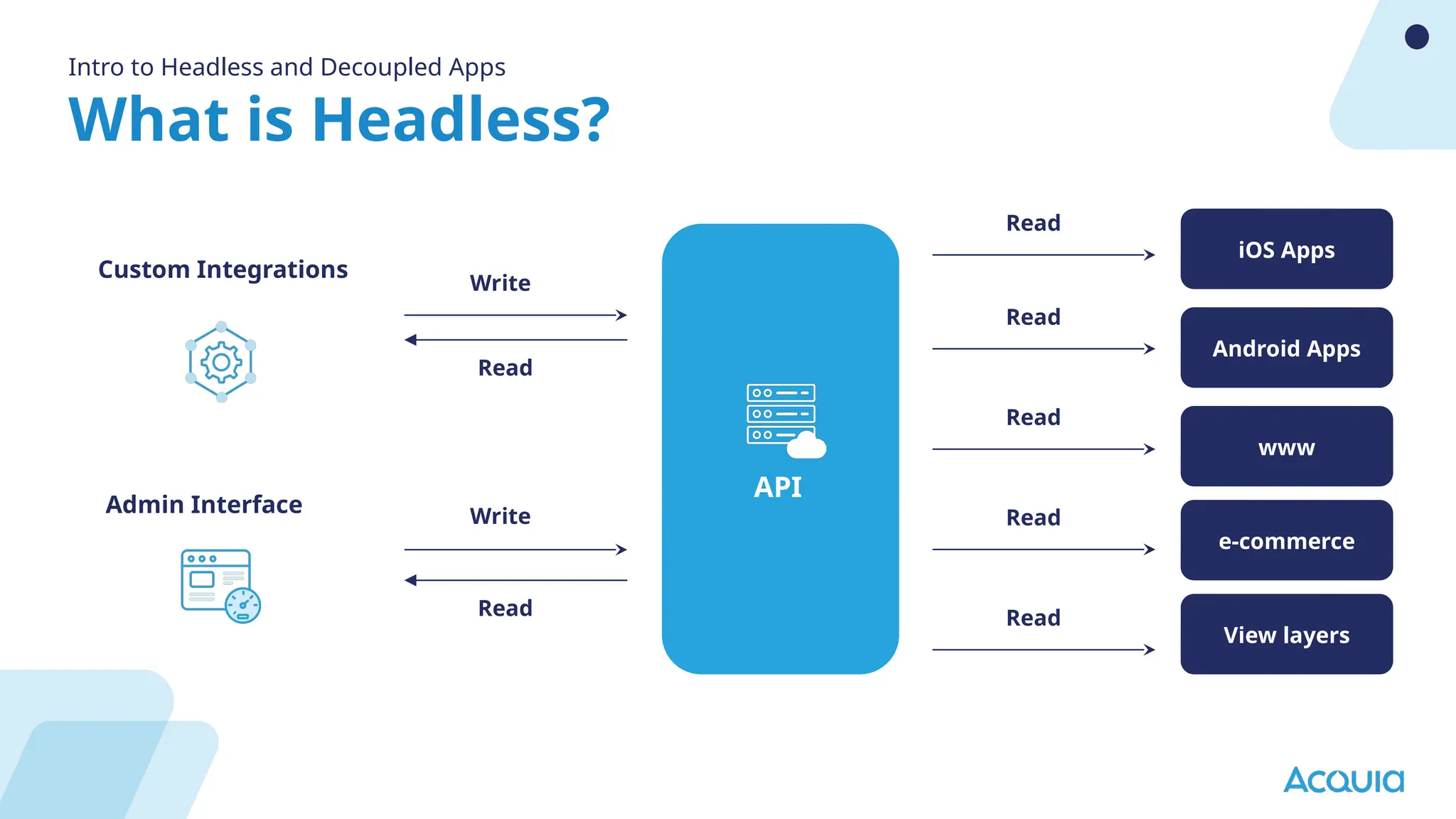
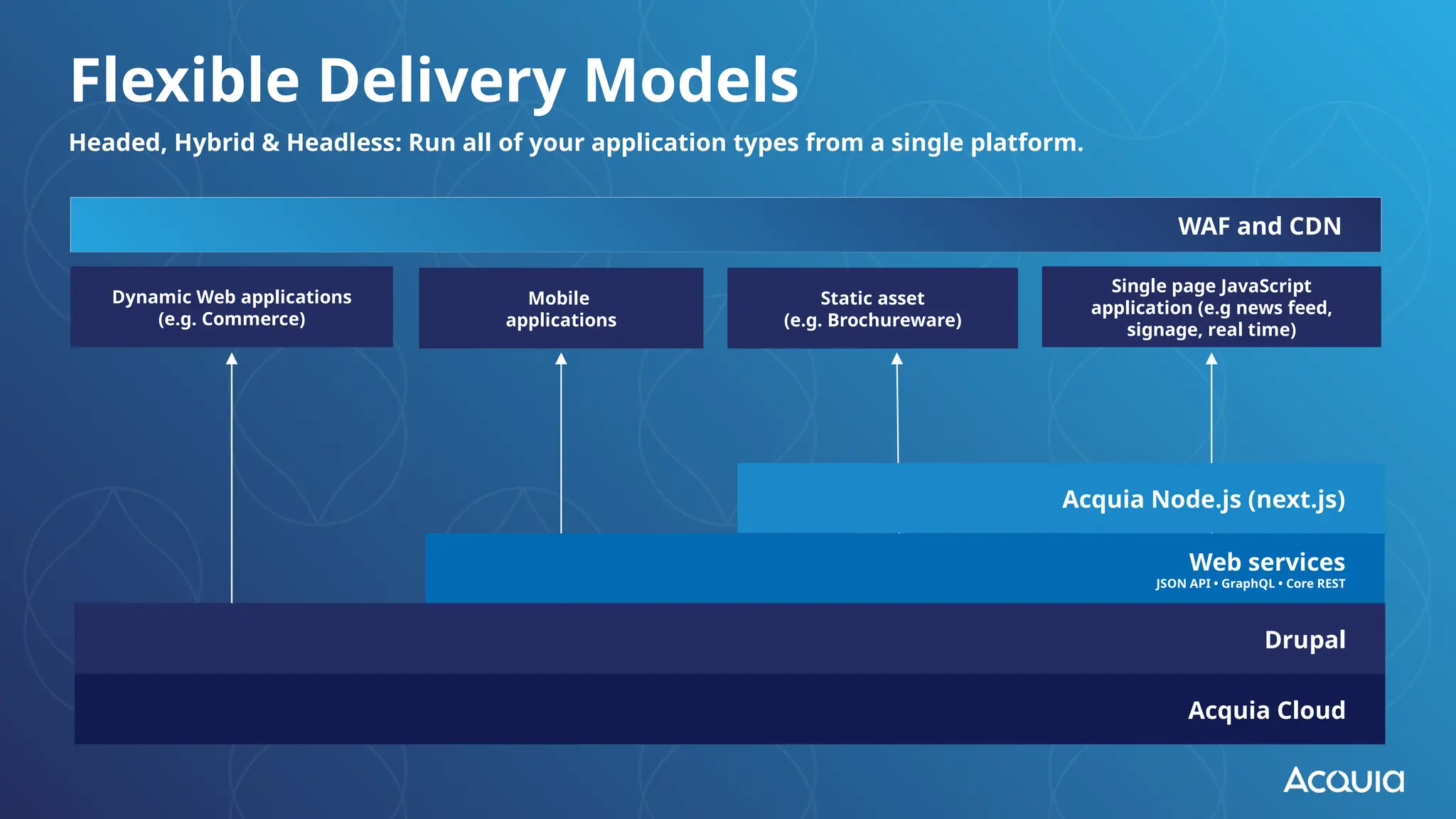
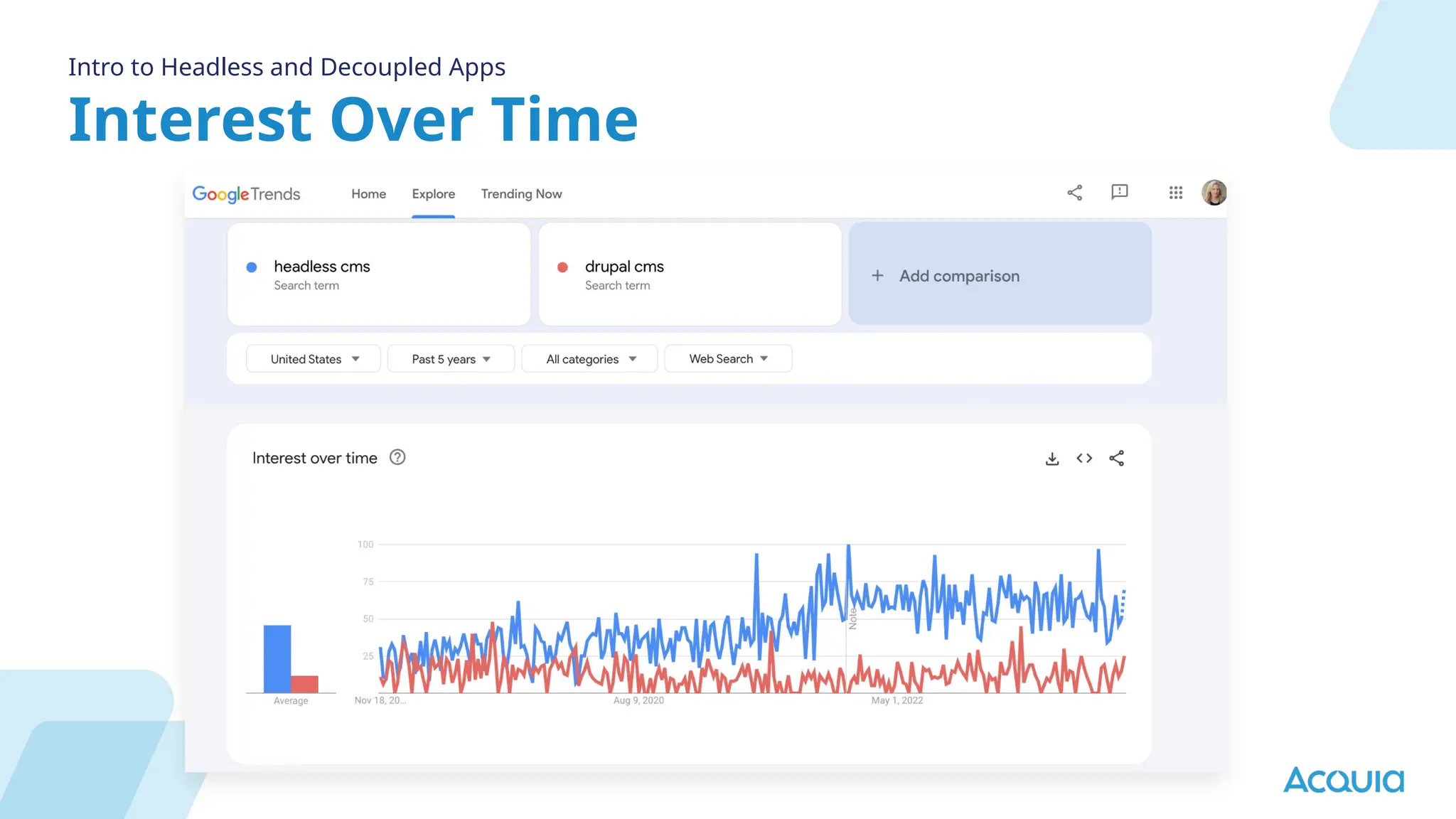
