water has more molecules per unit volume than air, enabling more heat transfer by conduction. C) Air is made mostly of nitrogen which is too heavy an element to conduct heat. D) Air is a gas and gases do not conduct heat. 13) Which state of matter conducts heat the best? A) Gases, because the molecules move faster B) Solids, because the molecules are closest together C) Gases, because they molecules collide more frequently D) Liquids, because the molecules have the most freedom to move 14) Covalent compounds display which of these properties? A) They are hard, brittle solids B) They have high melting and boiling points C) They display luster. D) Their intermolecular forces are relatively weak compared to stronger intramolecular forces. 15) Which is the state of matter shown in this figure? A) solid B) liquid C) gas D) plasma
- 5. 16) Which has the strongest attractive forces at room temperature? A) Cl2, a gas B) Br2, a liquid C) I2, a solid D) H2, a gas 17) The table below shows the boiling points of butane, a common fuel used in disposable lighters, and water. Boiling Points of Butane and Water Compound Boiling Point (°C) butane -0.5 water 100.0 Based on these boiling points, which statement about the forces in these molecules is correct? A) Butane has stronger ionic bonds than water. B) Water has stronger ionic bonds than butane. C) Butane has stronger intermolecular forces than water. D) Water has stronger intermolecular forces than butane. 18) Which statement best explains why chlorine is a gas at room temperature and iodine is a solid at room temperature? A) Chlorine has stronger dispersion forces than iodine. B) Iodine has stronger dispersion forces than chlorine. C) Chlorine has stronger covalent bonds than iodine. D) Iodine has stronger ionic bonds than chlorine. 19) A substance is composed purely of a Group 2 element. Which type of bonding does this substance have? A) ionic B) metallic C) nonpolar covalent D) polar covalent 20) Which elements within a molecule containing hydrogen allow for the formation of hydrogen bonds? A) carbon, sodium, and oxygen B) carbon, uranium, and nitrogen C) fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen D) fluorine, nitrogen, and phosphorus 21) Water has a much higher boiling point than methane (CH4). Which statement best explains why water’s boiling point is higher than methane’s? A) There is hydrogen bonding between water molecules, but not between methane molecules. B) There is covalent bonding between water molecules, but not between methane molecules. C) Methane has more hydrogen atoms per molecule than water. D) Water has a higher molecular weight than methane.
- 6. 22) The diagram shows water molecules. Which types of bonds are represented by the dashed lines? A) ionic B) hydrogen C) covalent D) double 23) An engineer needs a metallic substance that is malleable. Which statement describes this property? A) This property enables a substance to conduct an electric current. B) This property enables a substance to be pulled into a thin wire. C) This property makes a substance very hard and brittle. D) This property enables a substance to be shaped into a pliable, flat sheet. 24) Which is a property of substances that exhibit metallic bonding? A) high boiling points B) rigid and brittle C) low melting points D) poor conductors of electricity 25) Sodium fluoride has a melting point of 995°C, while water has a melting point of 0°C. Why is the melting point of sodium fluoride so much higher than the melting point of water? A) The radioactivity of NaF is higher than that of H2O. B) The molecular weight of NaF is higher than that of H2O. C) The forces between the atoms of each molecule are stronger for H 2O than for NaF. D) The forces between the ions of NaF are stronger than the forces between the molecules of H2O. 26) At room temperature, glucose (C6H12O6) is a solid and ammonia(NH3) is a gas. Which statement explains the differences in the states of matter of these two compounds? A) Sugar has stronger ionic bonds than ammonia does. B) Ammonia has stronger ionic bonds than sugar does. C) Sugar has stronger intermolecular forces than ammonia does. D) Ammonia has stronger intermolecular forces than sugar does.
- 7. 27) Which is the state of matter that has a definite shape and definite volume? A) solid B) liquid C) gas D) plasma 28) Based on bond forces, which substance would be expected to have the highest melting point? A) H2 B) NH3 C) NaCl D) H2O 29) A scientist obtains a sample of a pure-liquid compound and records several measurements while examining the sample. Which measurement, by itself, provides the most important information regarding the structure of the molecules that make up the liquid compound? A) boiling point B) mass C) volume D) temperature 30) A school wants to use windows that do not conduct heat well since too much heat is transferred outdoors through windows during winter months. They are comparing single-pane windows with double-pane windows. A double-pane window has two glass panels with a gap between them filled with air. The diagram below shows cutaway views of both a single-pane and a double-pane window. Which of the following best compares the transfer of heat through each of the windows? A) There is more heat conduction through the double-pane window since air molecules move faster and can transfer heat more efficiently than molecules in glass. B) There is more heat conduction through the double-pane window since air molecules collide more frequently than molecules in glass. C) There is more heat conduction through the single-pane window since glass molecules are closer together than molecules in air, which creates more collisions and conduction of heat. D) There is more heat conduction through the single-pane window since glass molecules have more freedom to move than molecules in air, which creates more energy that can better conduct heat.
