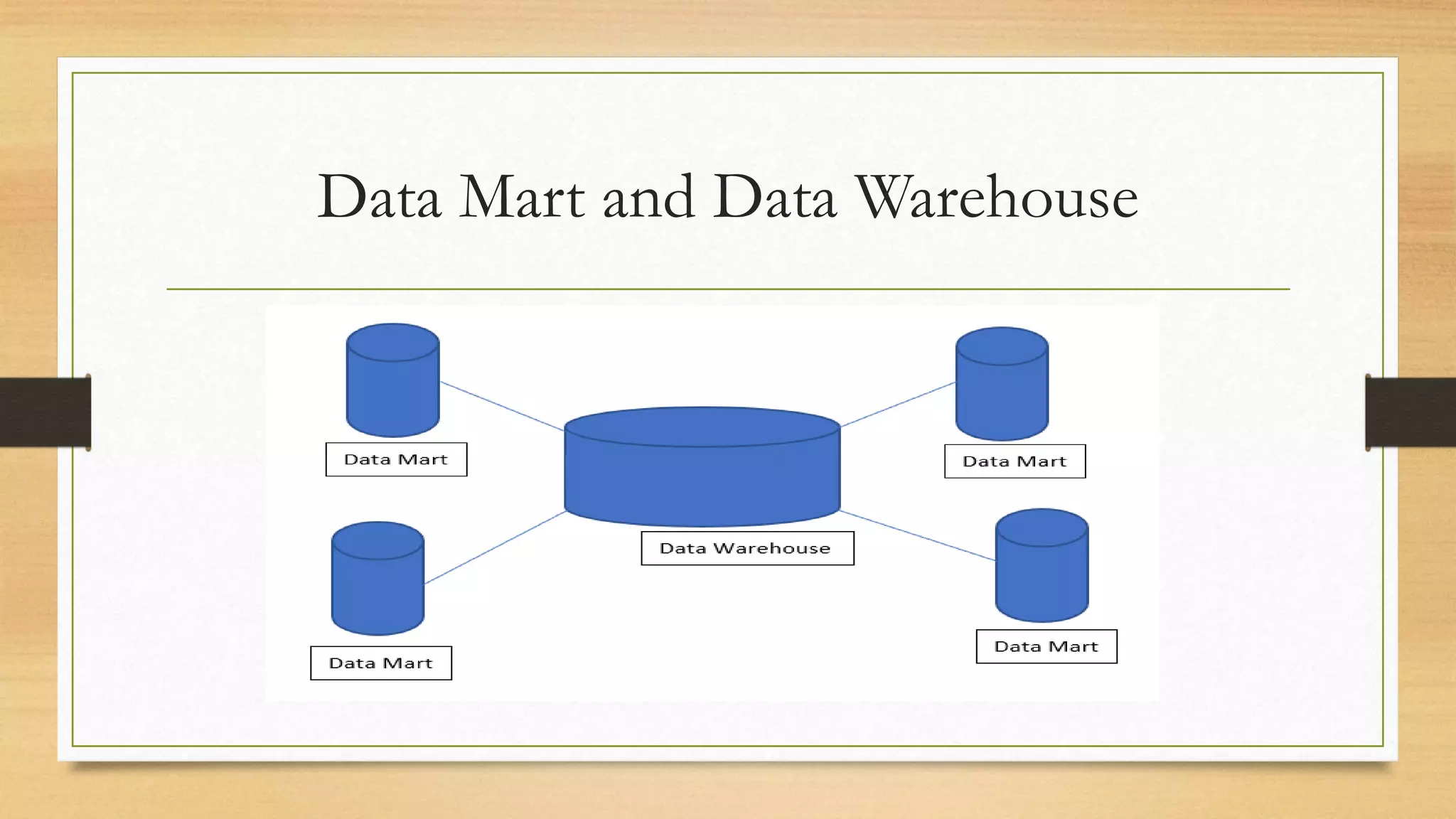
Via a database, redundancies can be eliminated, data mining is possible, and data marts and data warehouses can be created. A database allows data to be centralized, eliminating redundant storage of the same data in multiple locations. Data mining extracts useful information from data for purposes like generating sales. Data warehouses are central repositories for mined data to assist with enterprise-wide planning and decision making. Data marts serve specific areas of an organization and combine to form the overall data warehouse.