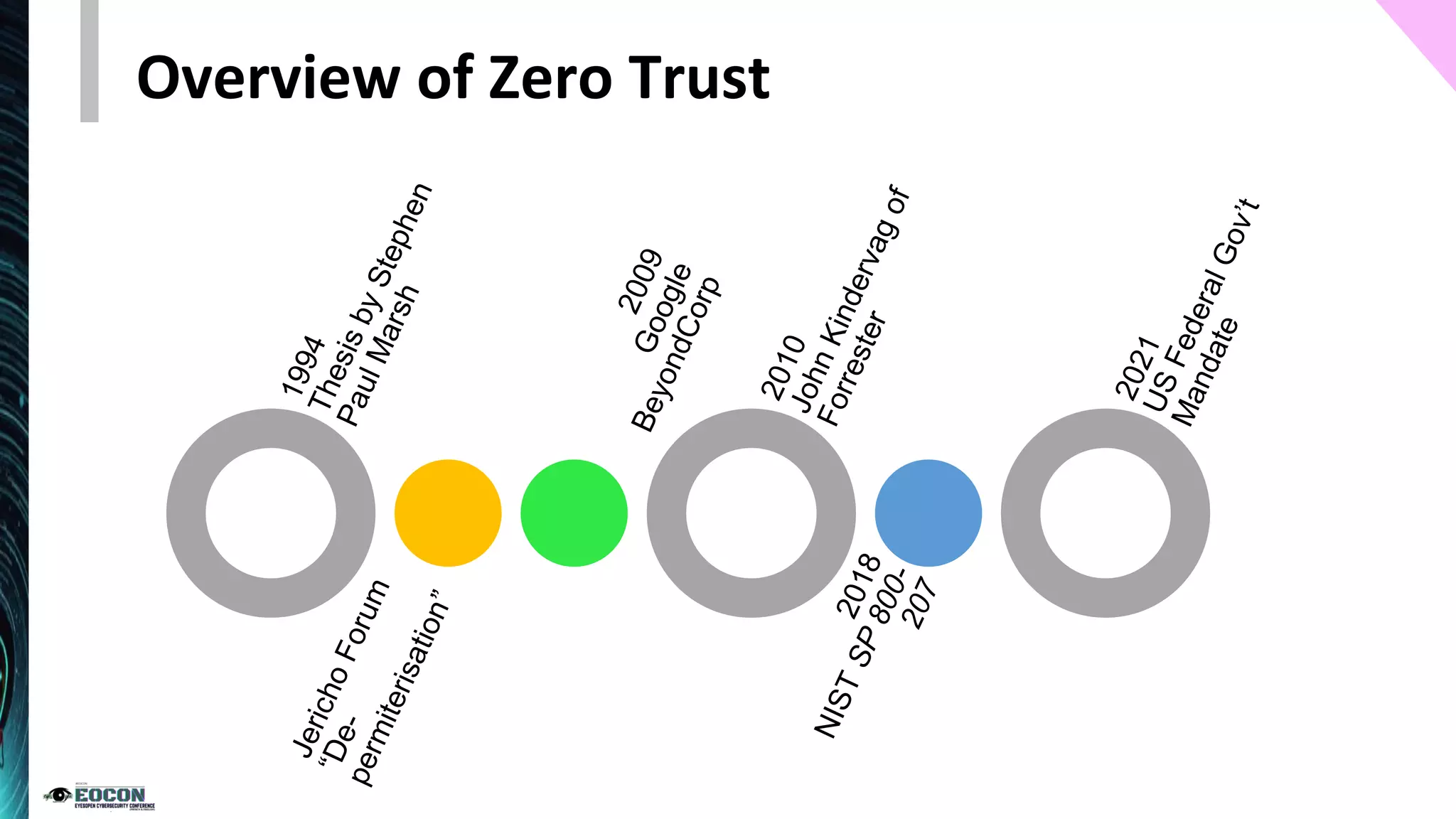
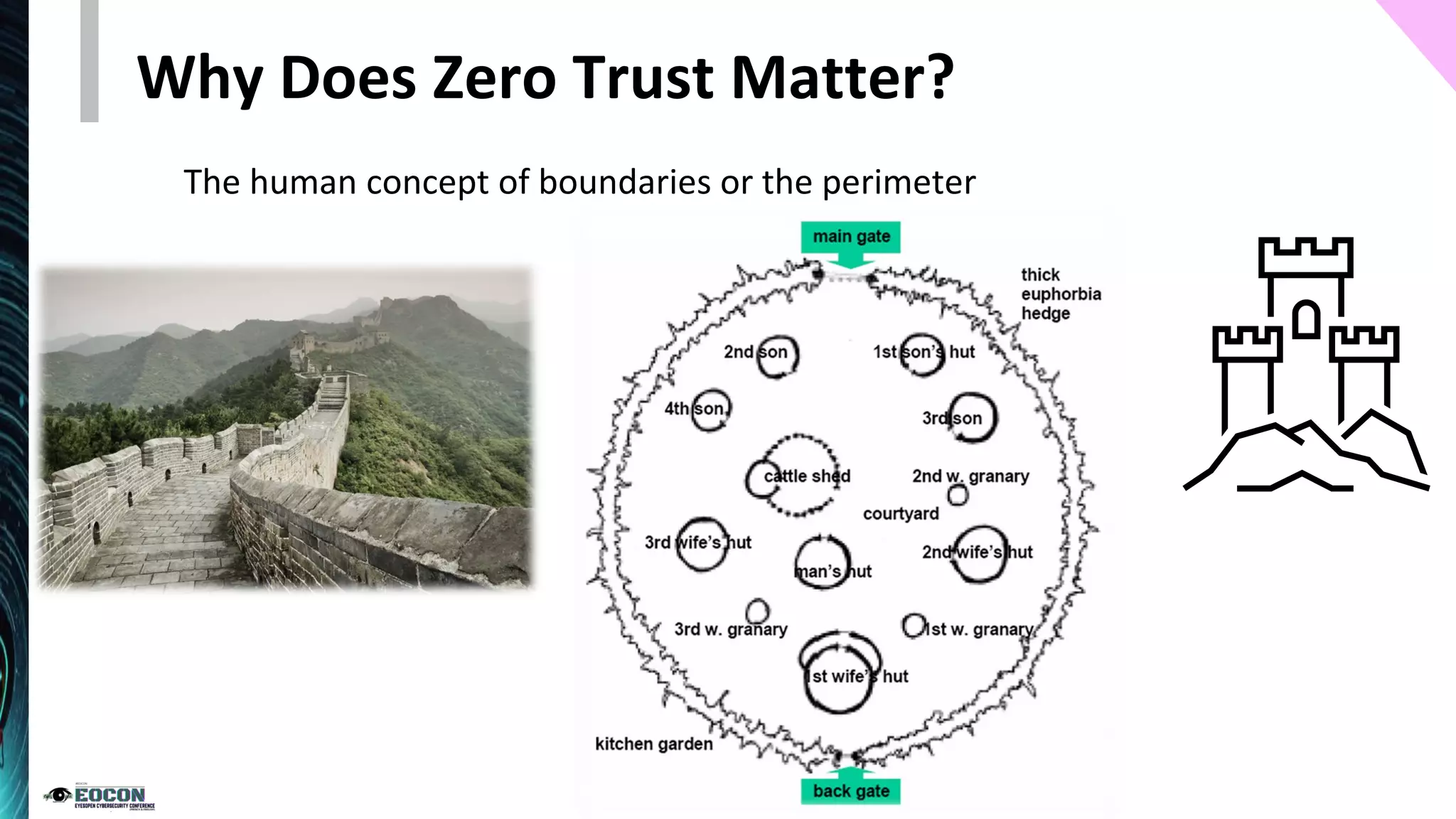
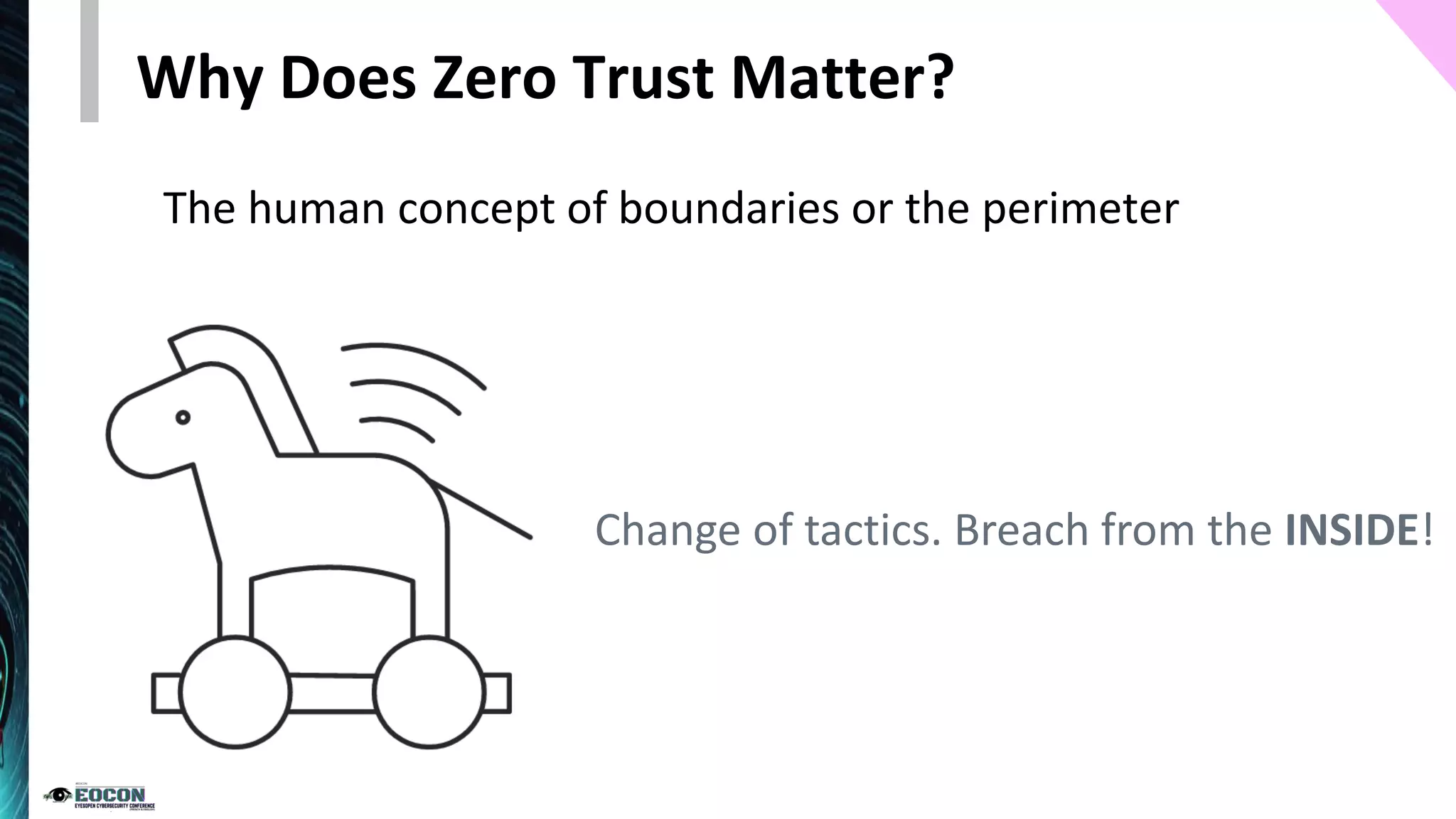
