Leadership Model Submitted for Publishing
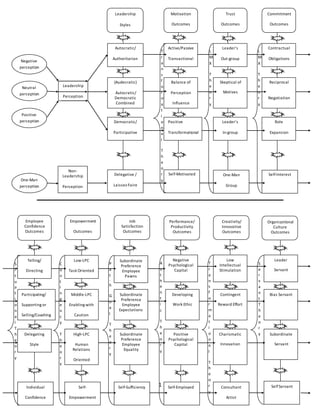
- 1. 1 Leadership Perception Model Negative perception Neutral perception Positive perception Non- Leadership Perception Styles One-Man perception Leadership Styles Autocratic/ Authoritarian (Audecratic) Autocratic/ Democratic Combined CombinedDemocratic/ Participative Delegative / Laissez-Faire Motivation Outcomes Active/Passive Transactional Balance of Perception Influence Positive Transformational Self-Motivated T r a n s f o r m a t i o n a l T h e o r y Trust Outcomes Leader’s Out-group Skeptical of Motives Leader’s In-group One-Man Group L M X T h e o r y Commitment Outcomes Contractual Obligations Reciprocal Negotiation Role Expansion Self-Interest L M X T h e o r y Employee Confidence Outcomes Telling/ Directing Participating/ Supporting or Selling/Coaching Delegating Style Individual Confidence S i t u a t i o n a l T h e o r y Empowerment Outcomes Low-LPC Task Oriented Middle-LPC Enabling with Caution High-LPC Human Relations Oriented Self- Empowerment C o n t i n g e n c y T h e o r y Job Satisfaction Outcomes Subordinate Preference Employee Pawns Subordinate Preference Employee Expectations Subordinate Preference Employee Equality Self-Sufficiency P a t h G o a l T h e o r y Performance/ Productivity Outcomes Negative Psychological Capital Developing Work Ethic Positive Psychological Capital Self-Employed A u t h e n t i c T h e o r y Creativity/ Innovative Outcomes Low Intellectual Stimulation Contingent Reward Effort Charismatic Innovation Consultant Artist T r a n s f o r m a t i o n a l T h e o r y Organizational Culture Outcomes Leader Servant Bias Servant Subordinate Servant S e r v a n t T h e o r y SelfServant
- 2. 2 Multi-Dimensional Leadership Model for Multi-Dimensional Firms with Multi-Dimensional Critical Follower Outcomes involving Four Leadership Styles with a Full Range of Possibilities based on Individual Perceptions and Leadership Theories Submitted for publishing by Jeff Taylor 2012 Leader- Follower Relationship Effectiveness Level Leader- Follower Satisfaction Level Minimal Debatable Maximum Non-existent Limited Confusing Elevated Incomplete One-Sided GovernmentorOutside Influences whichmeansnocontrol,no logic,or no stabilitywhichisinserted everywhere inthe model to symbolize forcesthatare unpredictableandnothingwill make any sense like the government bailoutsforWall Streetthatviolated economiclaw andwere politically motivated.
- 3. 3 Overview Managers are always asking which leadership style works best so I developed a leadership model based on a range of critical follower outcomes according to the four leadership styles. Each style has an individual perception associated with its principles and a leadership theory that explains the range of outcomes for that theory style based on influential theory clarity that is used as a reference for each range. The line of outcomes for each leadership style ultimately leads to the leader/follower effectiveness level which leads to the leader/follower satisfaction level as the end result. Each path will bring any leader to a designated end result which can help him or her decide which path is right for them individually. In other words, which sides of the leader/follower pendulum- swing will they be drawn too. I also included a government or other outside influence variable which changes the total dimension of my leadership model if it comes into play. The range of nine critical follower outcomes that I used include: motivation, trust, commitment, employee confidence, empowerment, job satisfaction, performance/productivity, creation/innovation, and organizational culture. The four leadership styles I used are authoritarian/autocratic, audecratic (autocratic and democratic combined), democratic/participative, and laissez faire respectively. The four perceptions I used include: negative, neutral, positive, and one-man and each is attached to a specific leadership style. I included all seven leadership theories that we studied as a reference to explain each range of four possibilities for each critical follower outcome and these theories include: transformational, LMX (Leader-Member Exchange), Situational, Contingency, Path-Goal, Authentic, and Servant. Each leadership style leads to a leader/follower relationship effectiveness level that includes minimal, debatable, maximum, and non-existent. The final end result involves a leader/follower
- 4. 4 satisfaction range that includes: limited, confusing, elevated, and incomplete one-sided. It also needs to be noted that I based my perceptions on the literature accepted majority conclusions associated with each style of leadership. I also chose each leadership style based on influential clarity that I believe is the most relevant theory reference for each range of possibilities for that outcome. The model isn’t a perfect science and exceptions can exist as a possible reality. I believe this leadership model is relevant because it offers a range of probable outcomes based on default perceptions and it lets a manager what he or she is up against if one path is chosen over the other three. Managers are reported to be the most frequent perpetrators of influential leadership action from a target/employee point of view (Rayner, Hoel, and Cooper, 2002) (Hoel, Glaso, Hetland, Cooper and Einarsen, 2010). It all depends on the relationship effectiveness satisfaction level that he or she wants to have with individual workers. I’m