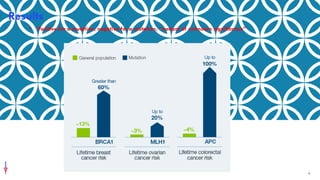
The document explains genetic testing, which analyzes a person's germline genes to assess inherited cancer risks, and its differences from screening and biomarker testing. It outlines the benefits, limitations, and potential insurance coverage issues associated with genetic testing, as well as its implications under the Affordable Care Act. Overall, genetic testing can inform health decisions for individuals and their relatives, though it may come with financial considerations and privacy risks.