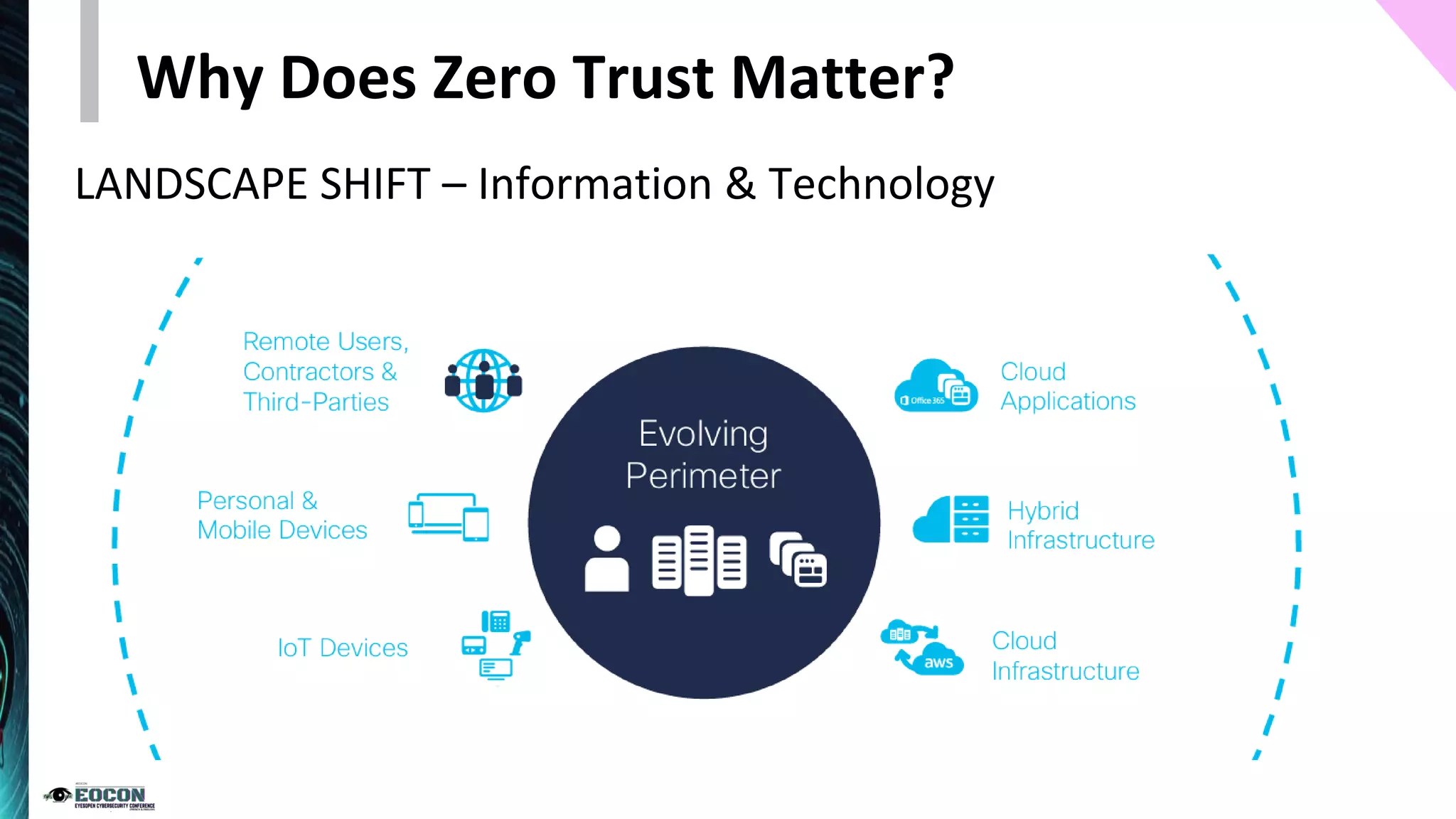
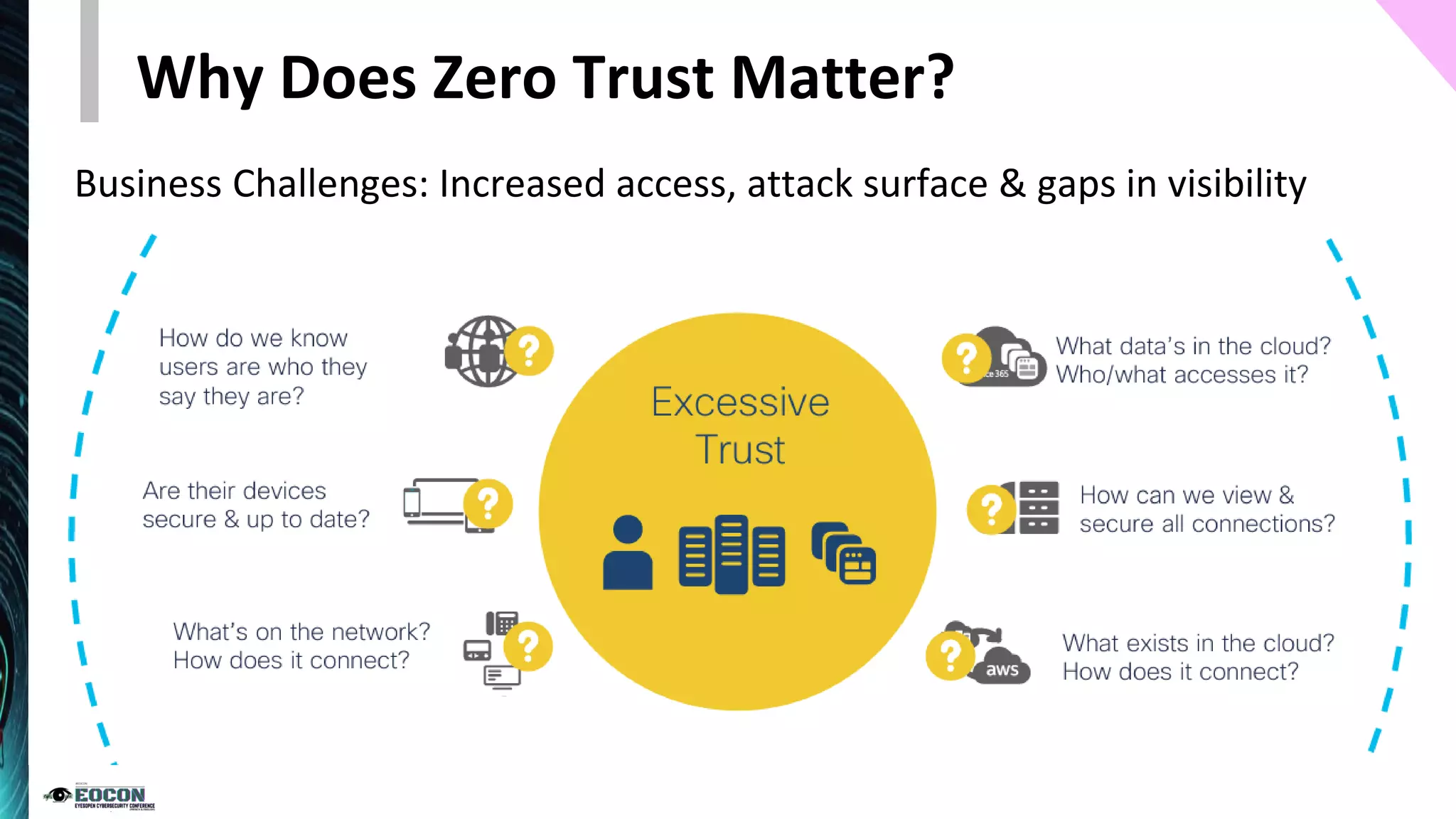
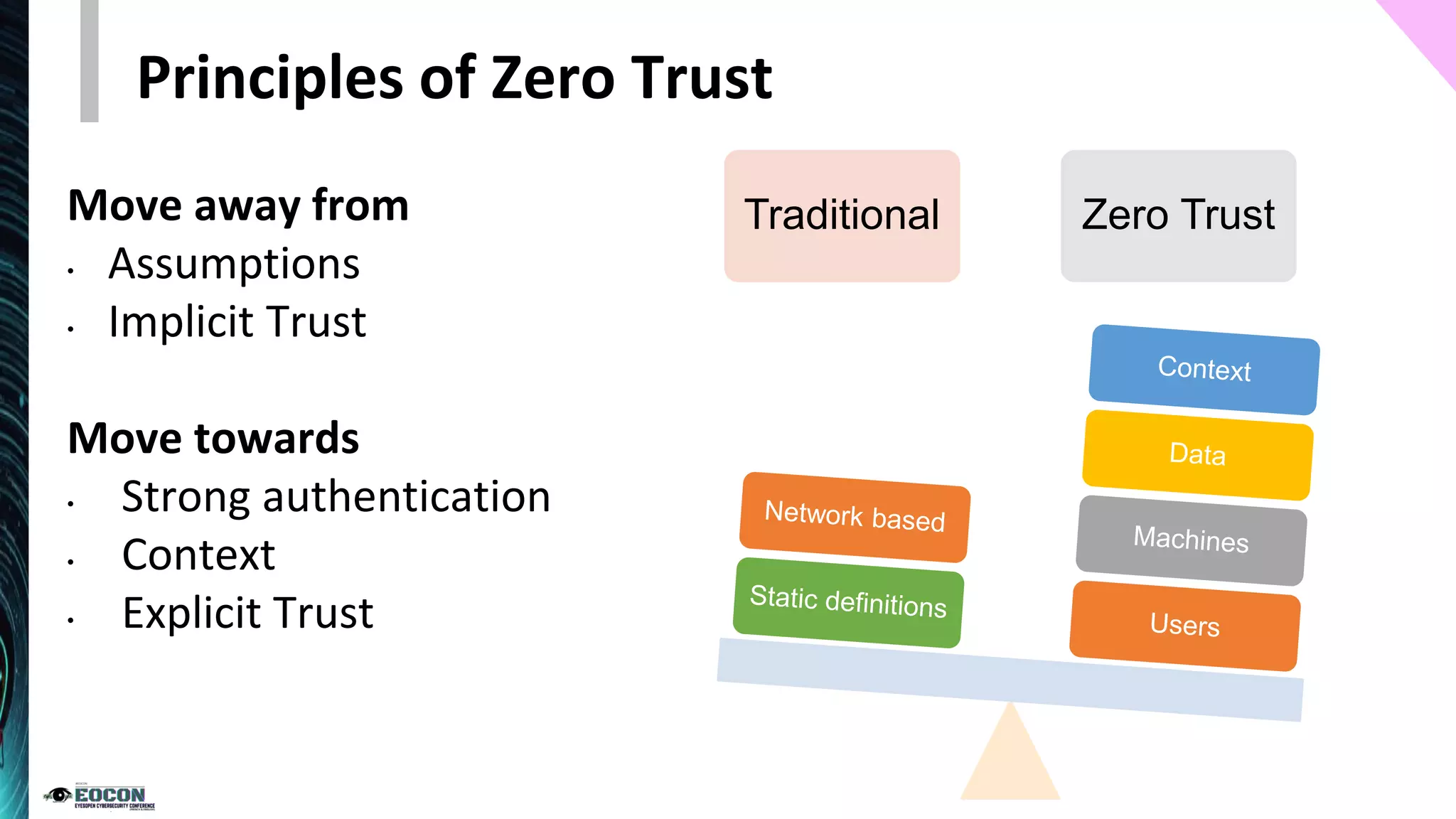