not endorsing one leadership style over another but I’m painting a humanistic reality that is likely to occur based on sample testing and reviews that have a literature based backing. In other words, the results are based on what we know and the decision is based on individual managerial preferences. Leadership Model Path Explanation Now let’s look at my leadership model more in depth. Before we get into the actual critical follower outcome ranges, let’s begin by looking at the four leadership styles and the perception associated with that style. The first leadership style that we will look at involves autocratic/authoritarian leadership which carries a negative employee perception. Authoritarian leadership is defined as a leadership style in which a leader dictates policies and procedures, decides what goals are to be achieved, and directs/controls all activities without any meaningful participation by the subordinates (Casal, 2002). An autocratic leader is one who is perceived to be dictatorial in nature and has a “my way or the highway” approach to managing employees.
- 5. 5 This style of management is practiced in a lot of third world countries where workers aren’t educated as much in relation to western civilizations. This style establishes no meaningful relationship with any subordinate because it’s one sided in nature. Authoritarianism is one of the most reviled concepts in western management. No management textbook recommends it and many employees who have worked with autocratic leaders only have nightmarish experiences. What kind of masochist would want to work for a manager who is punitive, demanding, dictatorial, and one who is not looking for a meaningful leader/subordinate relationship (Smither, Nov 1991). Autocratic leaders have to be challenged and will put down anyone who challenges their power scope. They prefer to have political influences (who you know) to advocate self- serving projects and interests. Authoritarian leadership is intrinsically motivated, since intrinsically motivated behavior is defined as the motivation to engage in work primarily for self serving outcomes and self determination for the individual (Casal, April 2002). So why are autocratic managers associated with this individual perception? Can it be assumed that a leadership style can really be that bad? Authoritarians combine the worst elements of human personality, being power hungry, unsupportive of equality, manipulative, amoral, social dominators, while being dogmatic and religiously ethnocentric leaders/manager in general (Altemeyer, Aug 2004). A recent example of an authoritarian leader was Mommar Quadafi in Libya who used every trick to hold on power even as the capital was falling to rebel forces. He used nepotism to get his own children in high ranking government positions based on his own personal narcissism. That’s not saying that it doesn’t have a place but I think this style works best for individuals who are military or criminal justice leaders whose employees require a domineering presence. Now let’s look at another leadership style which is democratic/participative leadership. This style of leadership is the exact opposite of
- 6. 6 autocratic/authoritarian leadership because it promotes a positive meaningful relationship between a leader and his or her followers. Democratic leadership is the performance of three functions: a. Distributing responsibility among the membership, b. Empowering group members, and c. Aiding the group’s decision making (Gastil, Aug 1994). This form of leadership is the most popular and the most practiced in western management today because it promotes accountability. This style also promotes individual interactions and lets each individual or team member know that his or her opinion matters. In fact, this leadership style has spawned a revolution in autocratic middle-eastern countries because absolute power has corrupted these countries for many decades and people are fed up with a few individuals who make all the decisions for them. The idea of joint participation comes from the participative aspect of this leadership style which encourages positive dialog and multiple view points to achieve greater efficiency levels. Participative decision making (PDM) has a variety of benefits which include: increasing the quality of decision making (e.g., Sally, Kirkpatrick and Locke, 1995) to positively contribute to an employee work quality (e.g., Stomech, 2002) and to increase an employees’s work commitment, work motivation, job satisfaction (e.g., Locke and Latham, 1990)(e.g. Armenakis,Harris, and Mossholder, 1993; Yammarino and Newton, 1992)(Smylie, Lasarus and Brownlee-Conyers, 1996)(Somech, Dec 2003). Democratic leaders have a “checks and balances” work environment which keeps them honest and accountable to their subordinates. Workers are able to display their dissatisfaction if they believe they are ultimately being treated or have a complaint concerning another worker. This style of leadership is associated with a positive individual perception which promotes a feeling of teamwork. It needs to be noted that the positive perception is mostly based on a western management standpoint which shows that it’s not a global viewpoint. Someone in another country might have different viewpoints that could
