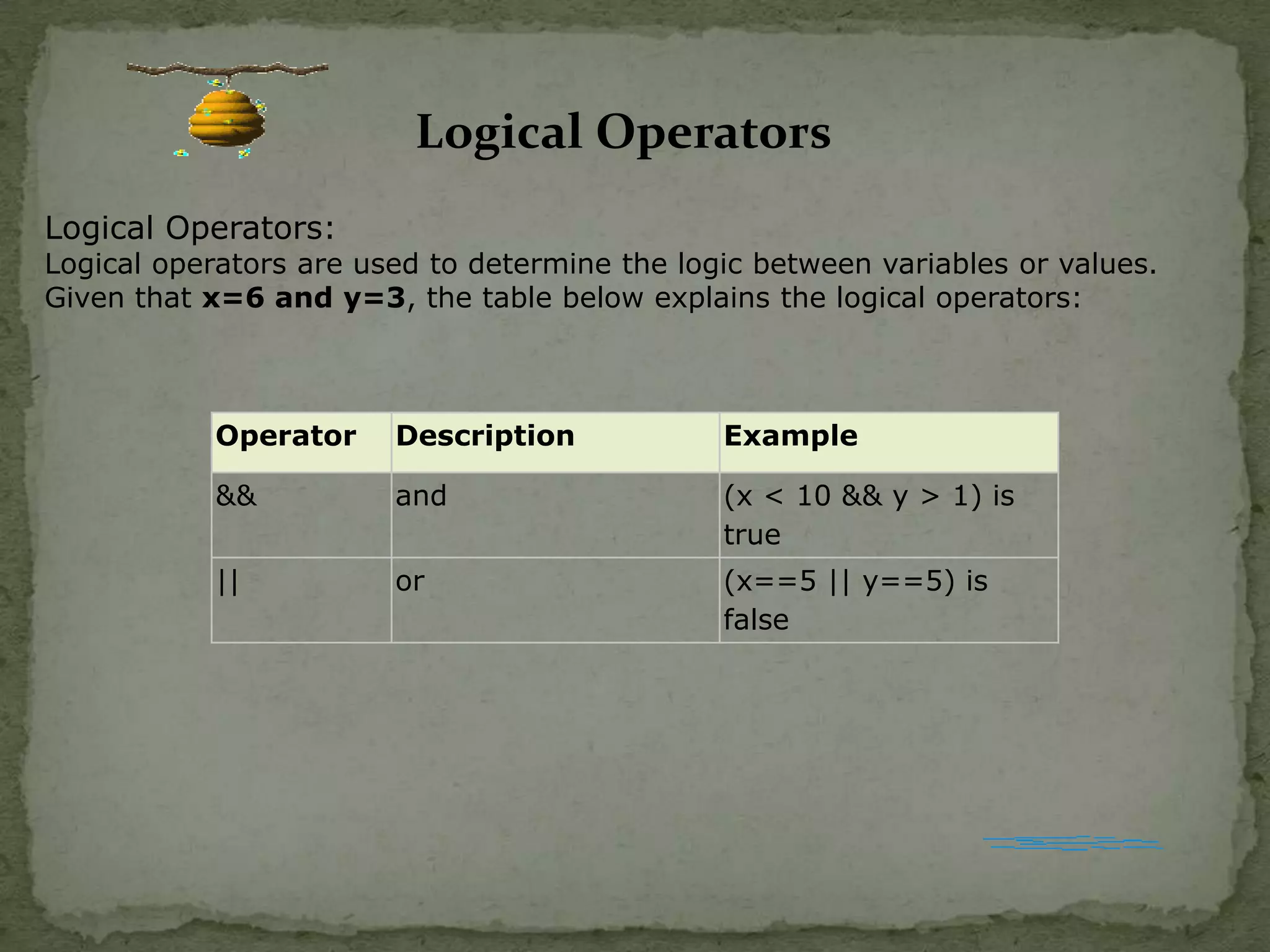
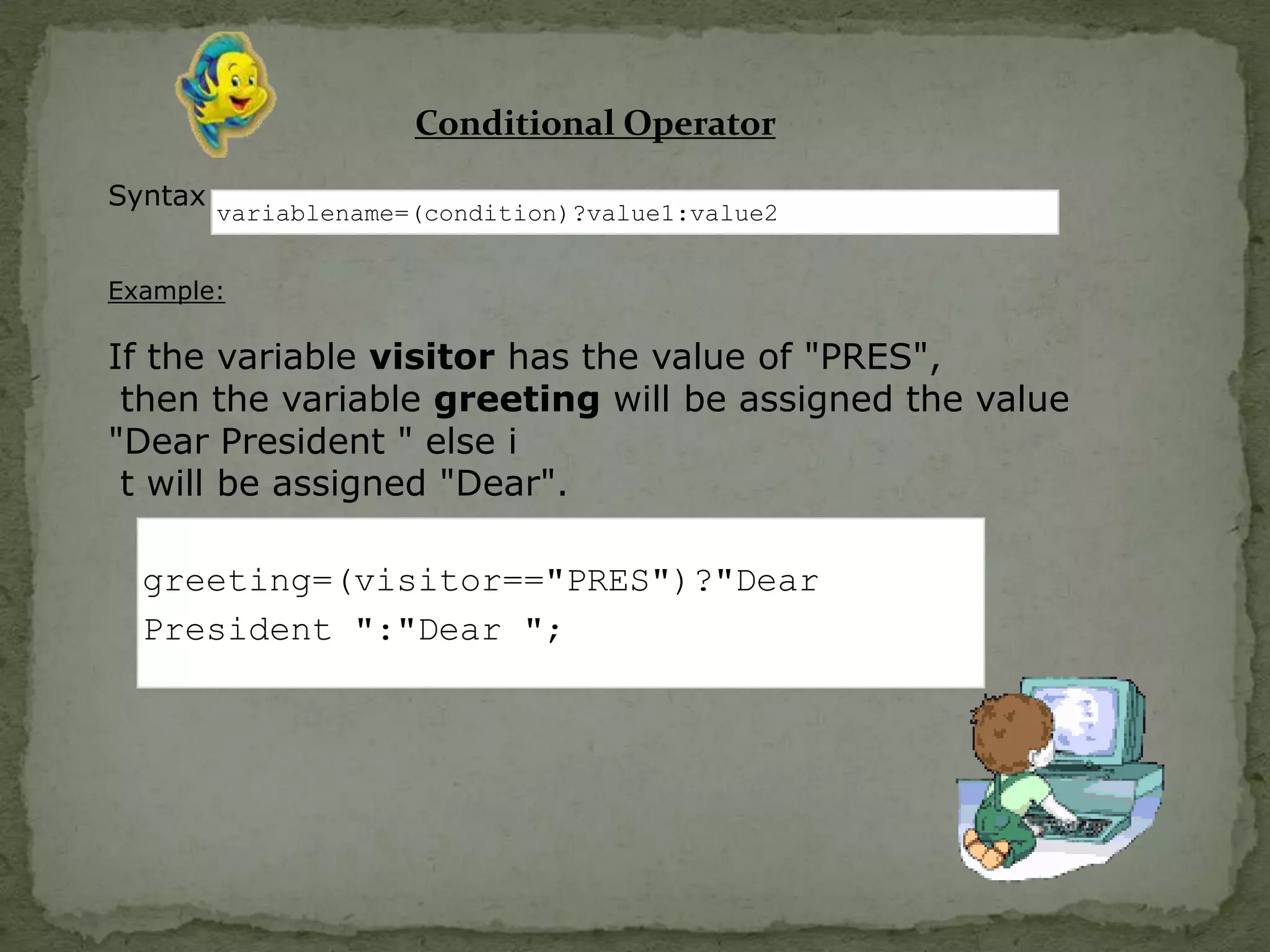
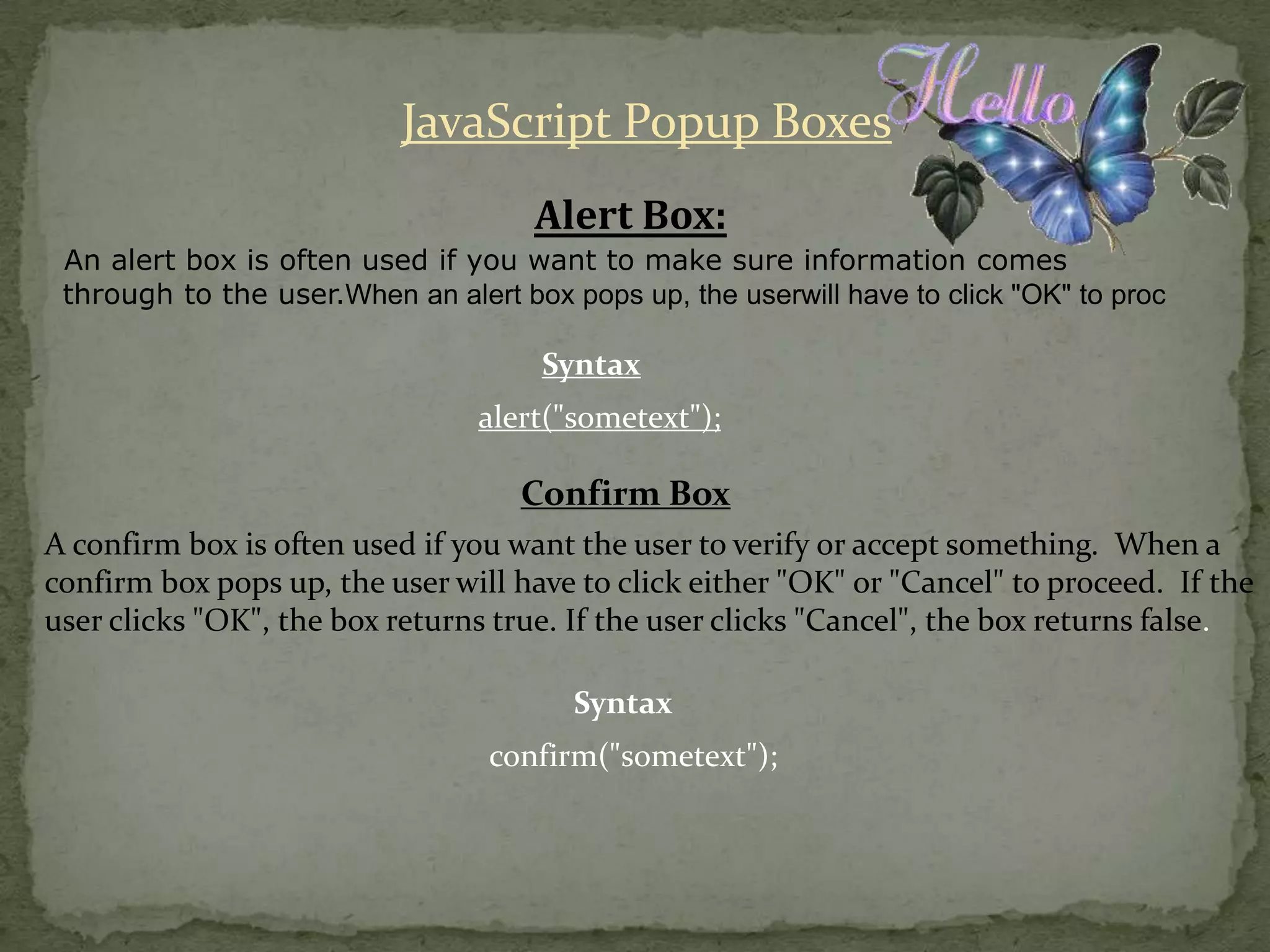
JavaScript is a scripting language that allows adding interactivity to HTML pages. It can be used for client-side form validation and integration with user plugins. JavaScript is case-sensitive and allows variables, functions, conditional statements, and objects. Common uses include pop-up boxes, event handling, and cookies.