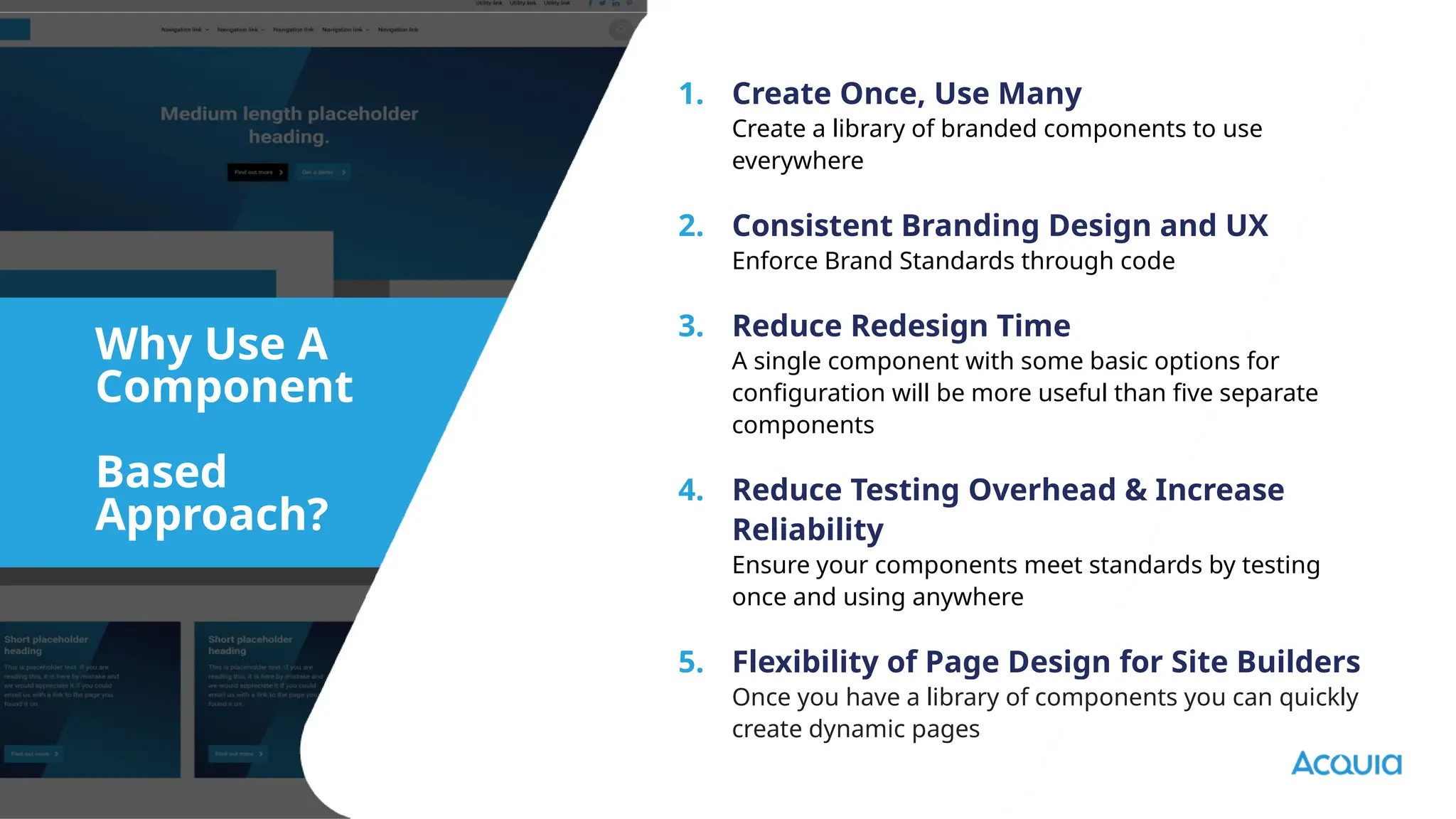
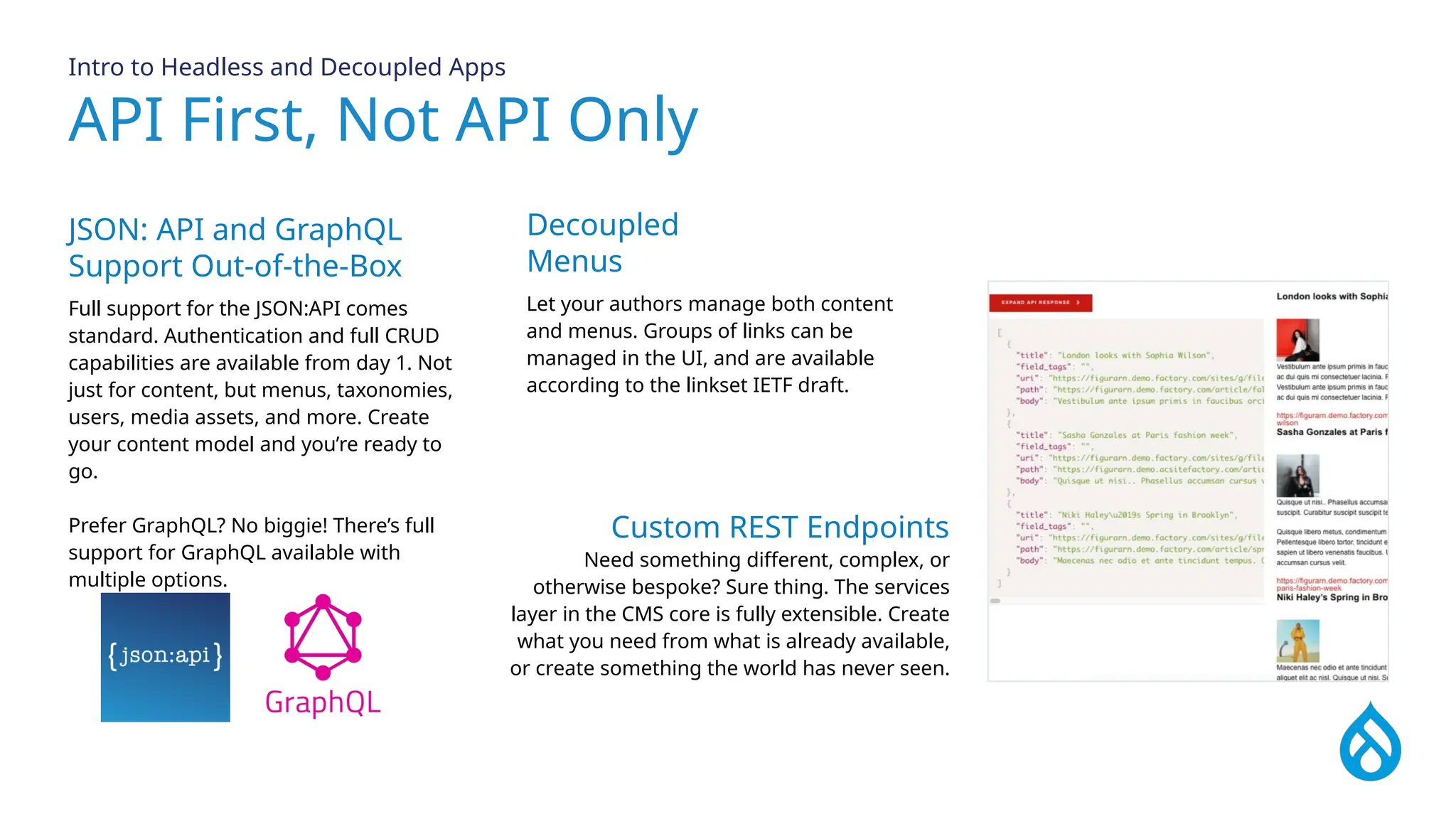
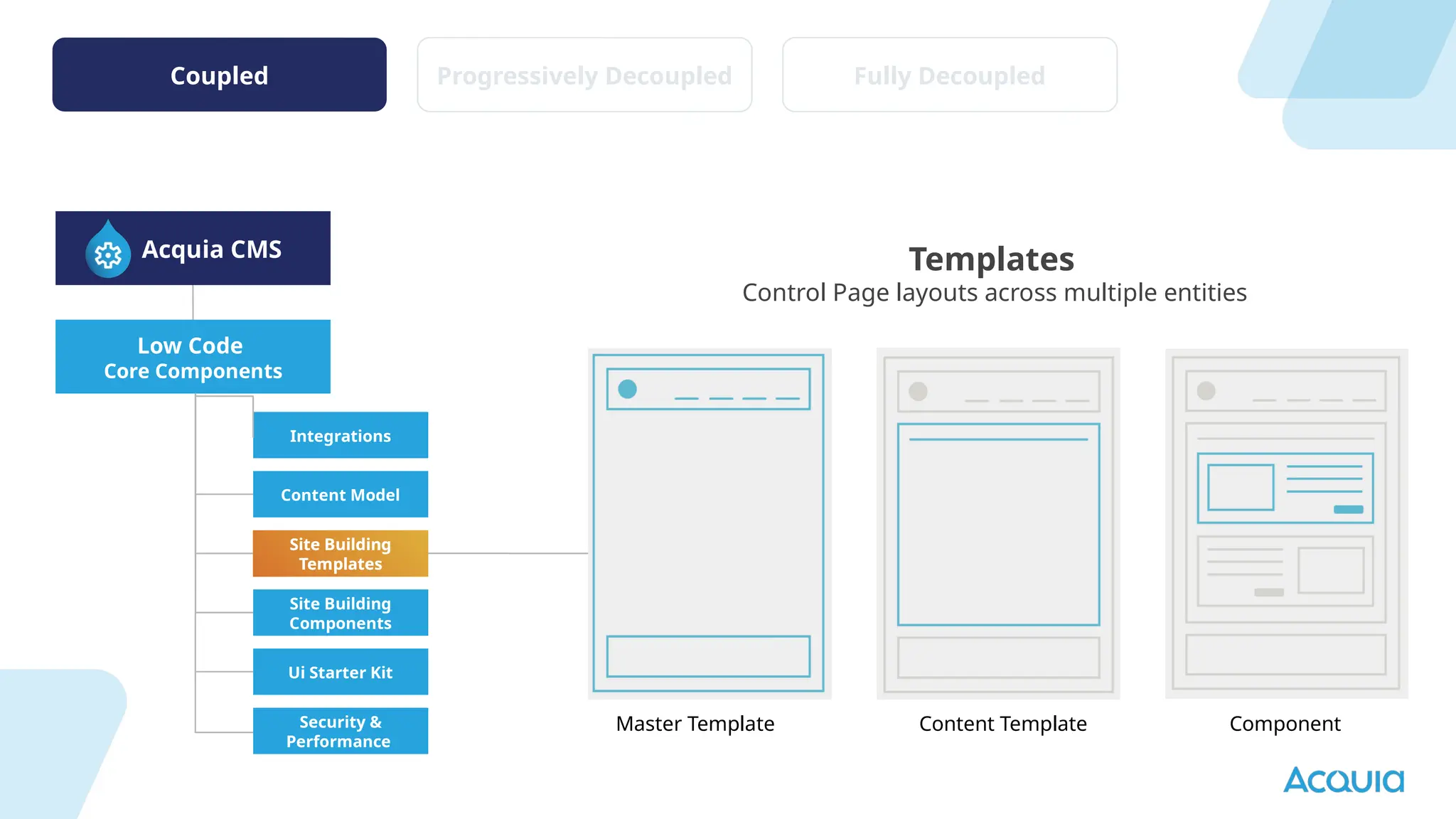