- 7. 7 arise from a number of variables. So why is democratic/participative leadership viewed through a positive lens? It has to do more with a defined behavioral reaction than a position of power. A participative leader let’s his or her actions do the talking. In other words, they walk the walk if they talk the talk. Leadership is behavior, not position (Bass, 1990) and this is very true of democratic leadership (Gastil, Aug 1994). All of these views are also based on many research samples and real world reviews which prove that it enhances the mental well being of employees (Soonhee, March/April 2002). So we can see that democratic leadership represents the other extreme in relation to an autocratic style. Now let’s look at laissez-faire or (non-leadership) approach. This method is originally part of transformational but for my model I have used it as one of the main styles in this example. Laissez-faire leadership consists of several types of non- leadership which includes: avoiding responsibility, not responding to problems, being absent when needed, failing to show up, resisting expressing views, and delaying responses which represent its core continuum (Hinkin, 2008). It seems like this would be associated with a negative perception but this is not the case with everybody. Sometimes workers are self starters and work better on their own so I’ve associated this leadership style with a “one man” perception since it’s based on an individual’s preference. Laissez-faire may involve a little bit of leadership but it remains minimal so this may not work well for employees who need constant attention to complete their tasks. Unlike authoritarian/autocratic this leadership does not appear to be motivated and intentional; it simply involves little or no contact with a leader’s subordinates (Hinkin, 2008). This form of leadership is used in industries where situations of uncertainty present themselves in a variety of ways. One logical example is in a hospital setting where doctors and nurses have to make split second decisions because they don’t always have enough time to debate the possible rewards and consequences for their decisions. The results show that
- 8. 8 laissez-faire leadership is favorable in a hospital setting where physicians have to make quick decisions (Xirasagar, 2008). In other words, the concept of self regulation can be very valuable when you are dealing with life and death decisions where time is of the essence. Another area where this leadership shines is in government where decisions have to be made for the masses. There are so many opinions regarding government decisions and the president may have to declare war or make tough decisions based on his or her personal beliefs. It’s clear that this leadership isn’t reserved for the masses. To say, that this leadership is mostly associated with unclear results is not giving this style the credit it deserves. For my model I’m using this style as an opposite alternative to the other three for a different path to follow which allows a worker to be more self-sufficient. It is also possible for a positive leadership style like passive to become destructive if leaders fail to act in line with clear expectations that need to be carried out (Hoel, Glaso, Hetland, Cooper, and Einarsen, 2010). The fourth style that I chose is a style that I developed based on half autocratic and half democratic which I call audecratic. I developed this style because in a perfect world there is hardly any leadership style that doesn’t have a mixture or is totally 100% pure autocratic or democratic respectively. This style of leadership has a neutral perspective associated with its foundations. My neutral assumption is based on the fact that both styles could potentially even each other out if a decision becomes too far left or too far right and a middle ground is desired. For this style, I’m pointing out that a work environment will have a wide range of employee personalities and that one style may not be the best solution for some firms or industries they operate in. Employee emotions were strongly associated with the quality of leader follower relationship perceived (Hoel, Glaso, Hetland, Cooper and Einarsen, 2010). This leadership style allows leaders to have another option while allowing an integration of two unique styles. We will assume that autocratic is still under a negative perception and
- 9. 9 democratic is under a positive perception but it allows for leader flexibility when tough decisions have to be made. This is only one of my own personal improvements to build a better mouse trap through my leadership model. The other factor that I want to mention before talking about the critical follower outcomes involves government or other outside influences that act as a wild card outcome. My leadership model is based on certain variables and styles that follow a set amount of characteristics and principles. However, we have seen in the last five or six years that governments have gotten into certain economic affairs which has changed the logic and rules of the game. If I were making this model before 2008, I probably wouldn’t include this situational variable in my model but I think it’s relevant to mention given the outcomes that have occurred over the last few years. When you look at any leadership model, we would be naïve to think that everything would happen 100% according to our model and routes within it. That’s why I put explosion signs throughout my model because it allows for outside influences to change the actual result if model defaults are ignored for self serving agencies or bureaucracies like the federal government. “People across the country are angry and frustrated, as they should, that this economy, the United States of America, got into a position where enormous damage has been done as a consequence of long period of excess risk taking without meaningful adult supervision” (Poole, Nov/Dec 2009). The bailouts are a good example which affected many different critical follower outcomes especially in the banking industry alone. Leadership Model Heart Explained
