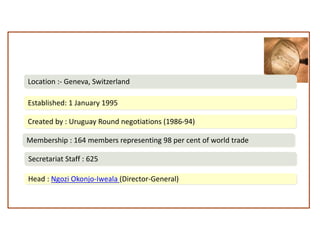
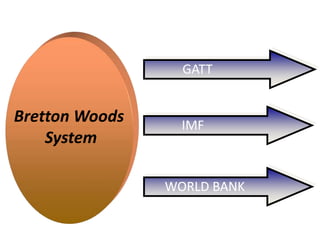
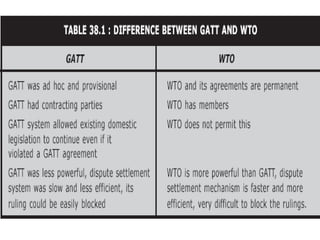
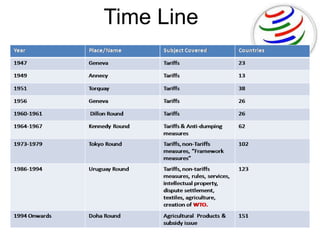
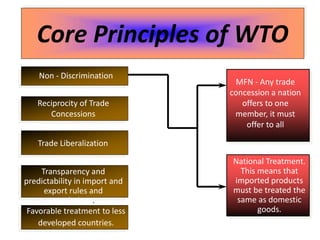
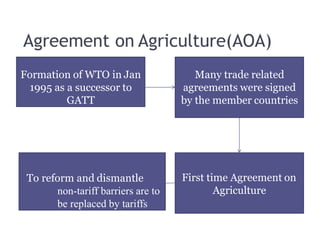
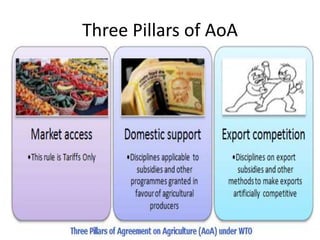
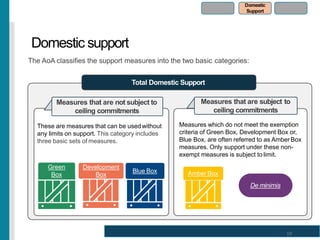
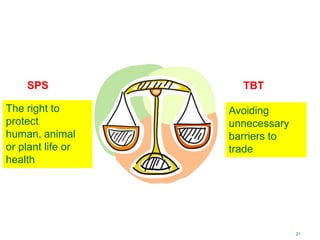
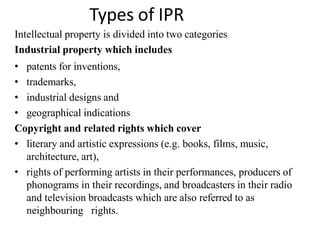
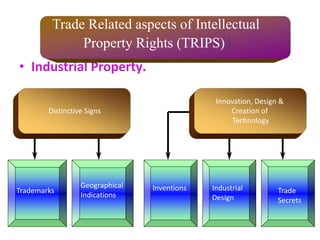
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an international body that regulates global trade rules, aiming to ensure smooth and predictable trade flows among its 164 member countries. Established in 1995, it facilitates negotiations, offers a dispute resolution framework, and promotes trade liberalization while adhering to core principles like non-discrimination and transparency. Key agreements under the WTO include the Agreement on Agriculture, the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS), and regulations on intellectual property rights (TRIPS).