- 8. 31) A(n) _____ reaction occurs when more energy is released during product bond formation than is required to break bonds. A) exothermic B) endothermic C) ectoplasmic D) reversible 32) During the winter in Michigan, a salt (potassium chloride) is put on roads to prevent icy conditions. Which statement accurately describes the reason for this practice? A) The water does not freeze since the salt causes an increase of the freezing point of the pavement. B) The water does not freeze since the salt causes a decrease of the freezing point of the pavement. C) The water does not freeze since the salt causes a decrease of the freezing point of the water. D) The water does not freeze since the salt causes an increase of the freezing point of the water. 33) _____ solutions contain more dissolved solute than a saturated solution at the same temperature and are very unstable. A) saturated B) supersaturated C) suspended D) unsaturated 34) Which liquid sample will boil at the highest temperature? Liquid Samples to be Boiled Liquid Sample Contents 1 pure water 2 2.00 grams of NaCl in 50.0 mL of water 3 3.00 grams of NaCl in 50.0 mL of water 4 2.00 grams of NaCl in 75.0 mL of water A) liquid sample 1 B) liquid sample 2 C) liquid sample 3 D) liquid sample 4
- 9. 35) The diagram below shows the changes in potential energy during a chemical reaction. Which of the following represents the amount of activation energy for the reaction? A) Y B) Z C) X-Y D) X-Z 36) A/An _____ is a substance that lowers the activation energy required for a reaction to take place and increases the rate of a chemical reaction. A) catalyst B) inhibitor C) reactant D) product 37) Which of the following activation energy graphs represents an exothermic reaction that takes the longest time to go to completion? (Assume the y axis represents the enthalpy (H) of the reaction components.)
- 10. 38) If we increase the temperature of a reaction, what happens to the collisions between particles and to the reaction rate? A) There are fewer collisions, reaction rate decreases B) There are the same number of collisions but they have more energy, reaction rate stays the same C) There are the more collisions and they have more energy, reaction rate increases D) There are the more collisions but they have less energy, reaction rate increases 39) The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 700.0 K is 0.44. → What is the concentration of carbon dioxide gas, if [H2O] = 0.16 mol/L, [CO] = 0.15 mol/L and [H 2] = 0.14 mol/L? A) 0.0014 mol/L B) 0.075 mol/L C) 0.16 mol/L D) 0.75 mol/L 40) What effect does doubling the concentration of a reactant have on the rate of a reaction? A) No effect on reaction rate B) Reaction rate decreases C) Reaction rate increases D) Reaction rate halves 41) Suppose that more H2 is added to the reaction 2H2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2H2O(g), which is in equilibrium at a constant temperature. Which of the following will not change? A) the entropy of the system (S) B) the concentration of O2 C) the concentration of H2O D) the value of the equilibrium constant (K) 42) What change can result in a shift in equilibrium during a reaction? A) change in concentration B) change in temperature C) change in volume and pressure D) all of the above 43) For which system would an increase in pressure lead to an increase in the relative concentration of the reactants at equilibrium? A) 2NO(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2NO(g) B) N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) C) H2(g) + Cl2(g) ↔ 2HCl(g) D) C(s) + H2O(g) ↔ CO(g) + H2(g)
- 11. 44) The table below shows some reaction constants between hydrogen and some halogens. Assume the reactions are at the same temperature and pressure. Some Reaction Constants for Hydrogen Reacting with Halogens Reaction ΔH ΔS Keq (kJ) (J/K) 1 H2(g) + F2(g) → 2HF(g) -539 347 5.32 x 1095 2 H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g) -184 373 2.46x1033 3 H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g) -72 397 1.88x1019 4 H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g) 5 512 6.17x102 Based on information in the table, which reaction will have the greatest concentration of product when the reactions are at equilibrium? A) reaction 1 B) reaction 2 C) reaction 3 D) reaction 4 45) When the Keq ___ 1, products are favored at equilibrium. A) < B) > C) + D) = 46) A _____ reaction is a chemical reaction that can occur in both the forward and reverse directions. A) complete B) forward C) reversible D) incomplete 47) Which formula represents a compound classified as an inorganic acid? A) CH4 B) HBr C) NaOH D) CH3CH2OH 48) Complete the reaction: HCl + NaOH ______ + ________ A) H2O + NaCl B) HNa + ClOH C) OH- + H+ D) No reaction will occur