- 10. 10 Now let’s discuss the critical follower outcome ranges for each style. The first critical follower outcome deals with motivation and we are using transformational theory as a reference for clarity involving this range. The first outcome is active/passive transactional and this is associated with an autocratic style. When you talk about autocratic leader, they aren’t very good at people skills and both active/passive transactional deal with the negative side of transformational leadership. Active transactional is correcting someone on the spot for not following expected norms and passive transactional is correcting someone after the fact with reviews which autocratic leaders are likely to do. This is very de-motivating for a leader’s workers over all. The next outcome deals with audecratic leadership which is a balance of perception influence. If you have both styles being used by the leader then the outcome will be based on which style he or she uses more thoroughly over the long run. One of the many challenges with theories on transformational leadership, is that they are strong on the characteristics needed but not as clear on the actual skills needed to change and transform organizations (Warrick, Dec 2011). The outcome associated with democratic is positive transformational since it will motivate a worker at the highest level for significant improvement. The laissez-faire outcome is self motivation since it deals with an individual’s desire to perform or not perform. They may also assess the extent to which the external environment facilitates the level of acceptance of transformational leadership (Beugre, William A., and William B., 2006). The next critical follower outcome deals with trust and we are using LMX theory as our reference point. The first outcome deals with autocratic and it is the out-group element. When you think of an autocratic situation, you think of employees who have less than positive experiences with their leaders because their interests are based on self-promotion. If an employee tells them something in confidence, then they will most likely use it against them at some point.
- 11. 11 Therefore, the trust level is one of a formal relationship and the employee is looking out for his or her self interests. The workers in the out-group are most likely out of the trust circle which is based on formality (Dae-Seok and Stewart, 2007). The outcome for the audecratic style is a balance of perception influence. It mainly depends if the employee gets a majority of the in- group tasks or the out-group tasks from the leader in charge. The outcome associated with democratic style is the in-group phenomenon. Basically, it’s the opposite of the out-group where trust levels are high and communications levels are minimal. Therefore, a high quality LMX relationship will encourage employees to take on higher job tasks that they normally wouldn’t do (Bernerth, Armenakis, Field, Giles and Walker, 2007). The laissez-faire outcome deals with a one-man group since the group members involve me, myself, and I. The next critical follower outcome deals with personal commitment and it uses LMX theory as its reference point too. The first outcome is associated with an authoritarian leader which is contractual obligations. Employees who work for an autocratic leader aren’t highly committed to him or her personally because workers are a means to an end to move up the corporate leader. Therefore, it is logical to assume that employees will do just enough to keep their jobs in order to avoid getting canned. This is also an important variable in the leader-member exchange theory because it verifies the relationship level that has been achieved and what needs to be done to improve it. The LMX theory of leadership focuses on the degree of emotional support and the exchange level achievement bar (Dae-Song and Stewart, 2007). The outcome associated with audecratic leadership is reciprocal negotiation which is a positioning strategy to see how far a manager will support his or her employees. As a result, the worker will give or reciprocate the same level that is received. The outcome associated with passive involves role expansion. Supervisors assign work roles based on the degree to which a relationship is either positive or negative. The laissez-
