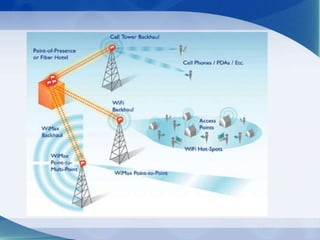
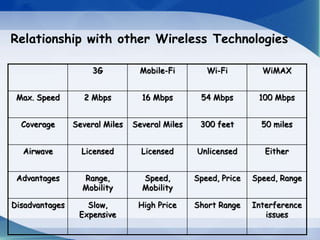
The document provides an overview of WiMAX technology, detailing its definition, building blocks, services, security functions, and specifications. It highlights the characteristics of WiMAX as a wireless communication technology that enables broad coverage and high-speed data transmission without the need for cables. Additionally, it compares WiMAX to other wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, emphasizing its advantages in speed and range.