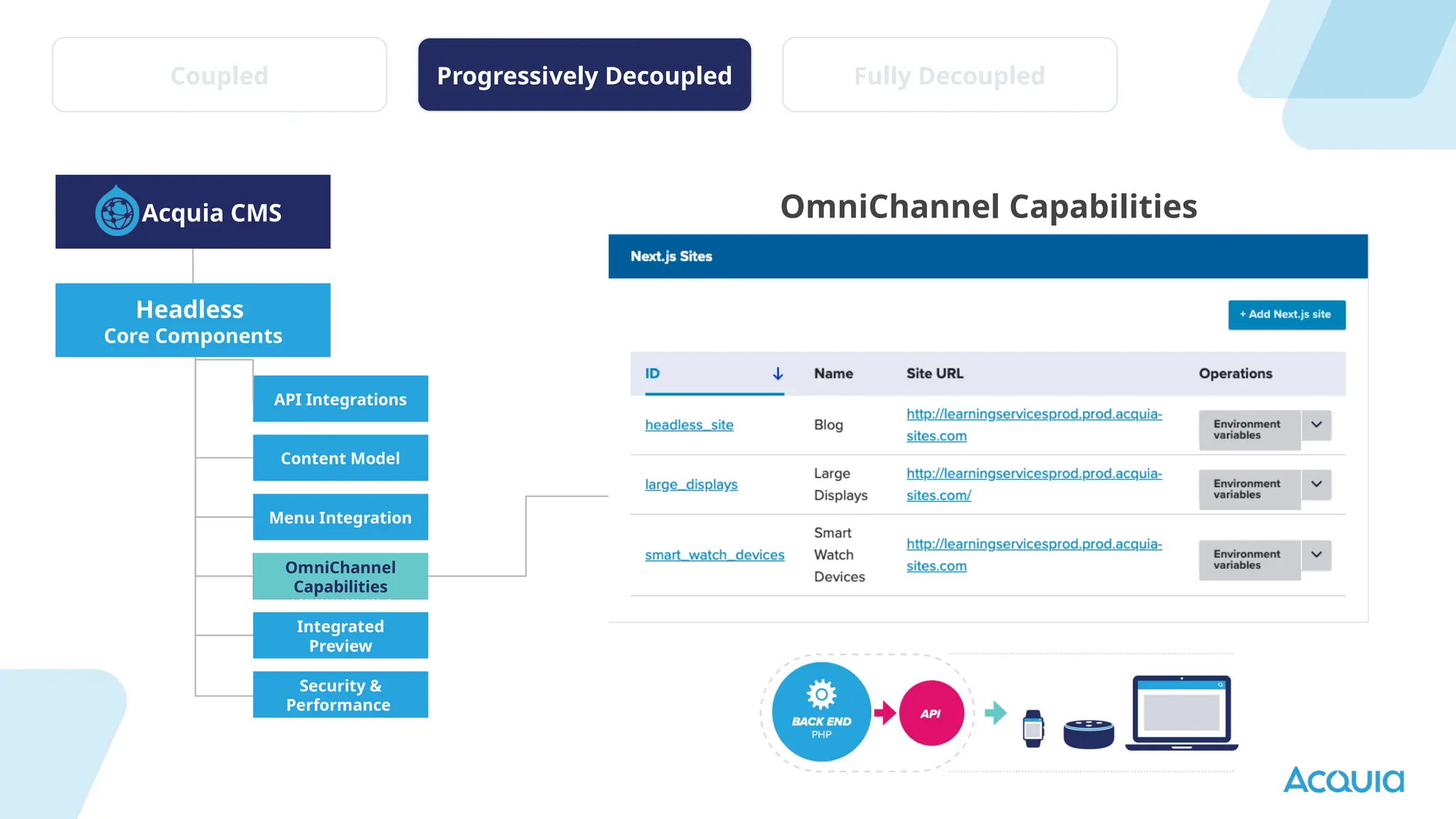
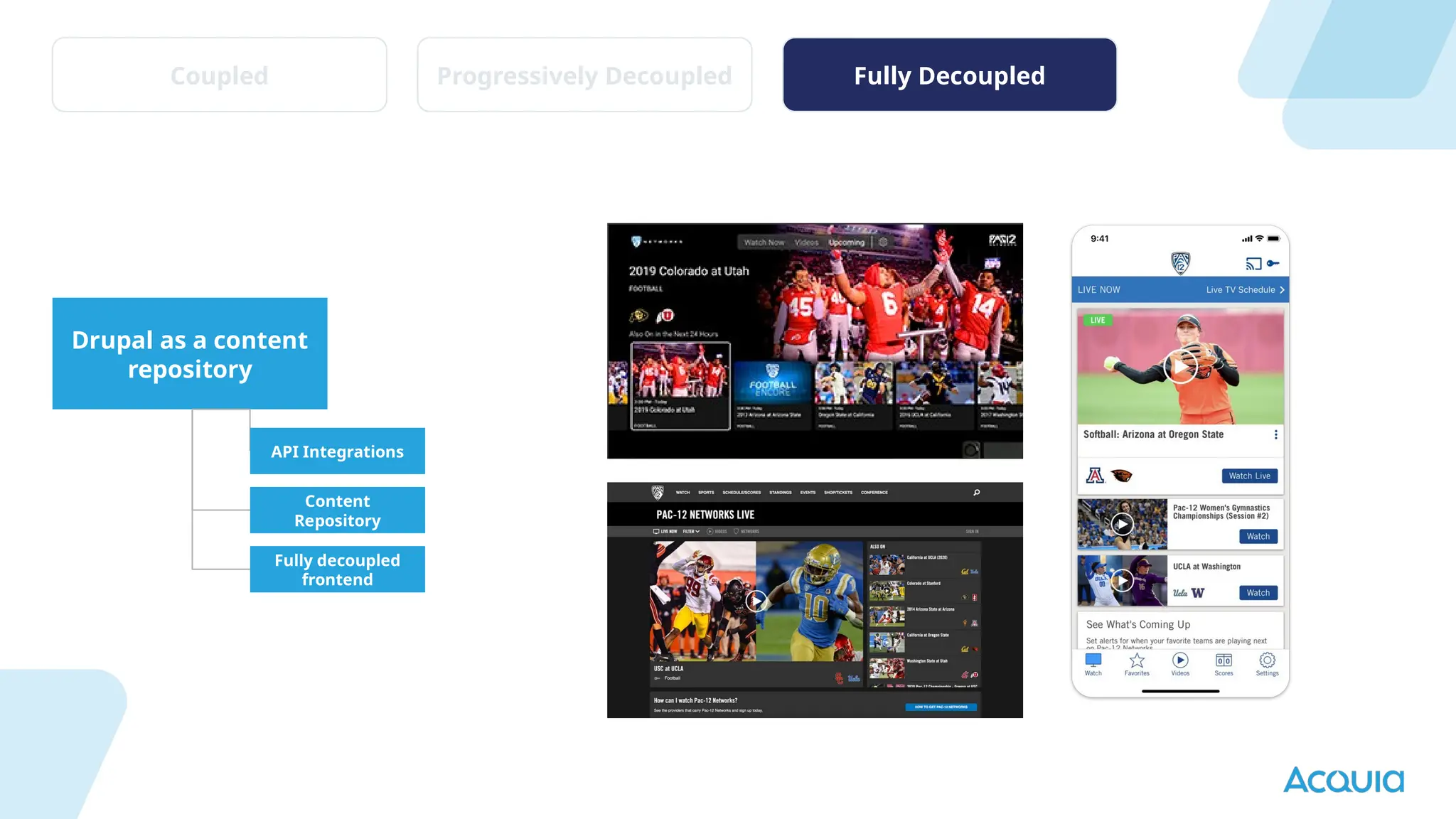
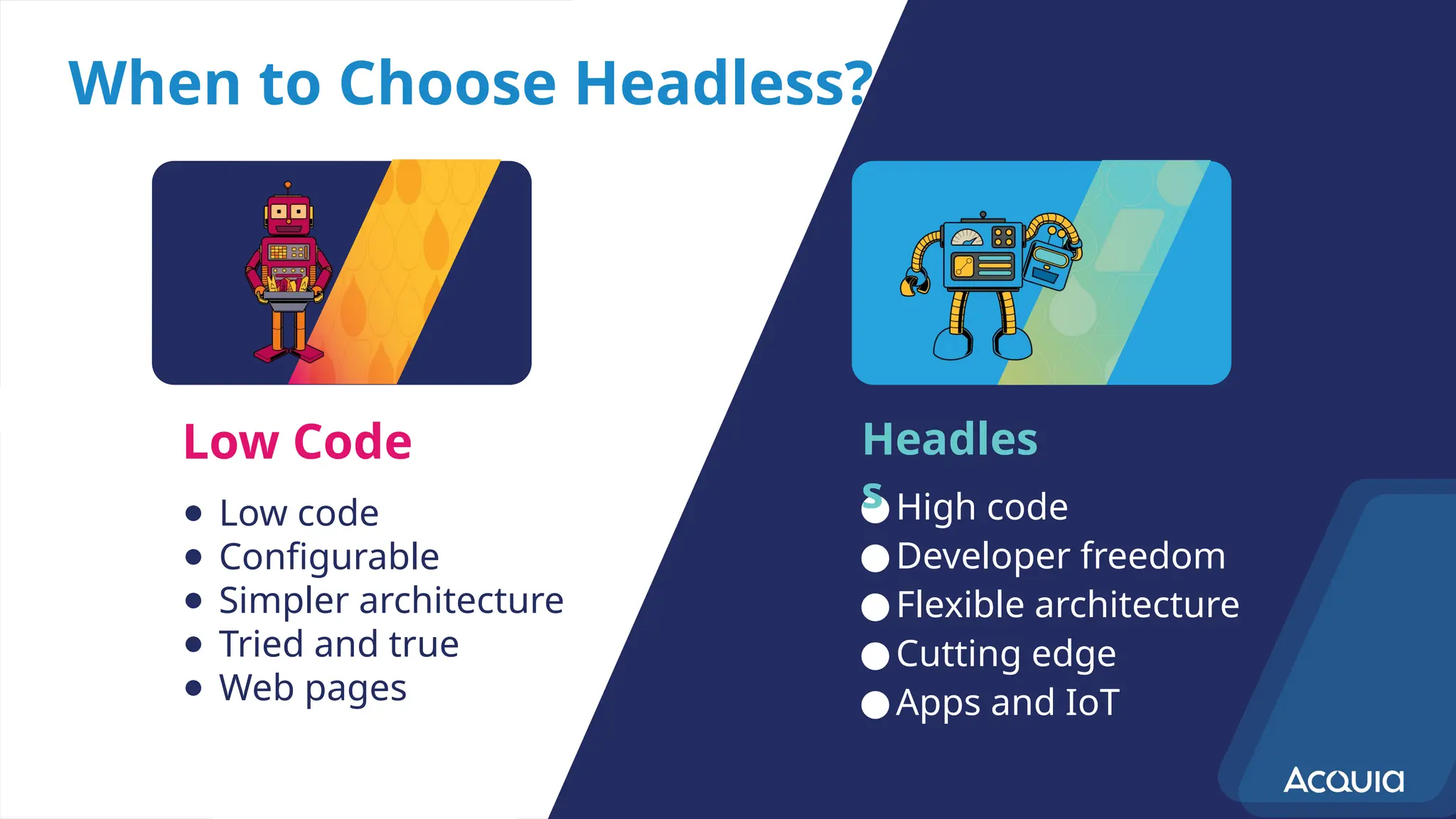