- 12. 12 faire outcome involves self-interest commitment and this involves a one track mind result. A fourth critical follower outcome has to do with employee confidence and uses situational leadership as its reference point. Our first outcome is connected with autocratic leadership which is the telling phase. The telling phase involves people who are given specific task directions and people who are closely supervised (Hersey, Blanchard, and Natemeyer, Dec 1979). This is a high task, low relationship style that includes low employee feedback and a direct authority approach that leads to autocratic leadership which is known for low employee confidence levels. This reality happens because autocratic ideology is one-sided and doesn’t involve constructive input from either party. The outcome for audecratic leadership involves selling for the low end and participating for the high end. On the lower end of audecratic there is still no delegation but there is still some coaching going on which leads to the beginning of a confidence relationship that is established. On the upper end of audecratic there is a participative action because the leader is starting to loosen the reins and lets workers participate which boosts their confidence levels further. The outcome for democratic leadership is a delegating action which allows group members to take full responsibility for their actions and their confidence levels will be at their highest. The key to situational leadership is to accurately access the maturity level of the follower which has a correlation with leader confidence in each individual worker (Hersey, Blanchard, and Natemeyer, Dec 1979). The laissez-faire outcome is individual confidence since it is based on the individual’s ability level. Our next critical follower outcome has to do with employee empowerment and it uses the contingency theory as a point of reference. The first possibility that deals with autocratic leadership is Low LPC task oriented which signifies a low level of personal empowerment. Employees are likely to rate an autocratic leader low on the LPC scale because these leaders aren’t very people oriented. Autocratic leaders are more task-oriented
- 13. 13 since they rate personal relationships low on their to-do list. The basic thesis is that the relationship between the leader’s score on the LPC scale and group performance is contingent upon the work environment situation involved (Rice, Jan 1978). Thus little empowerment is received from the leader. The outcome for audecratic involves middle LPC enabling with caution because these leaders are willing to empower certain employees but will do so with caution. These leaders won’t judge until they’ve had a chance to evaluate their worker outputs and will choose empowerment levels accordingly. Most research has simply identified two groups: high and low LPC persons, but new datum suggest that middle LPC persons should be discussed in a third separate group altogether (Rice, Jan 1978). The outcome for democratic is a high LPC human relations oriented outcome. These leaders are high on personal relationships and are willing to give total empowerment to workers who have earned it. The laissez-faire outcome has to do with self- empowerment because the leader has little or no contact with the employee regarding productivity outputs on any level. Our sixth critical follower outcome involves employee job satisfaction and uses path-goal theory as its reference point. Our first outcome that is associated with authoritarian leadership involves subordinate preference employee pawns. I chose the subordinate preference component because it relates to how an employee will perceive a particular leadership style. Employees will associate an autocratic leadership style as being stressful and unsatisfying because it’s all about the leader’s needs and not their own. The employees are pawns on a chest-board and will be sacrificed or over-worked to protect the leader’s goal levels. The outcome for audecratic leadership involves subordinate preference employee expectations which can be satisfying/unsatisfying or stressful/non-stressful depending on the levels of worker inputs to outputs. In other words do the rewards equal the effort level needed and are the workers expectations levels met by the leader. Although structure was
- 14. 14 positively related to worker satisfaction, the real strength was seen through the paths of intervening variables associated with these styles (Sims and Szilagyi, 1975). Our next outcome deals with democratic and is subordinate preference employee equality. This is logical because when employees are treated as equals by their leaders, then their job satisfaction levels will be at their highest levels. Under conditions of high ambiguity, where roles are ill defined, leader initiating structure is perceived to be instrumental toward role clarification which leads to higher satisfaction levels (Sims and Szilagyi, 1975). The laissez-faire outcome is self sufficiency which is true because employees have to rely on themselves individually. The next critical follower outcome deals with performance/productivity and uses authentic leadership as a reference point. The first outcome of negative psychological capital has a connection with autocratic leadership. Authoritarian leaders want their workers to be productive but they do it through fear and intimidation which leads to low psychological capital. This will definitely affect their performance levels with varying degrees of negative reinforcement and that’s why an authentic leadership environment is important for higher output levels through personal self improvement and a leaders self awareness. Luthans and Avolio (2003) argued that self efficacy, hope optimisms, and resilience (positive psychological capital) is important to a leaders individual self awareness level through continued improvement (Harvey, Martinko, and Gardner, 2006). The outcome associated with audecratic is developing work ethic because it depends on which side of audecratic is being used more which will ultimately affect worker performance/productivity levels. This will depend on how their work ethic is shaped through leadership elements displayed in the relationship. The outcome associated with democratic is obviously positive psychological capital because an employee’s confidence, optimism, hope and resilience levels have been increased through heightened leader/follower interactions which increases overall