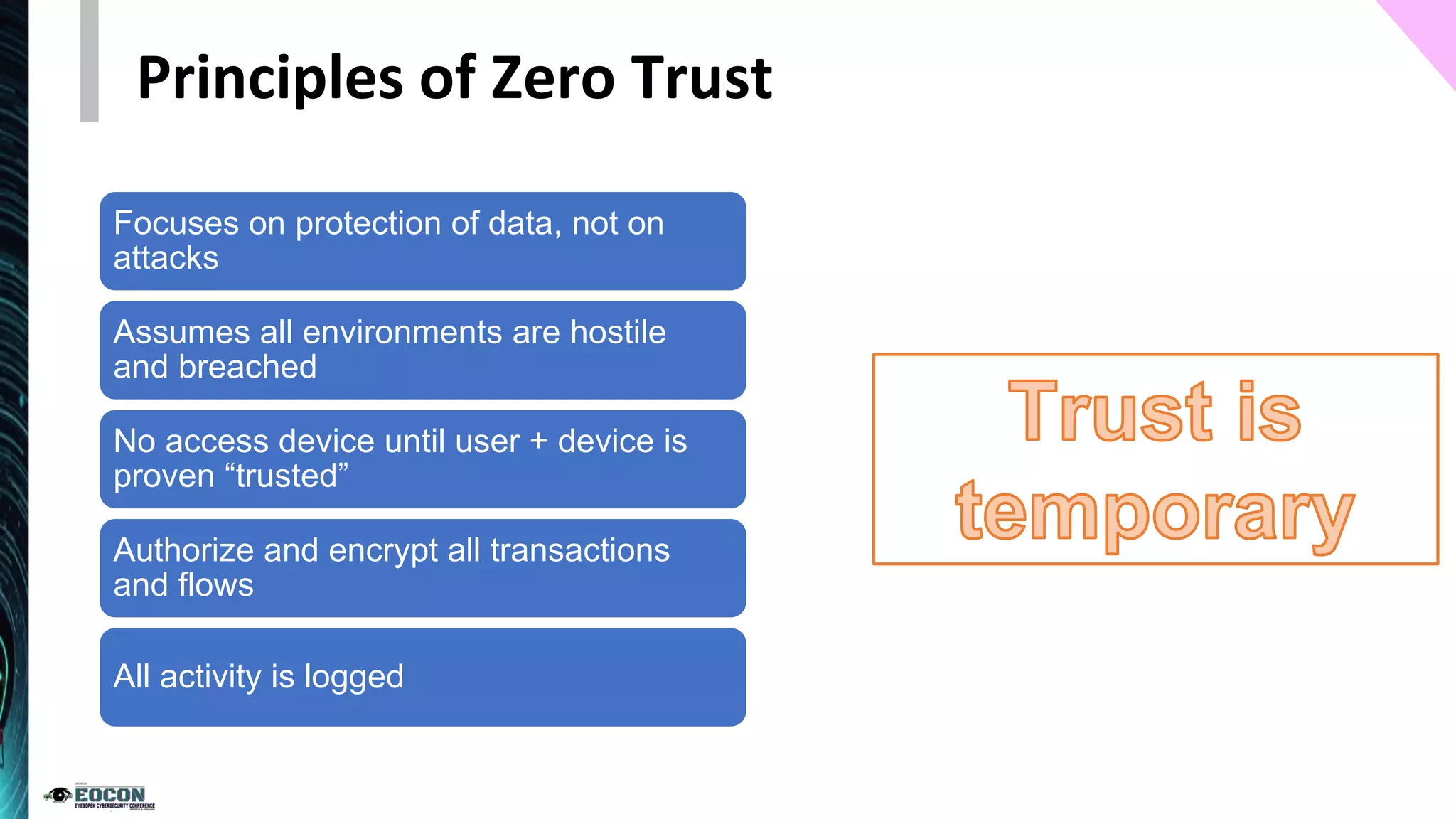
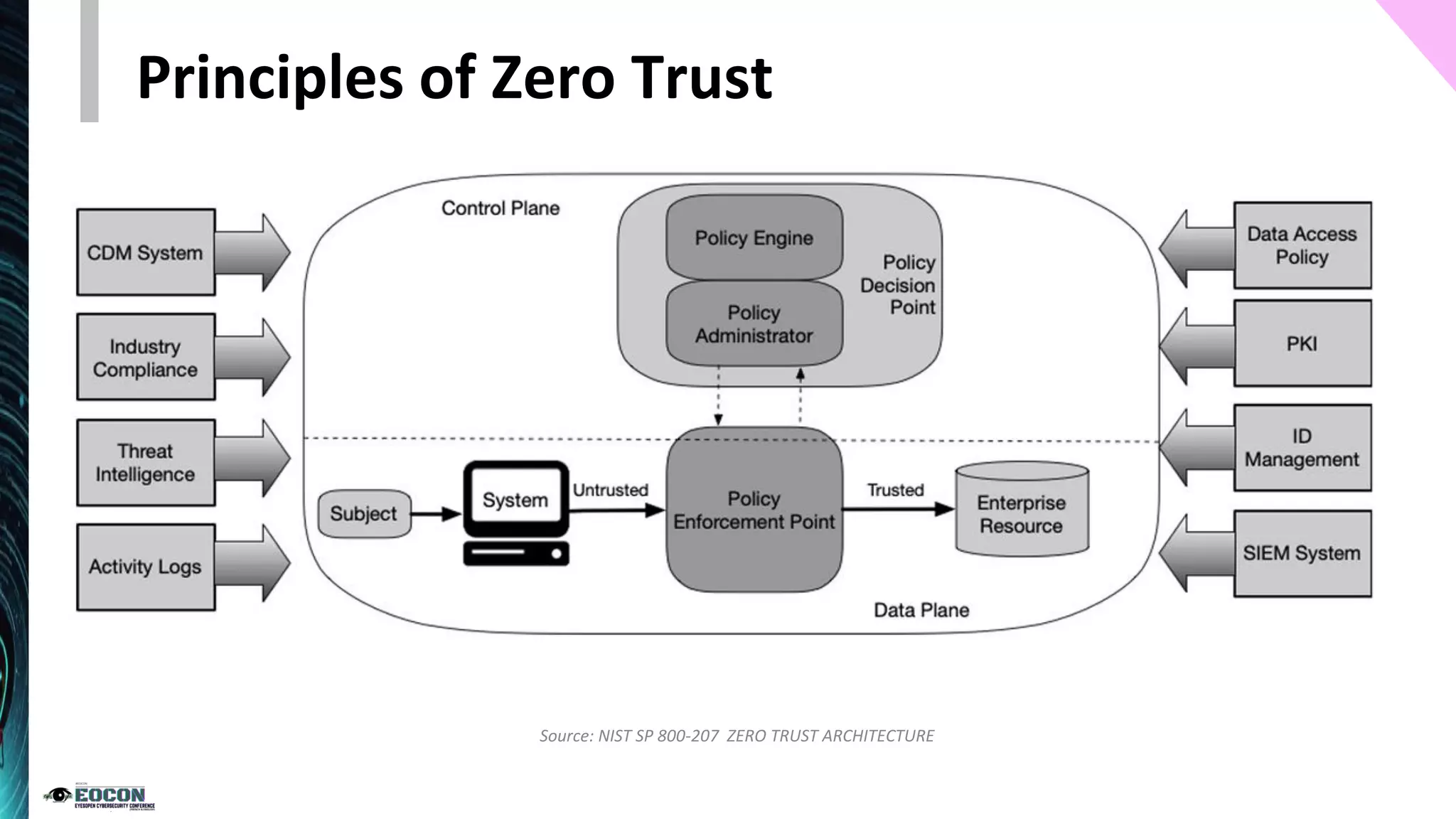
