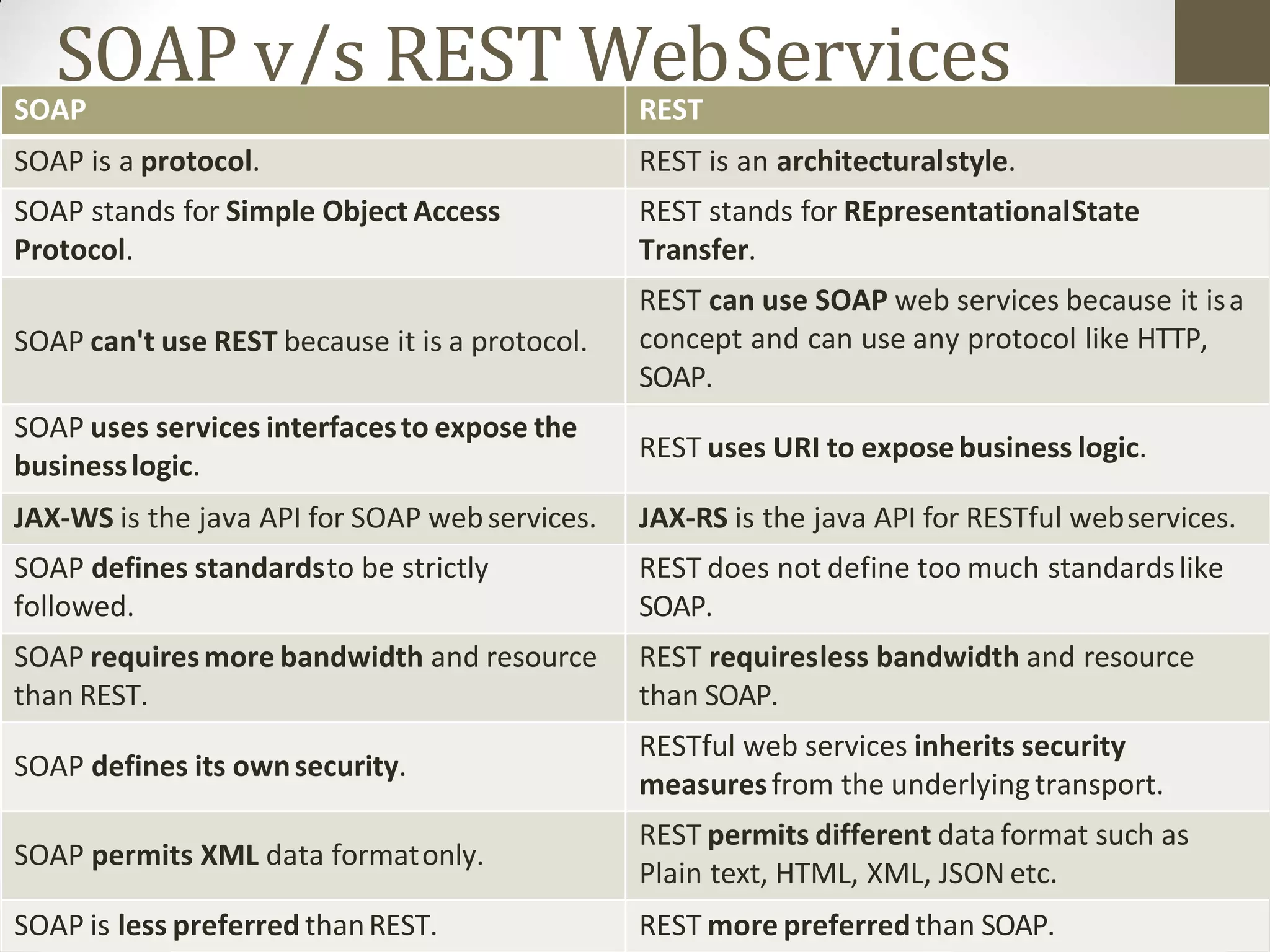
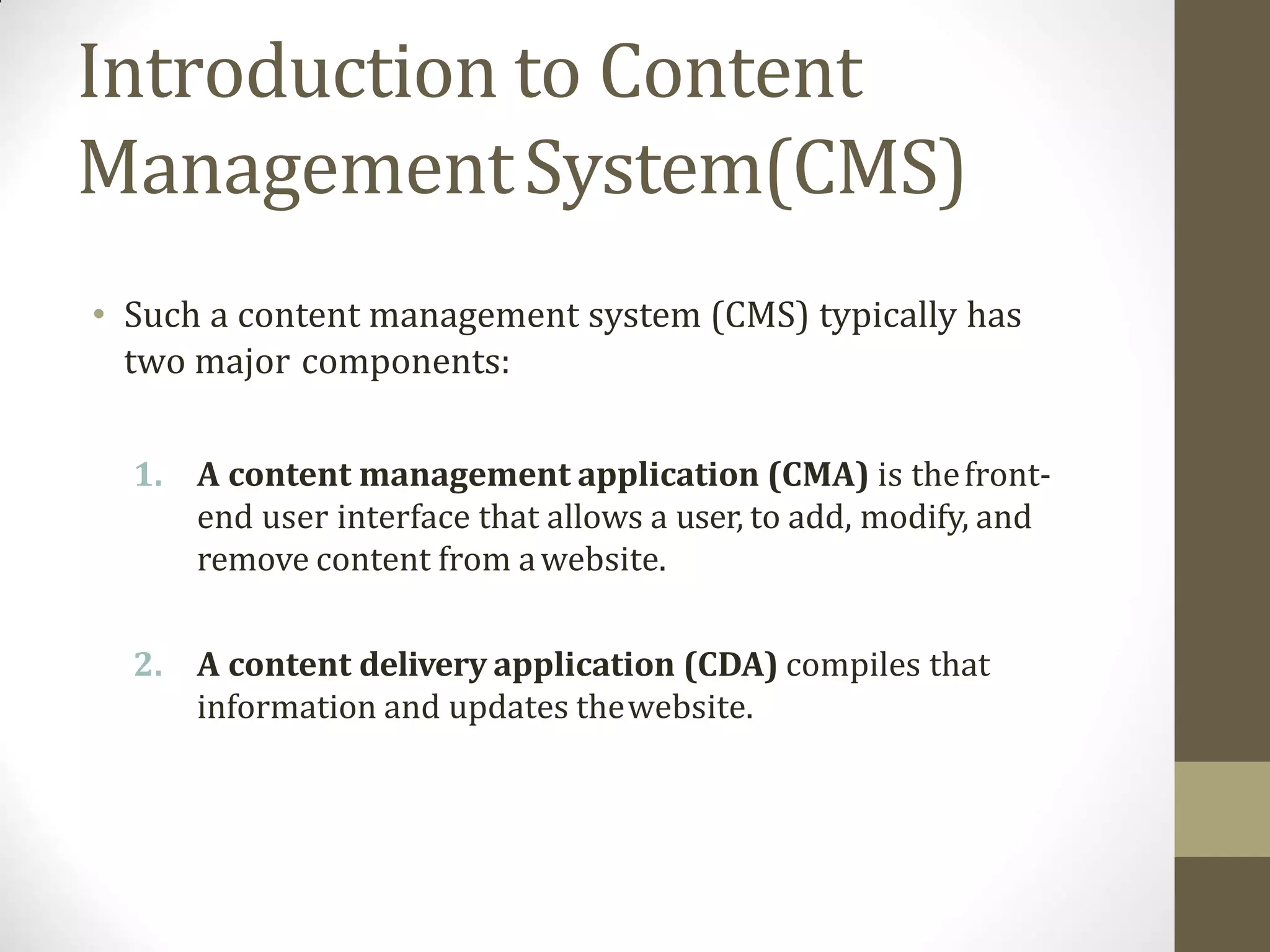
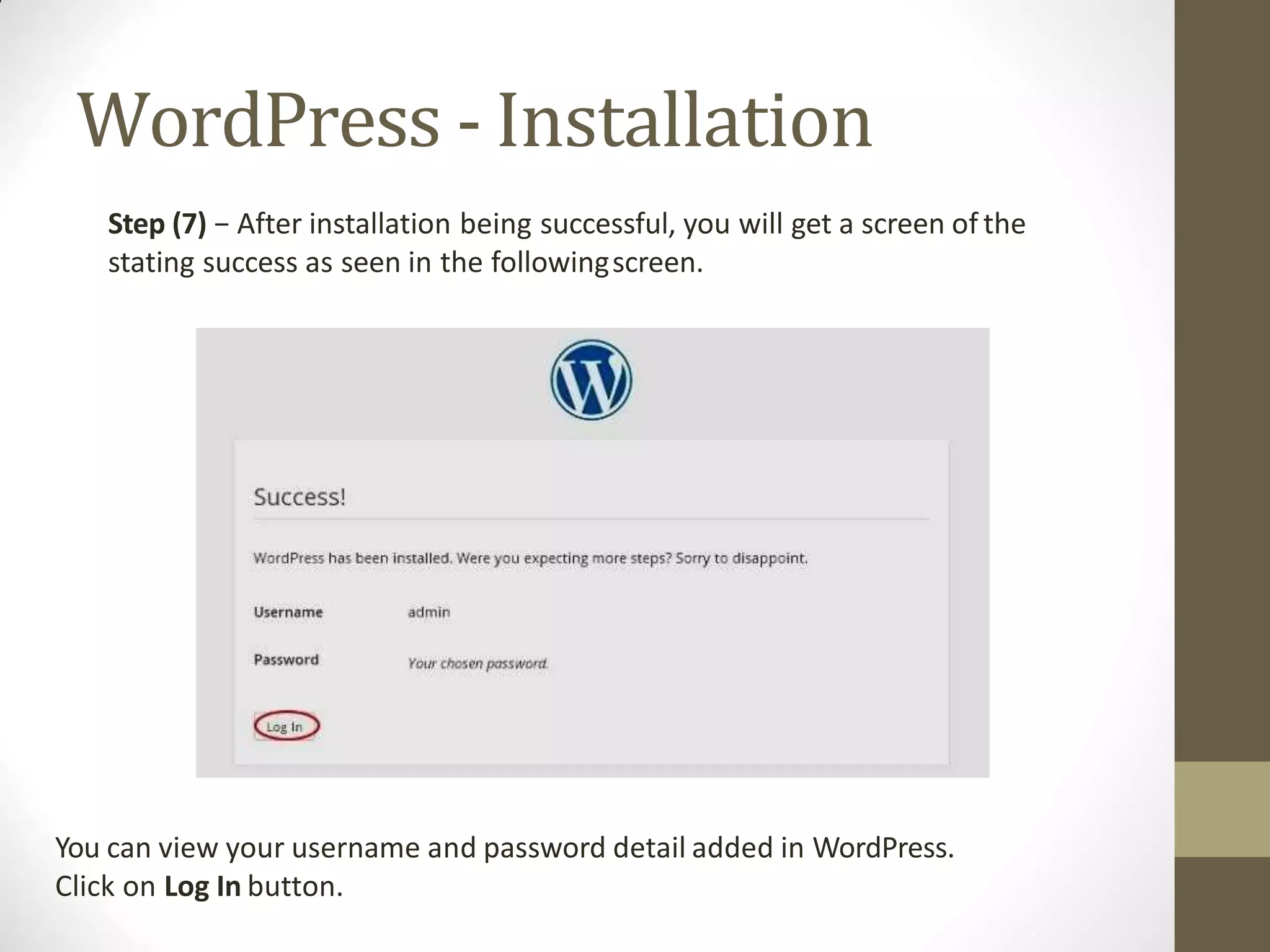