- 12. 49) Based upon these pH values, which substance would be classified as an acid? A) bleach B) pure water C) coffee D) baking soda 50) Why do lakes with calcium carbonate beds, such as those in many Michigan lakes, experience fewer adverse effects from acid rain than lakes with granite beds? A) Calcium carbonate reacts with the acid rain to neutralize it. B) Calcium carbonate in water does not let the acid rain dissolve in the lake. C) Granite reacts with acid rain to produce more acid. D) Granite-based lakes make the acid rain more acidic than it was when it fell as rain. 51) Hydrochloric acid and calcium hydroxide react as shown in the equation below: 2HCl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2H2O When 6 moles of hydrochloric acid completely react with calcium hydroxide, how many moles of water are formed? A) 2 moles B) 4 moles C) 6 moles D) 8 moles 52) The concentration of a hydrochloric acid solution is 0.0280 moles/liter. What is the pH of the hydrochloric acid solution? A) 1.55 B) -1.55 C) 2.80 D) -2.80
- 13. 53) What is the pH of 0.45 M of H2SO4? A) 0.0045 B) 0.045 C) 0.45 D) 4.50 54) What is the pH of blood, given the hydrogen ion concentration is 4.0 x 10 -8 M? A) 7.0 B) 7.2 C) 7.4 D) 7.6 55) How do sulfur oxides like SO3 and nitrogen oxides like NO2 contribute to acid rain? A) They are acidic in the gas state. B) They react with soil particles to form acids. C) They mix with ozone to form acids. D) They react with rain water to form acids. 56) Identify the acid and conjugate base pair in the following equation: HF + H2O ↔ H3O+ + F- A) HF & H20 B) HF & H30 C) HF & F- D) H20 & H3O+ 57) In the Bronsted-Lowry model of acids and bases, an _____ is a hydrogen donor and a _____ is a hydrogen acceptor. A) acid, base B) base, acid C) conjugate acid, conjugate base D) conjugate base, conjugate acid 58) Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution, given the concentration of hydroxide ions is 1 x 10 -5 M and the ion constant for water is 1 x 10-14. A) B) C) D)
- 14. 59) If a reaction has a positive ΔH and a positive ΔS, which statement best describes the spontaneity of the reaction? A) The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures. B) The reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature. C) The reaction is spontaneous at zero Kelvin. D) The reaction is spontaneous above some specific temperature. 60) What is the oxidation state of magnesium in the compound magnesium oxide (MgO)? A) +1 B) +2 C) +6 D) +7 61) What are the balanced oxidation and reduction half-reactions for the redox reaction of Fe + F2 → FeF3? A) 2Fe → 2Fe3+ + 6e- , 3F2 + 6e- → 6F- B) F2 + 3e- → 2F- , Fe → Fe3+ + 2e- C) Fe → Fe3+ + 3e- , F2 + 2e- → 2F- D) F2 + 2e- → 2F- , Fe + 3e- → Fe3+ 62) The diagram shows strengths of reducing agents, which are elements that reduce a substance in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Many underground pipes are made out of iron. An engineer wants to attach a piece of material to an iron pipe to prevent rust formation (oxidation). Based on the diagram, which of the following materials should the engineer use? A) gold B) copper C) silver D) zinc
- 15. 63) Redox reactions involve the _____ of electrons. A) combining B) sharing C) substitution D) transfer 64) The _____ the difference in potential energy between two electrodes, the larger the voltage. A) lesser B) greater C) balance of D) charge of 65) The electrode where reduction takes place is called the: A) anode B) cathode C) cell D) dry cell 66) Oxidation involves the _____ of electrons. A) gain B) loss C) displacement D) bonding 67) To find the heat change for an organic reaction, a chemist must use hexane as the solvent in her calorimetry experiment. If the reaction causes the temperature of 0.0700 kilograms of hexane to decrease by 3.57°C, what is the heat change for the reaction? (Hexane has a specific heat capacity of 2.26 kJ/kg • °C.) A) 0.111 kJ B) 0.565 kJ C) 5.90 kJ D) 115.0 kJ 68) How much heat is evolved from 54.0 g glucose (C6H12O6), according to the equation for calculating heat? C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) ΔH = -2808 kJ/mol A) 0.842 kJ B) 8.42 kJ C) 84.2 kJ D) 842 kJ 69) The reaction that occurs in cold packs is an example of _____ a reaction. A) exothermic B) endothermic C) ectoplasmic D) reversible