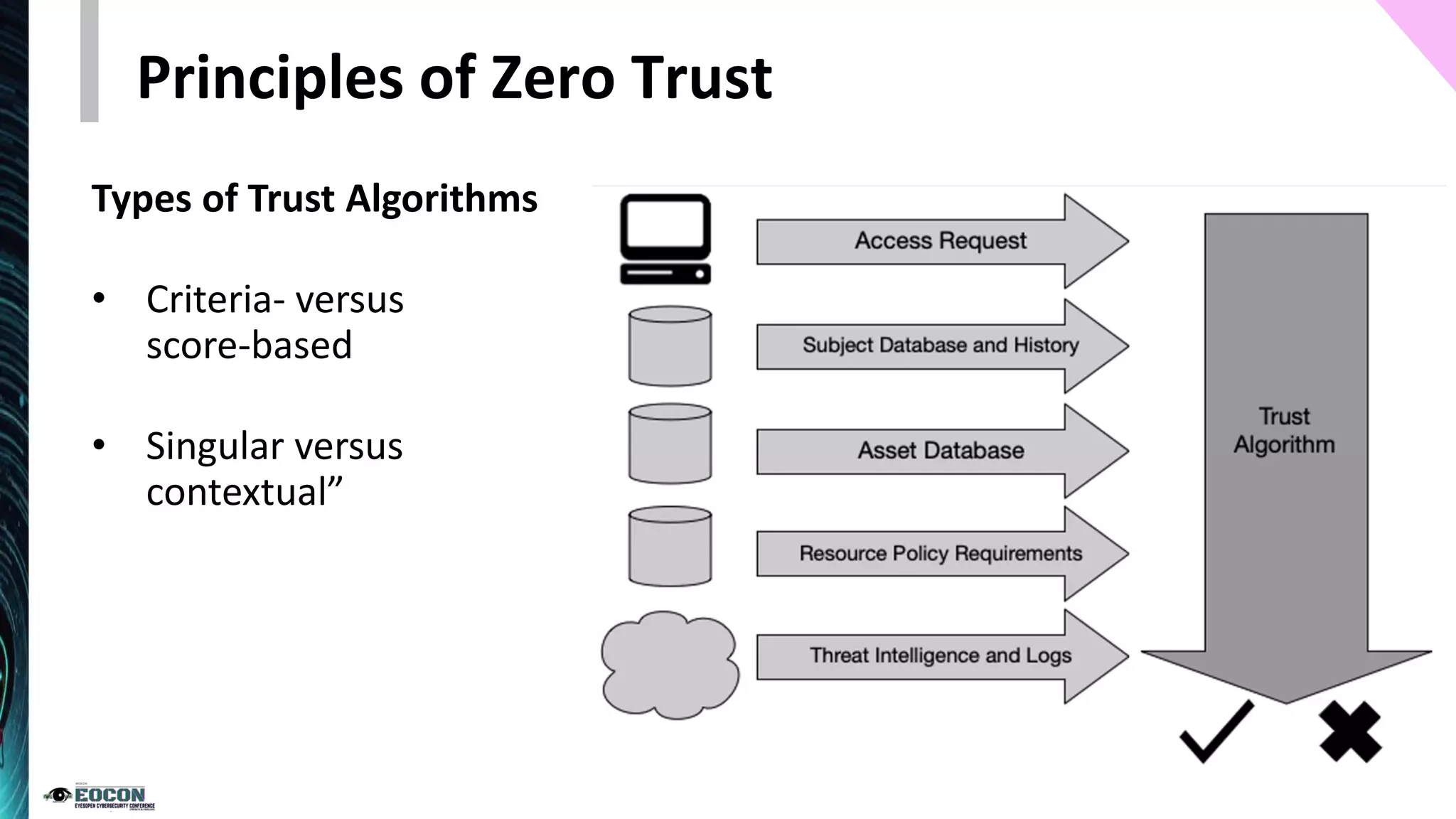
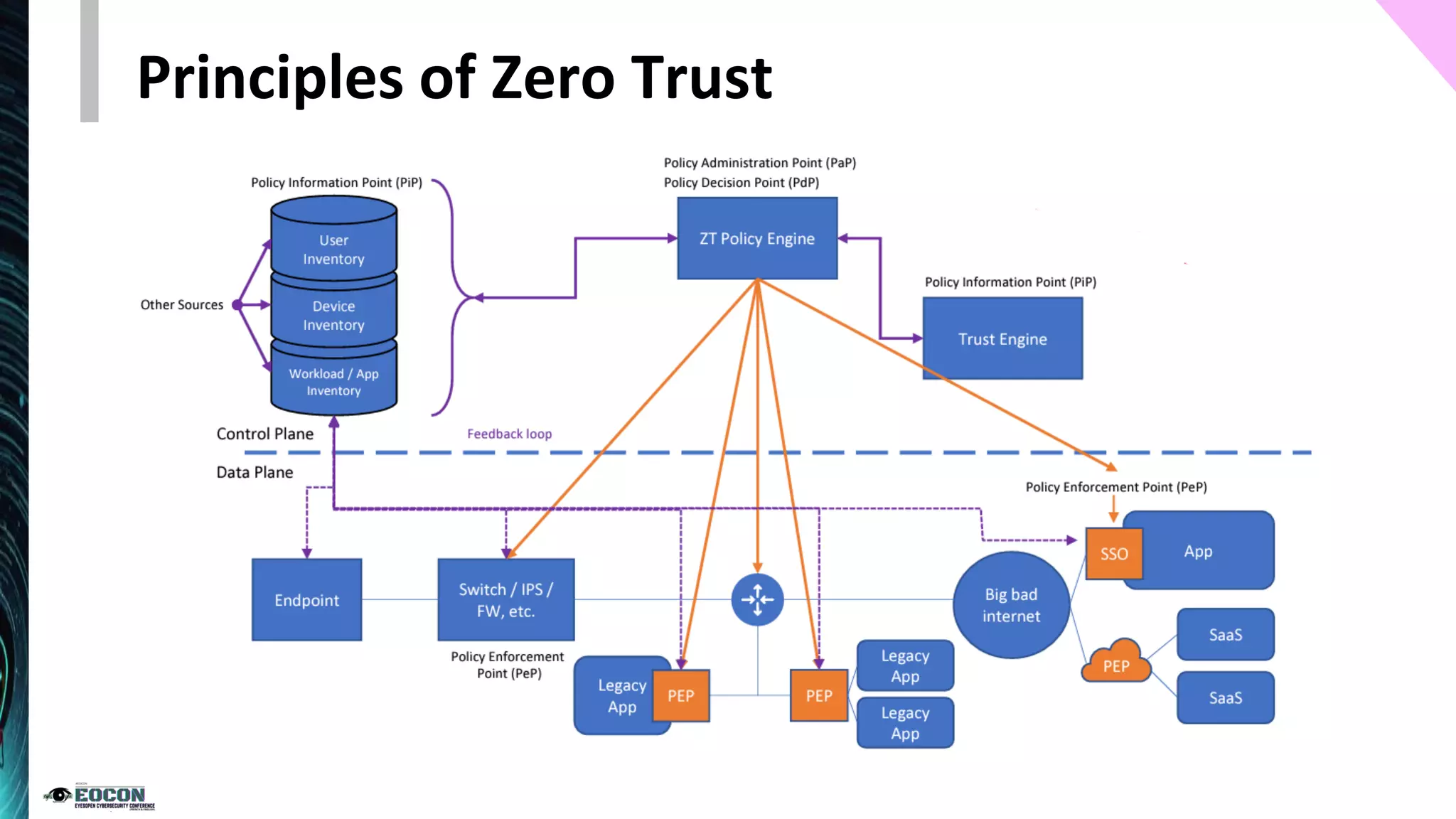
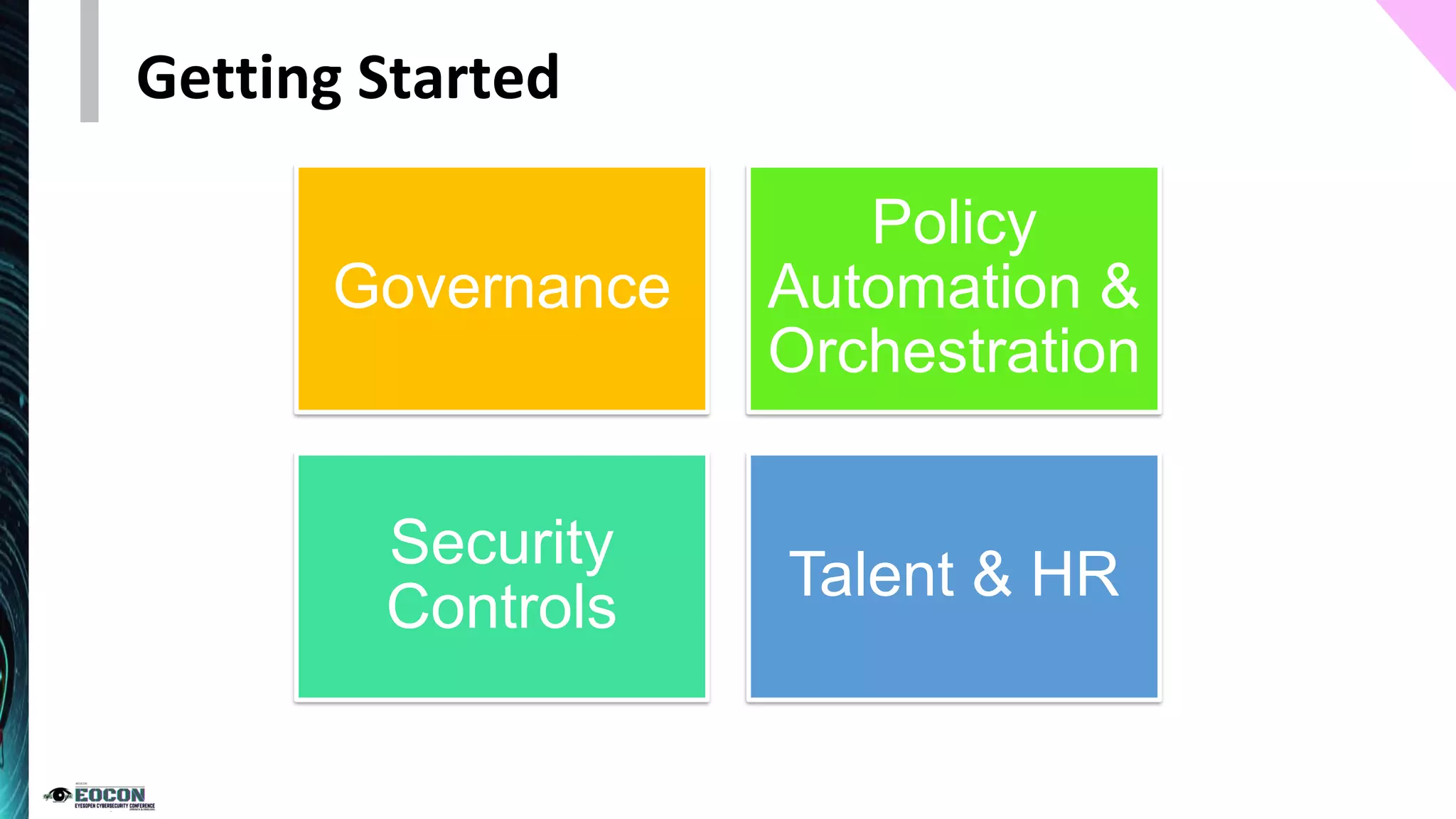