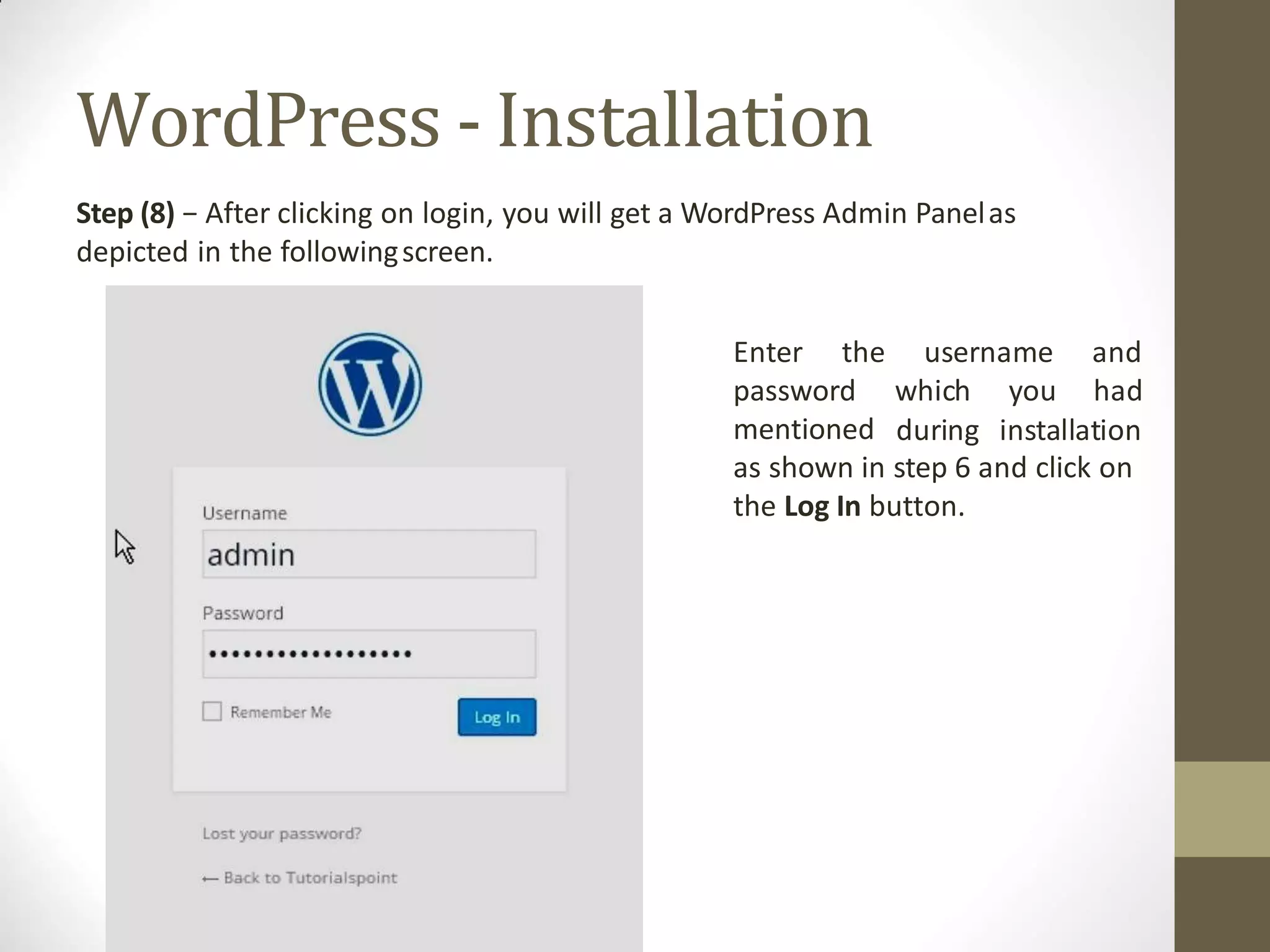
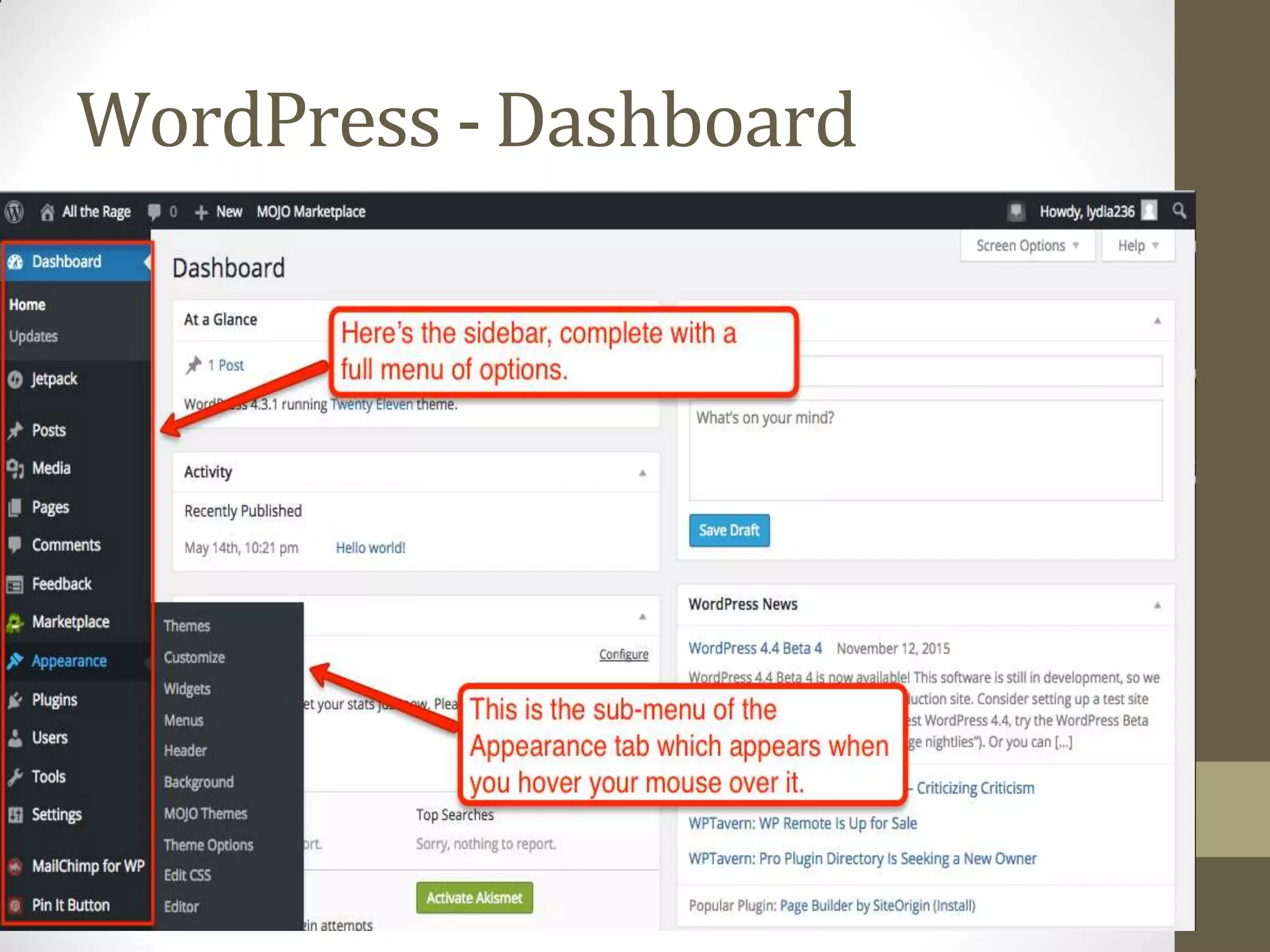
