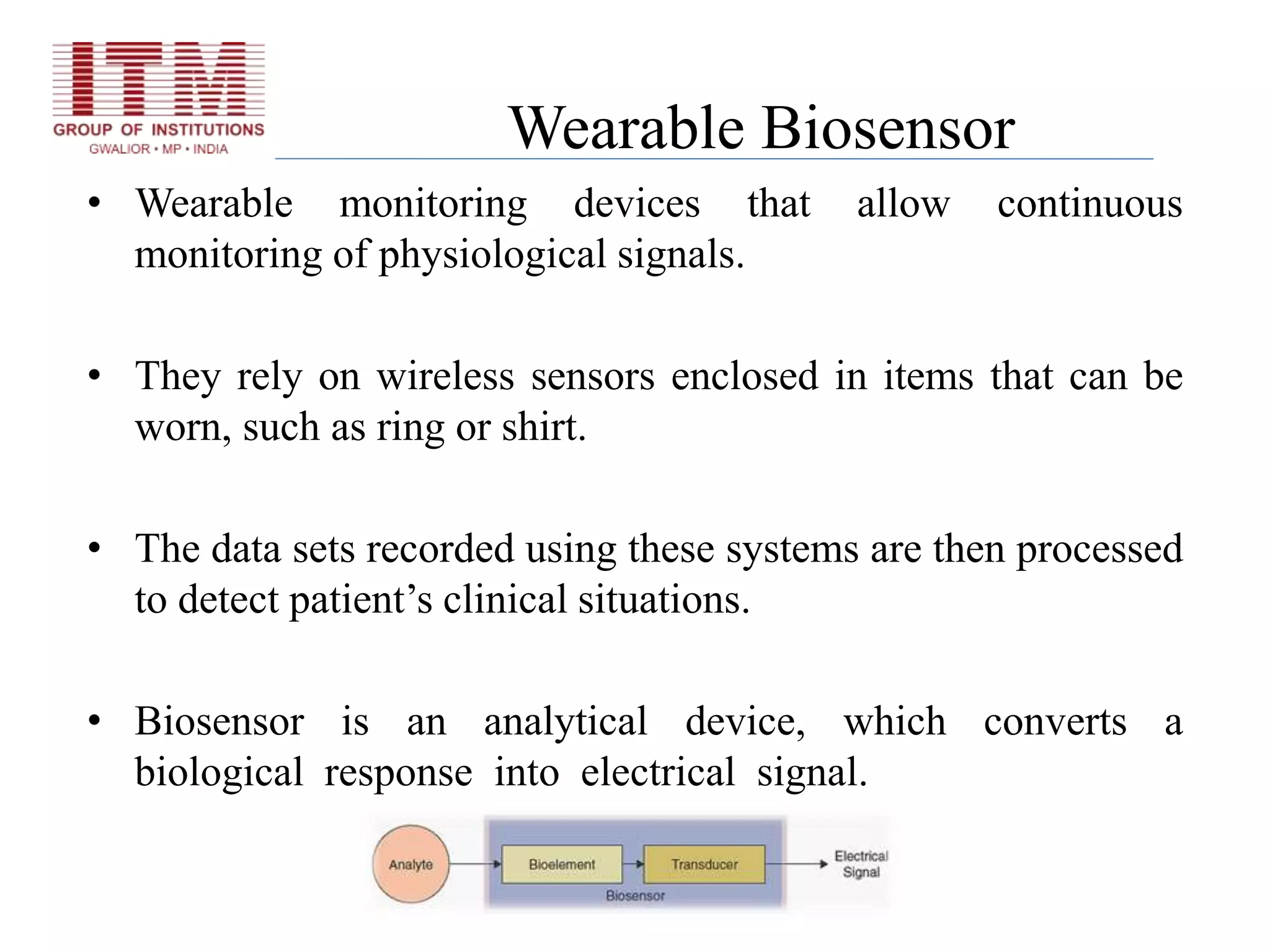
