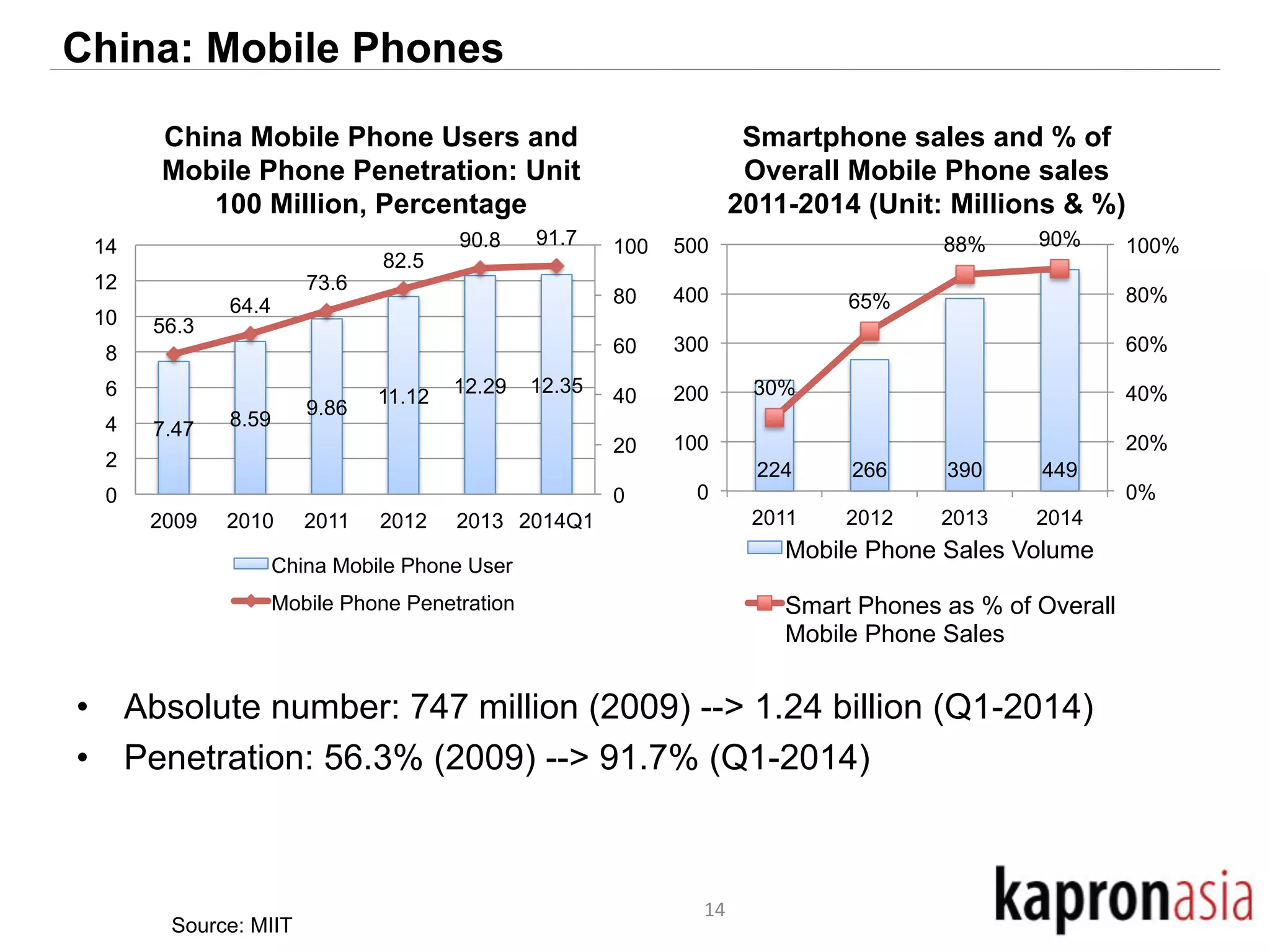
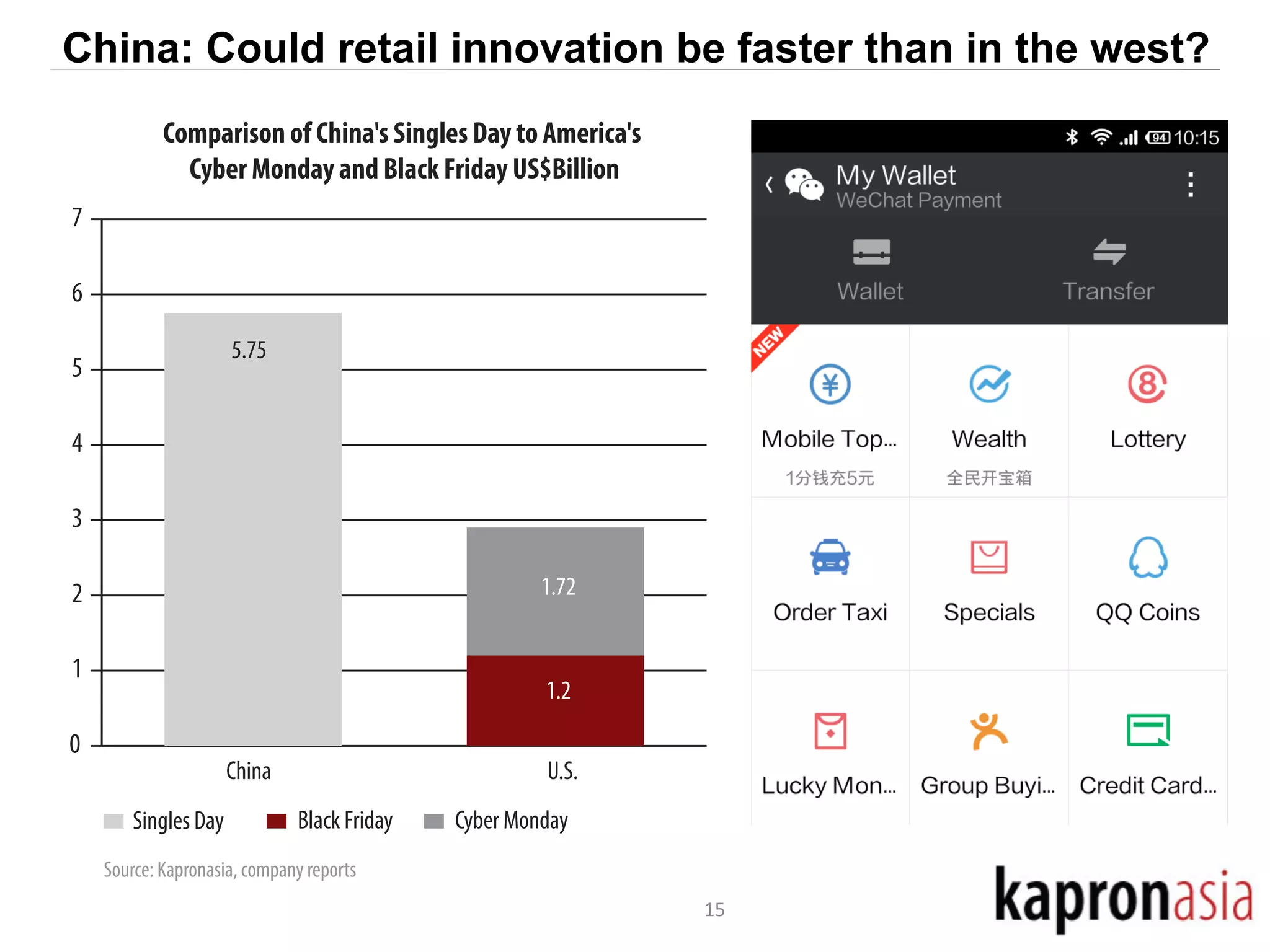
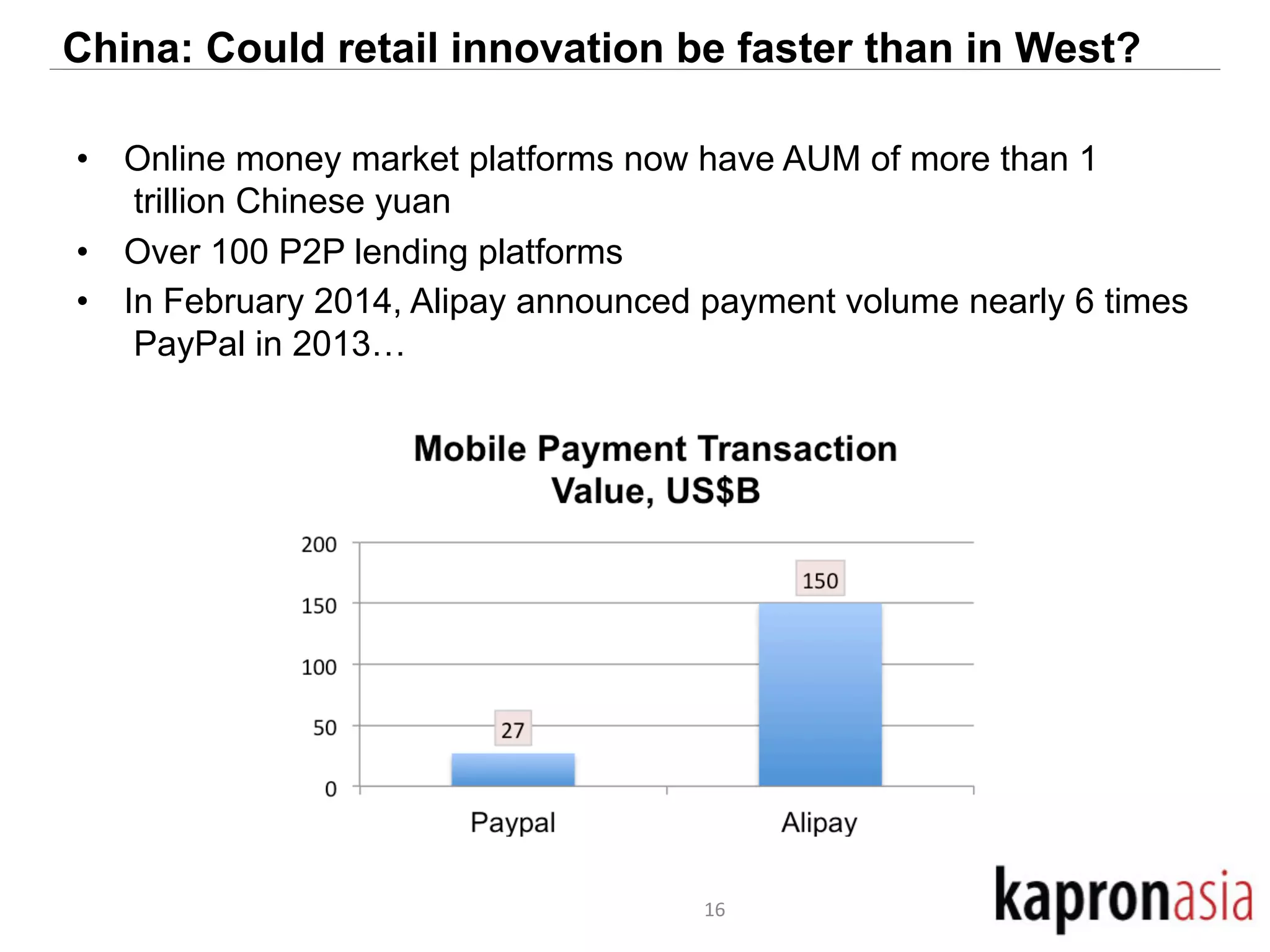
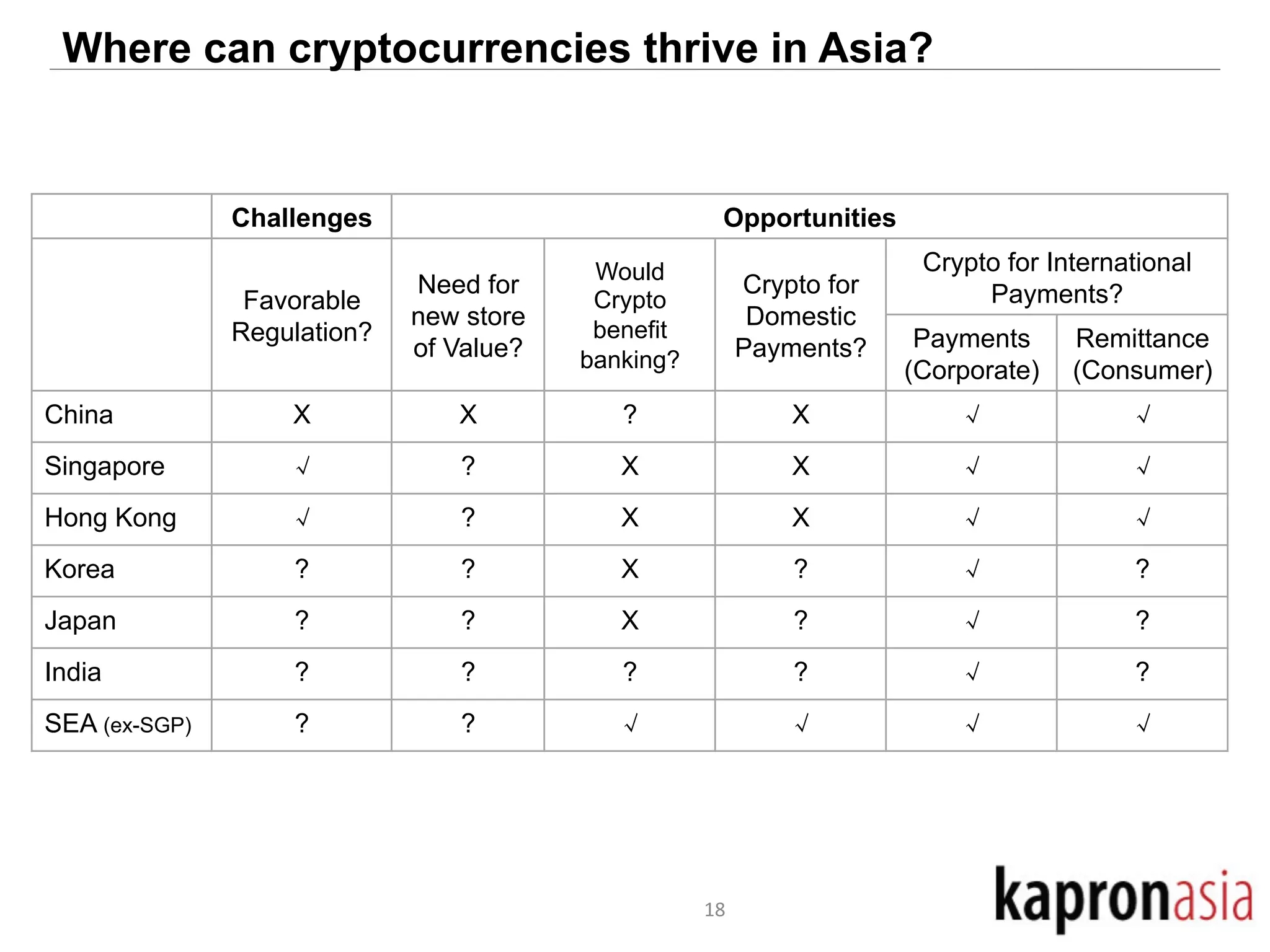
This document discusses cryptocurrency opportunities and challenges in Asia. It provides background on Kapronasia and an overview of Asia's financial services landscape and needs. Regulation of cryptocurrency has varied across Asia, with more developed markets like Singapore and Hong Kong taking a measured approach. In China, cryptocurrency speculation was regulated though innovation in payments is still encouraged. Overall, cryptocurrency is most likely to succeed in Asia by enabling cheaper and more convenient international and remittance payments.