- 15. 15 efficiency/performance levels. They assert that people with higher levels of positive psychological capital are more likely to see themselves in a more favorable light (Harvey, Martinko and Gardiner, 2006). The laissez-faire outcome of self-employed is logical because it depends on an individual’s output level with no guidance from anyone. The next critical follower outcome involves creativity/innovation and uses transformational leadership as a reference point. The first possibility associated with autocratic leadership is low intellectual stimulation. Intellectual stimulation involves leaders who encourage creativity and innovation by challenging normal group views and beliefs but we know that autocratic leaders do neither. They are happy with the status quo and want groups to stick to what’s expected which is creativity/innovation based on fear and firing threats. They expect creativity instead of inspiring it and can come down hard on anyone whose output is less than perfect. The outcome for audecratic is contingent reward effort because there is just enough autocratic influence to push workers to be creative for their own job survival but the rewards have to be there for them to put forth the necessary effort to achieve a certain output expectation level which is more democratic in nature. This is an autocratic/democratic element because the creativity level that is exerted will depend on their job favorability and their interest in the reward offered . The higher transformational relationships will increase creativity which will increase employee innovative levels for the greater good of the firm. Nothing will transform an organization faster and better prepare it for the future than successful skilled transformational teachers (Warrick, Dec 2011). The outcome associated with democratic involves charismatic innovation which involves leadership that gets workers to perform extraordinary things. This is ideal because participative styles allow for a greater creative flexibility range which means nothing is off limits. Thus, workers and leaders can participate in unusual and boisterous exchanges in order to reach the highest levels of creativity.
- 16. 16 The charismatic leader may often engage in unconventional behavior such as flamboyant speech or other behaviors that aren’t considered normal like shared leadership for creative teams (Murphy and Ensher, 2008). The outcome for laissez-faire is consultant artist because these employees will have to act like consultants since there are no leader/employee exchanges. The final critical follower outcome is organizational culture and it uses servant leadership as a reference point. The first outcome is leader servant which is a true follower/leader one sided pie chart because an autocratic leader is only committed to him or herself with no regard for serving anyone. The authoritarian leader is the server and the servee all in one package which represents a pie chart of 100% culture submission. The outcome associated with audecratic involves a biased servant which means the leader could serve himself or his workers depending on which brings the most efficient results. In other words, which style will influence his situation and thinking the most which can be influenced by other managers, the existing culture etc. The behavior of servant leaders can not only influence their followers’ behavior, but other servant leaders which could influence their leadership dispositions (Van Dierendorck, 2011). The outcome associated with democratic is a subordinate servant because true servant leaders serve this culture without authoritarian views which enhances a need to serve others. It’ important to realize that according to Greenleaf, the server of leader subordinates practices “primus interpares” (i.e. first among equals) which involves convincing/persuading rather than using personal power to make people heed your command (Van Dierendorck, 2011). The outcome for laissez-faire is self-servant because it’s like a fast food style where you help yourself. As we look at each leadership style path, we see that each leads to a leader/follower relationship effectiveness level which leads to an overall satisfaction level. Thus, we can conclude that if a leader wants a positive relationship outcome then democratic is preferred. If the leader is unsure,
- 17. 17 then audecratic is the path and if the leader doesn’t care about employee relationships then autocratic is the choice. Finally if you have a leader that doesn’t care about anything then laissez- faire is the answer. Final Thoughts I have developed a model that is simplistic in nature that offers a range of worker outcomes that can be used as indicators for managerial preference decisions. I was careful to use the literature research as a basis for my conclusions and observations while trying to eliminate any personal biases that could enter the equation through personal experiences. My model was developed under a “literature majority” as a basis for my conclusions which creates an ethical and peer-reviewed backing for critical outcome support. The ultimate leadership decision lies in the eye of the beholder. Some in the minority consider autocratic leadership a