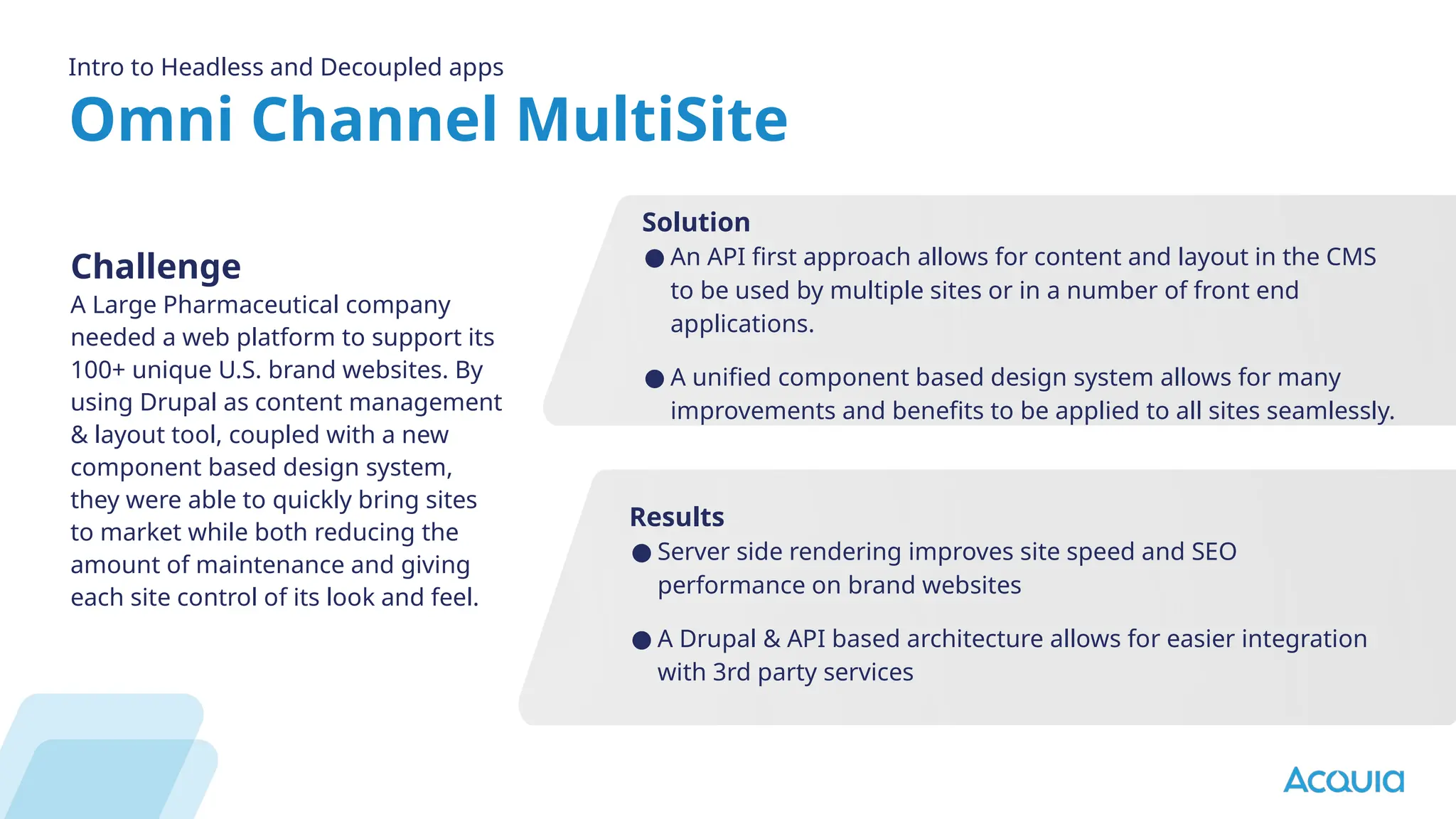
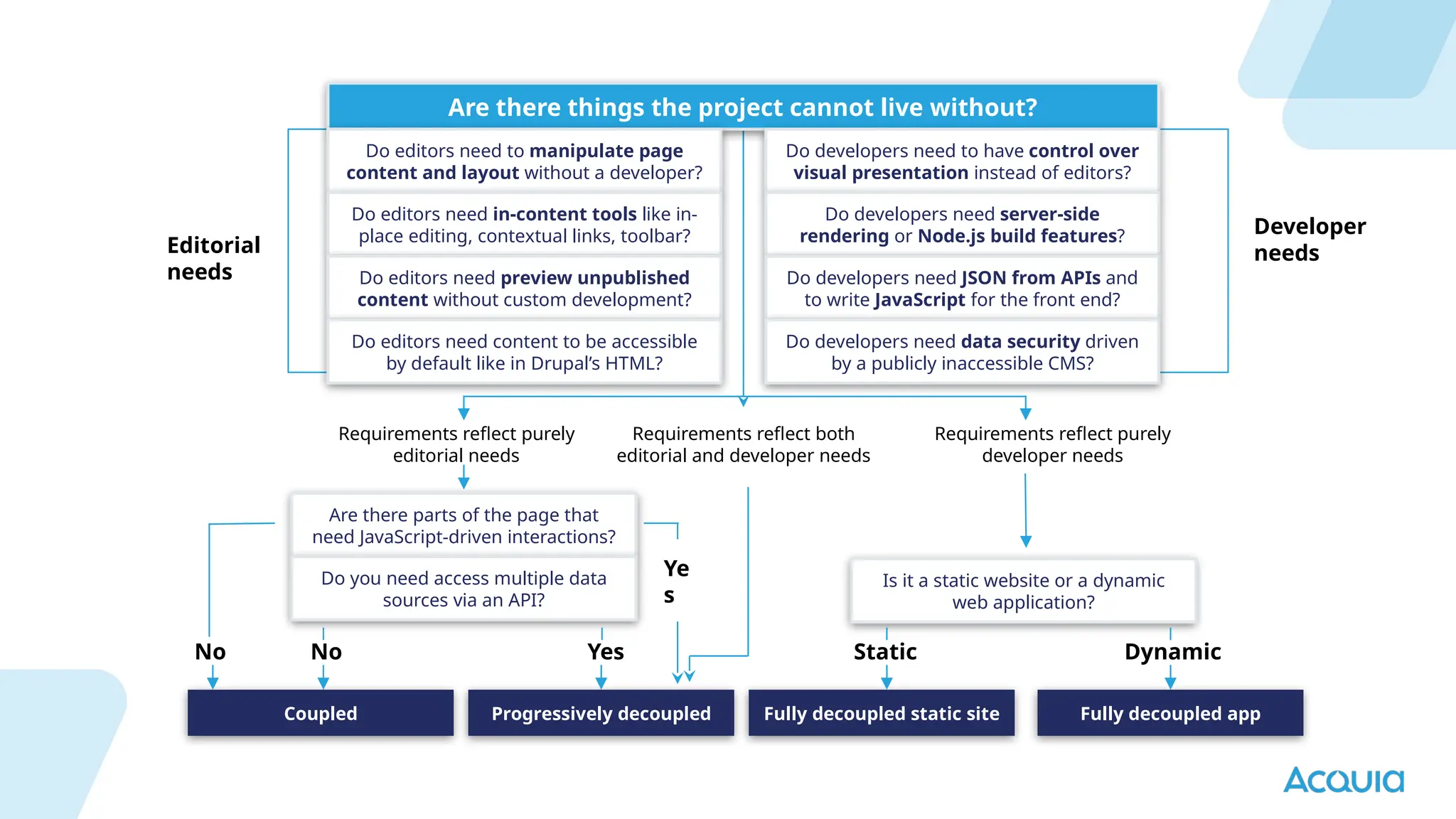
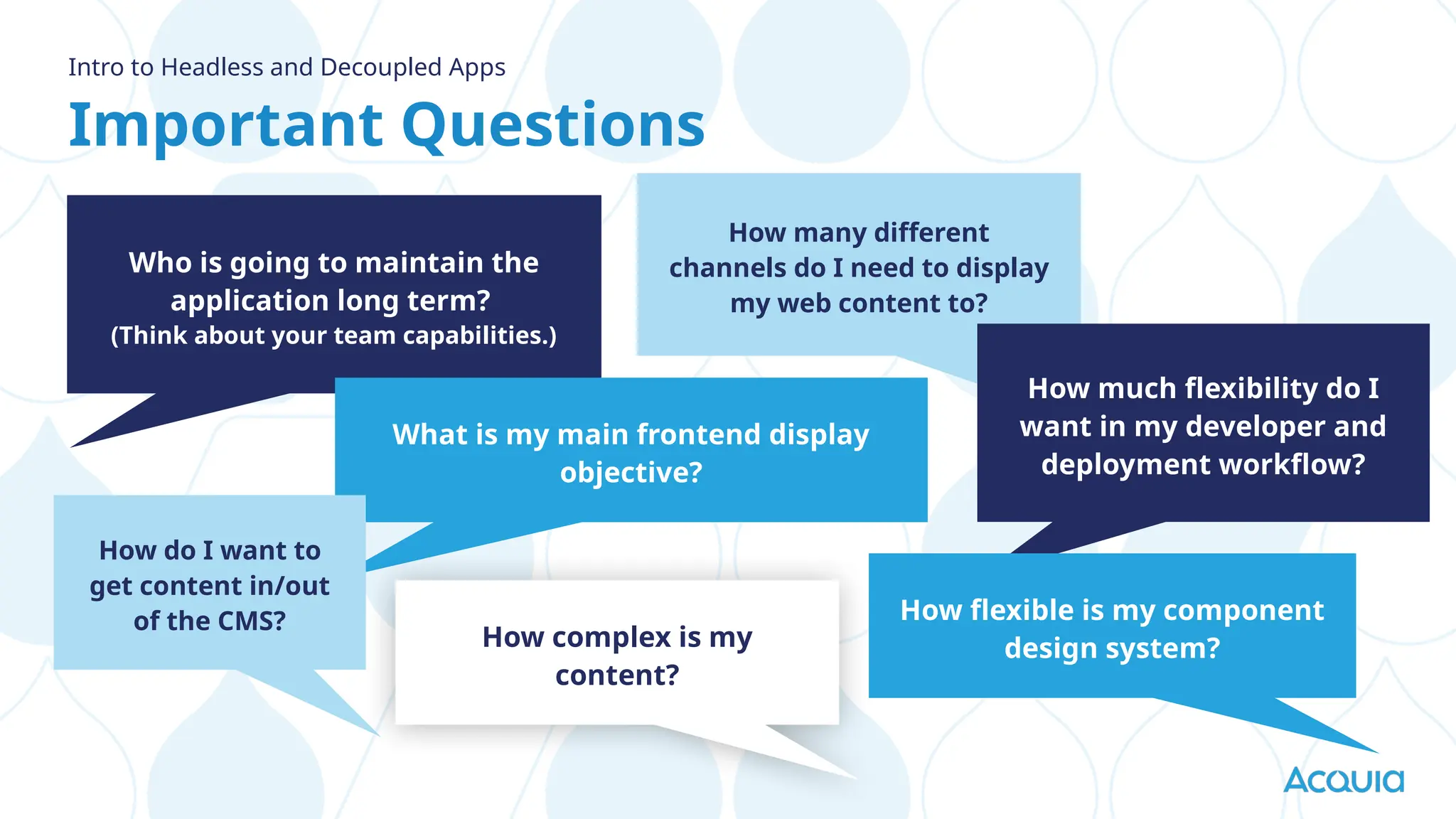
The document provides an overview of headless Drupal, explaining its definition, benefits, and architectural components. It discusses the separation of frontend and backend systems, the API-first approach, and examples of successful implementations such as Princess Cruises and Pac-12. Key features include flexible delivery models, composable architecture, modular design, and the ability to manage complex digital experiences across multiple platforms.