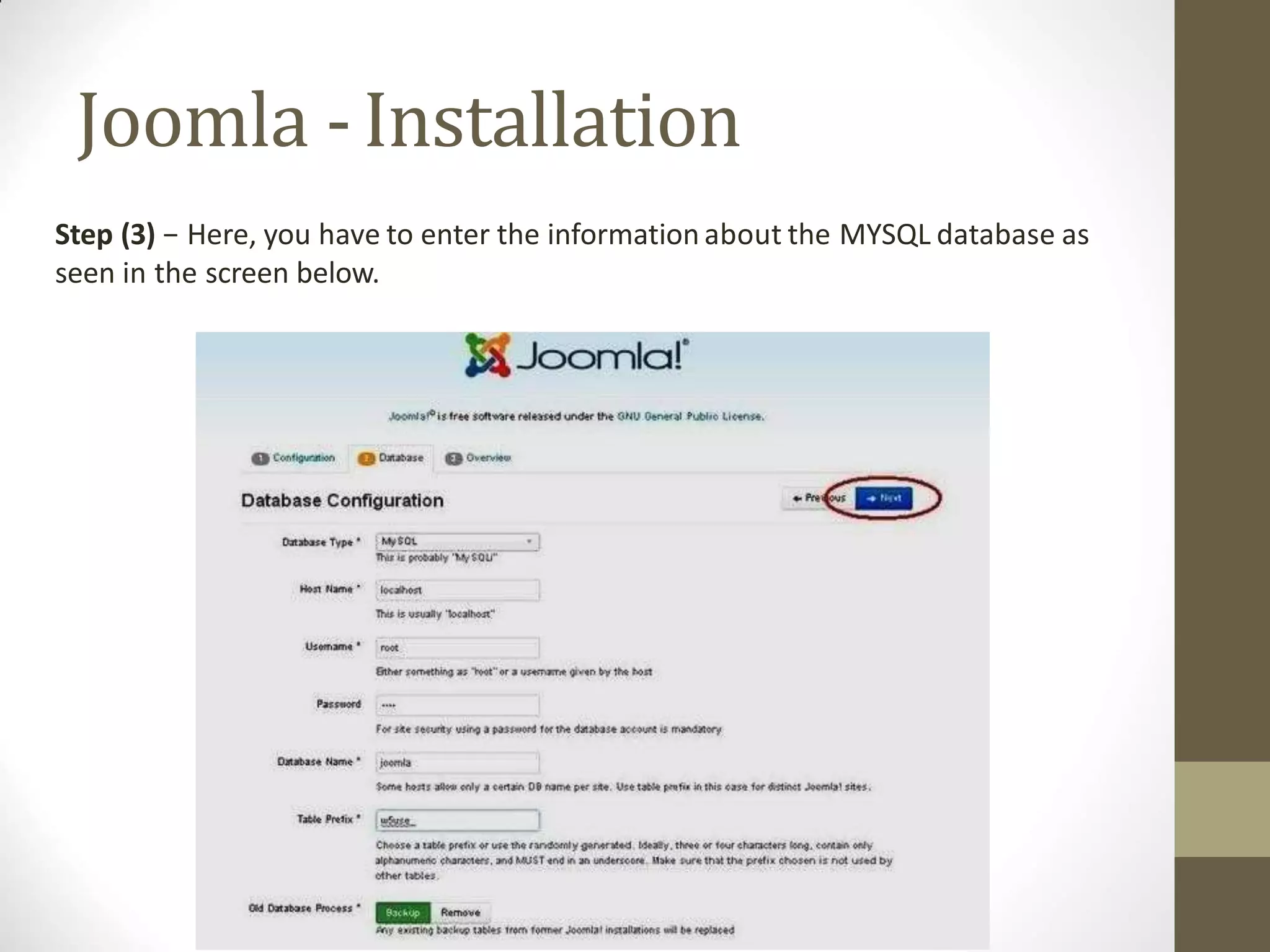
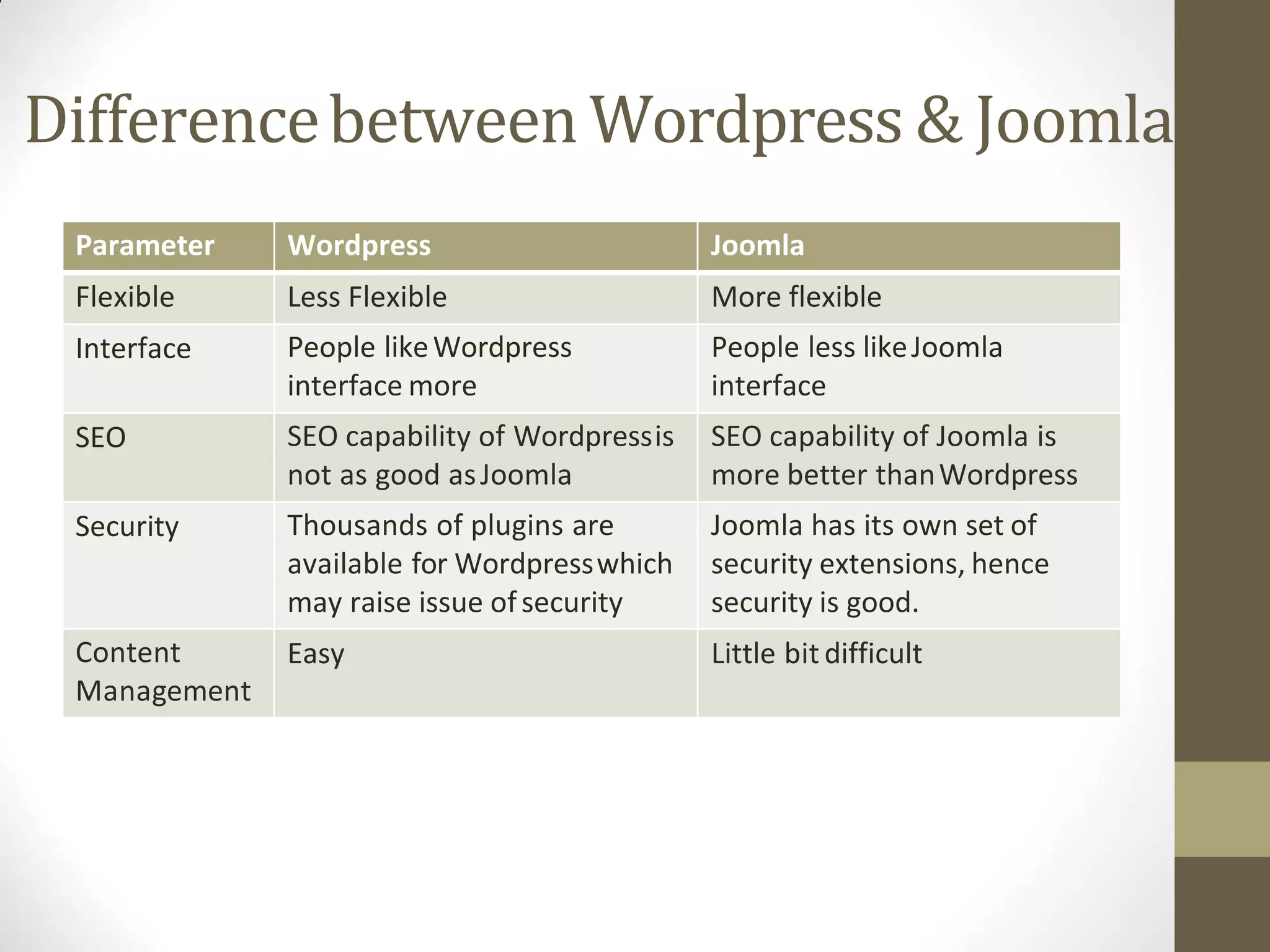
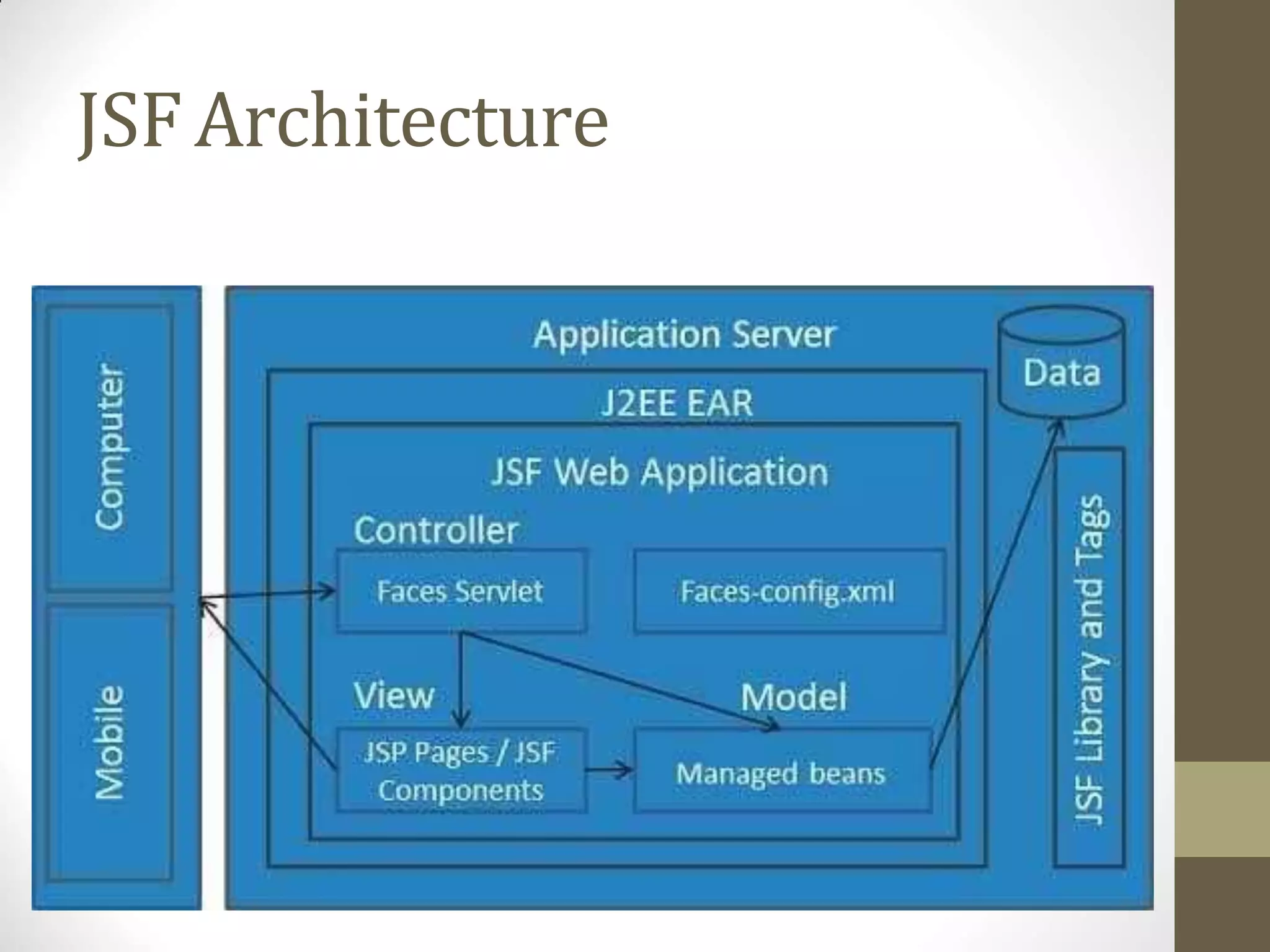
A content management system (CMS) is a software that allows for the creation and modification of digital content. It supports multiple users collaborating in a shared environment. CMS features include web-based publishing, formatting, version control, indexing, searching, and retrieving content. A typical CMS has two major components - a front-end content management application for users to add/edit website content, and a back-end database to store the content. Popular open-source CMS platforms include WordPress and Joomla.