reliable leader/ follower combination which is why it is important to recognize their view point. Therefore, even if seen as harsh by observers, punishment used by autocratic leaders may still be considered as legitimate by those at the receiving end and their levels of predictability might make them easier to deal or cope with in the long run (Hoel, Glaso, Hetland, Cooper and Einarsen, 2010). It was clear to me when I made this model that I also wanted to include leadership variables that weren’t discussed at length in our SOU’s and I was amazed at the connections between the leadership theories and major managerial styles that connect like an inner spider web of possibilities. I can say now that I truly understand why management is the most researched and the least truly understood concept in business academics. References
- 18. 18 Acar, William, and William Braun. "Transformational Leadership in Organizations: An Environment-Induced Model." International Journal of Manpower 27.1 (2006): 52-62. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 Altemeyer, Bob. "Highly Dominating, Highly Authoritarian Personalities." The Journal of social psychology 144.4 (2004): 421-47. ABI/INFORM Global; ProQuest Education Journals. 22 Feb. 2012 Bernerth, Jeremy B., et al. "Is Personality Associated with Perceptions of LMX? an Empirical Study." Leadership & Organization Development Journal 28.7 (2007): 613-31. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 Casal, Teresa. Authoritarian Leadership Style and Intrinsic Motivation. Kean University, 2002 United States -- New JerseyABI/INFORM Global; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses (PQDT). 22 Feb. 2012 Gastil, John. "A Definition and Illustration of Democratic Leadership." Human Relations 47.8 (1994): 953-. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 Harvey, Paul, Mark J. Martinko, and William L. Gardner. "Promoting Authentic Behavior in Organizations: An Attributional Perspective." Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies 12.3 (2006): 1-11. ABI/INFORM Global; ProQuest Education Journals. 22 Feb. 2012 Hersey, Paul, Kenneth H. Blanchard, and WALTER E. NATEMEYER. "Situational Leadership, Perception, and the Impact of Power." Group & Organization Studies (pre-1986) 4.4 (1979): 418. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012
- 19. 19 Hinkin T, Schriesheim C. An Examination of "Nonleadership": From Laissez-Faire Leadership to Leader Reward Omission and Punishment Omission. Journal Of Applied Psychology [serial online]. November 2008;93(6):1234-1248. Available from: Business Source Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed February 22, 2012. Hoel H, Glasø L, Hetland J, Cooper C, Einarsen S. Leadership Styles as Predictors of Self- reported and Observed Workplace Bullying. British Journal Of Management [serial online]. June 2010;21(2):453-468. Available from: Business Source Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed February 22, 2012. Kim, Soonhee. "Participative Management and Job Satisfaction: Lessons for Management Leadership." Public administration review 62.2 (2002): 231-41. ABI/INFORM Global; ProQuest Education Journals. 22 Feb. 2012 Poole, William. "Moral Hazard: The Long-Lasting Legacy of Bailouts." Financial Analysts Journal 65.6 (2009): 17,23,1. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 Rice, Robert W. "Psychometric Properties of the Esteem for Least Preferrred Coworker (LPC Scale)." Academy of Management.The Academy of Management Review (pre-1986) 3.000001 (1978): 106-. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 . Sims Jr. H, Szilagyi A. Leader Structure and Subordinate Satisfaction for Two Hospital Administrative Levels: A Path Analysis Approach. Journal Of Applied Psychology [serial online]. April 1975;60(2):194-197. Available from: Business Source Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed February 22, 2012.
- 20. 20 Smither, Robert D. "The Return of the Authoritarian Manager." Training 28.11 (1991): 40-. ABI/INFORM Global; ProQuest Education Journals. 22 Feb. 2012 Somech, Anit. "Relationships of Participative Leadership with Relational Demography Variables: A Multi-Level Perspective." Journal of Organizational Behavior 24.8 (2003): 1003-18. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 Stewart, Jim. "Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory of Leadership and HRD." Leadership & Organization Development Journal 28.6 (2007): 531-51. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 Susan Elaine Murphy, Ellen A. Ensher, A qualitative analysis of charismatic leadership in creative teams: The case of television directors, The Leadership Quarterly, Volume 19, Issue 3, June 2008, Pages 335-352, ISSN 1048-9843, 10.1016. 22 Feb. 2012 Van Dierendonck D. Servant Leadership: A Review and Synthesis. Journal Of Management [serial online]. July 2011;37(4):1228-1261. Available from: Business Source Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed February 22, 2012. Warrick, D. D. "The Urgent Need for Skilled Transformational Leaders: Integrating Transformational Leadership and Organization Development." Journal of Leadership, Accountability and Ethics 8.5 (2011): 11-26. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012 Xirasagar, Sudha. "Transformational, Transactional and Laissez-Faire Leadership among Physician Executives." Journal of Health Organization and Management 22.6 (2008): 599- 613. ABI/INFORM Global. 22 Feb. 2012