- 16. 70) Mary carried out a chemical reaction in the lab and concluded that the reaction was exothermic. Which of the following best supports her conclusion? A) A precipitate formed in the reaction mixture. B) A gas was released from the reaction mixture. C) The temperature of the reaction mixture decreased. D) The temperature of the reaction mixture increased. 71) This graph shows the changes in potential energy for the reaction of two hydrogen atoms as they move closer together to form a hydrogen gas molecule: 2H(g) → H2(g). Which statement about a point on the graph best explains how the potential energy and the bond strength between the two hydrogen atoms change as they come together to form a molecule? A) Point Q is the point where the potential energy is greatest and the bonds are most stable. B) Point R is the point where the potential energy is the lowest and the bonds are most stable. C) Point S is the point where the potential energy is the greatest and the bonds are most stable. D) Point T is the point where the potential energy is the lowest and the bonds are most stable. 72) What happens to the potential energy of two covalently bonded atoms as they are pulled farther apart? A) The potential energy of both atoms increases. B) The potential energy of both atoms decreases. C) The potential energy of one atom increases, and the potential energy of the other atom decreases. D) The potential energy of one atom stays the same, and the potential energy of the other atom either increases or decreases. 73) Nitrogen (N2) gas and oxygen (O2) gas react to make nitrogen dioxide (NO2) according to the following balanced reaction: N2(g) + 2 O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) Given that N2(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO(g) ΔH = +180.4 kJ 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) ΔH = -114.0 kJ What is the enthalpy change for this reaction? A) 66.4 kJ B) 180.4 kJ C) -114.0 kJ D) -294.4 kJ
- 17. 74) The table below shows values of enthalpy changes for some reactions. Which process listed in the table has an enthalpy diagram that looks like the diagram shown below? A) reaction 1 B) reaction 2 C) reaction 3 D) reaction 4 75) Carbon dioxide and water are produced by an exothermic process in which methane gas (CH4) reacts with oxygen. The reaction is not reversible. Which of the following chemical equations correctly represents the reaction? A) CH4 + 2O2 + heat → CO2 + 2H2O B) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + heat C) CO2 + 2H2O + heat → CH4 + 2O2 D) CO2 + 2H2O → CH4 + 2O2 + heat 76) Which picture below shows the enthalpy diagram for a one-step exothermic reaction? 77) You have a 10 g sample of water at 20oC and a 10g sample of gold at 20oC. You add heat into each sample and both undergo the same temperature change. Which had more heat flow into it? (cgold = 0.129J/goC) A) Neither; if the change in temperature is the same, the heat flow must be the same B) The water, because its specific heat is so large C) The gold, because its specific heat is so small D) The gold, because metals conduct heat better
- 18. 78) The graph below shows the heating curve of a sample of water, H2O, as it is heated at a constant rate from -25°C to 125°C. Along which line segments is the average kinetic energy of the H2O molecules increasing? A) Q and R B) R and T C) Q, S, and U D) Q, R, S, T, and U 79) Lithium reacts with water according to the reaction 2Li(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2LiOH(aq) + H2(g). What evidence from this reaction can be used to show that the entropy increases? A) The pH decreases. B) The water becomes a solvent. C) The total number of moles of gas increases. D) The total number of molecules decreases. 80) Thermal energy can be easily transferred in the form of current movement in a gas. Which term correctly describes this transfer of energy? A) combustion B) convection C) evaporation D) radiation 81) Which statement correctly describes why the freezing of water is an exothermic reaction? A) Water molecules speed up and lose kinetic energy. B) Water molecules speed up and gain kinetic energy. C) Water molecules slow down and lose kinetic energy. D) Water molecules slow down and gain kinetic energy. 82) Which statement best describes the kinetic energy of the molecules in a solid piece of wood and the atoms in a solid piece of metal, both of which are at room temperature? A) The wood molecules have a higher average kinetic energy than the metal atoms. B) The wood molecules have a lower average kinetic energy than the metal atoms. C) The wood molecules and metal atoms have the same average kinetic energy. D) The wood molecules and metal atoms do not have kinetic energy since they are in the solid state. 83) The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by one degree Celsius is defined as: A) a calorie B) heat C) a joule D) a watt
- 19. 84) How much heat would be released if 50.0g of water has a temperature change from 80oC to 60oC? A) 4184 J B) 6010 J C) 40,700 J D) 3.0 J 85) Which of these lists shows substances in order of increasing melting point? A) H2O, SO2, O2, Ca(OH)2 B) O2, SO2, H2O, Ca(OH)2 C) H2O, Ca(OH)2, SO2, O2 D) Ca(OH)2, SO2, H2O, O2