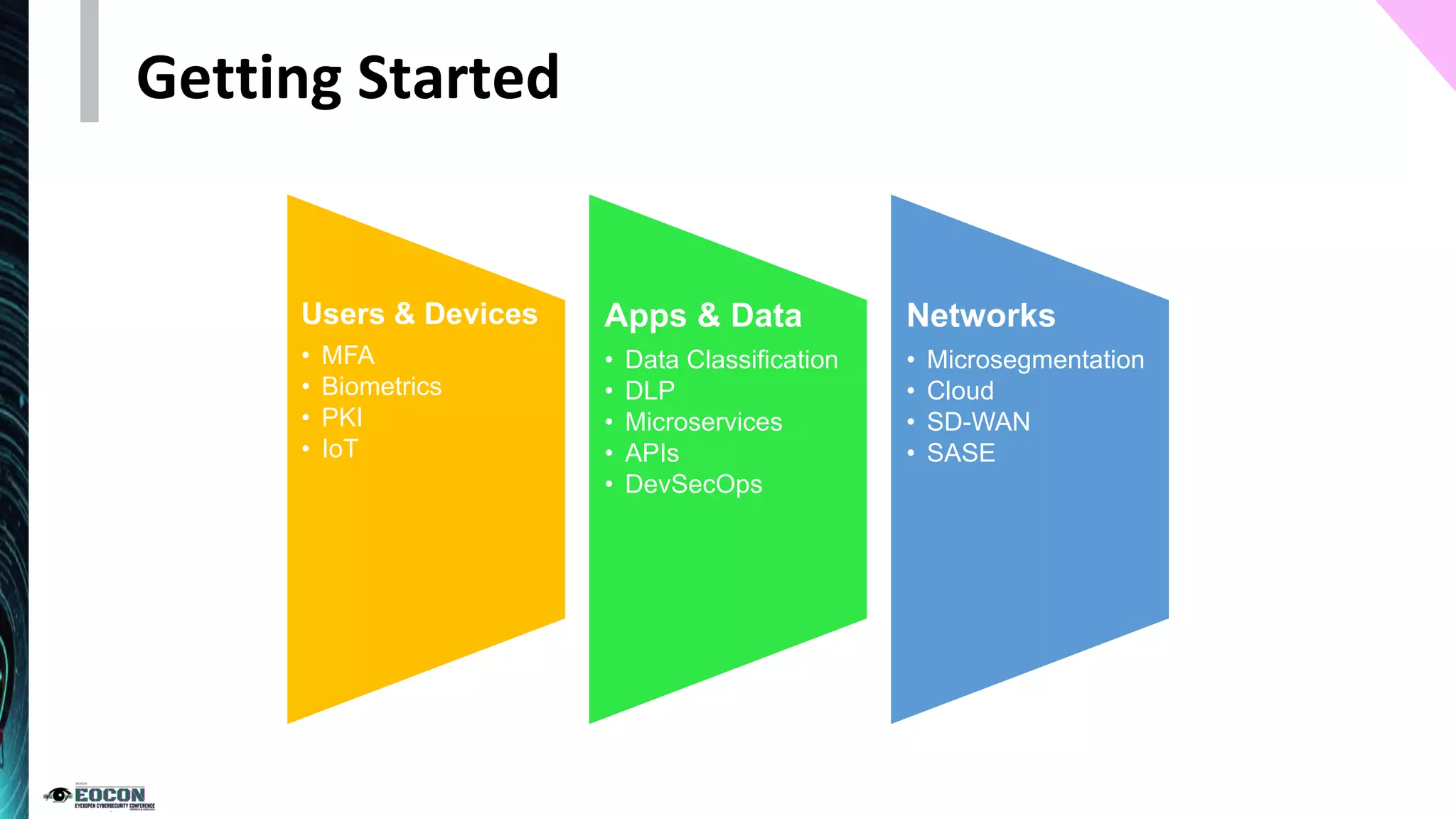
The document provides an overview of the zero trust security model, emphasizing the need for verification and protection in an evolving risk landscape. Key principles include strong authentication, dynamic policy enforcement, and the focus on securing data rather than trusting networks. Getting started involves identifying critical assets, governance, and implementing security controls across users, devices, and networks.