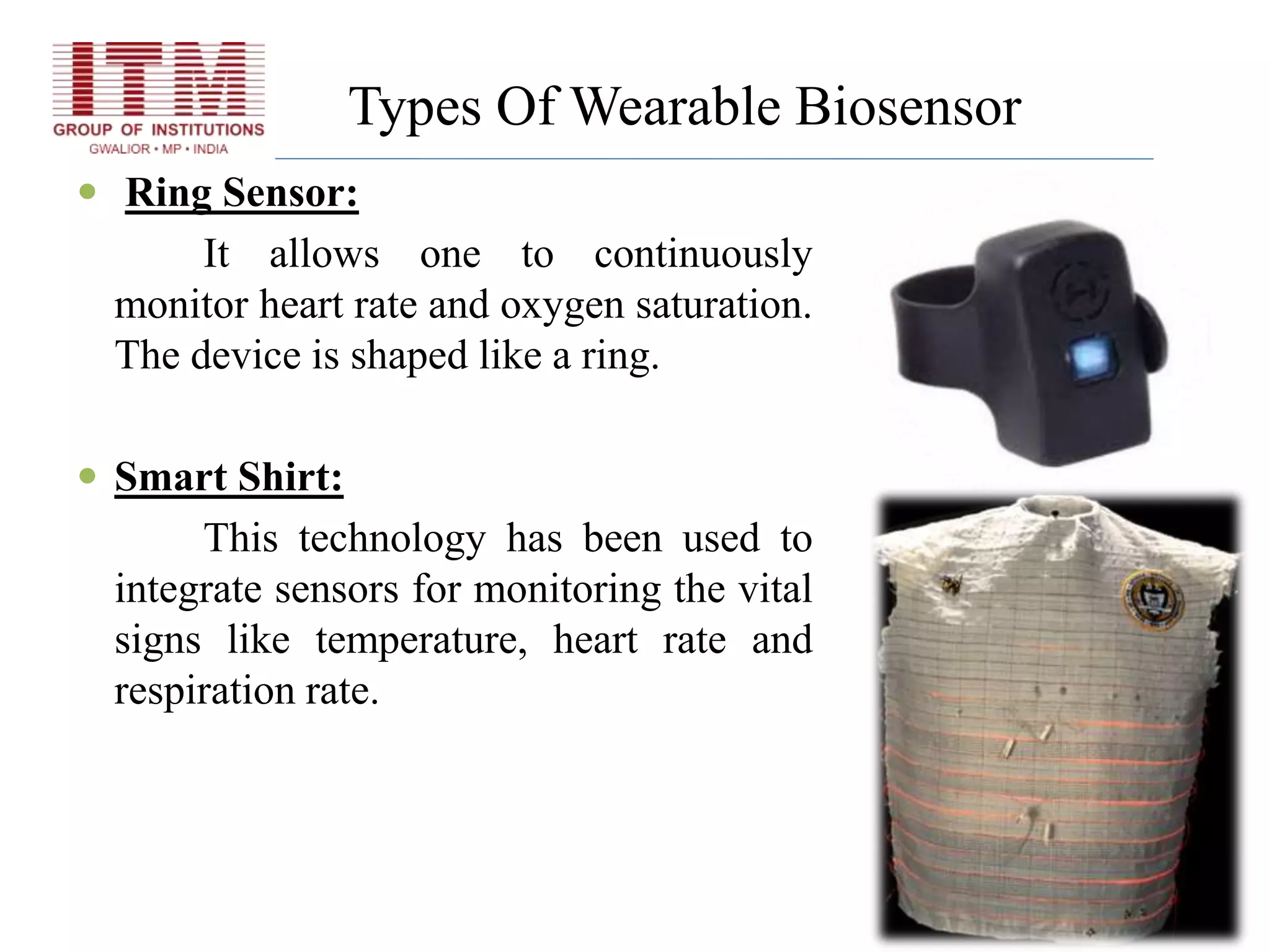
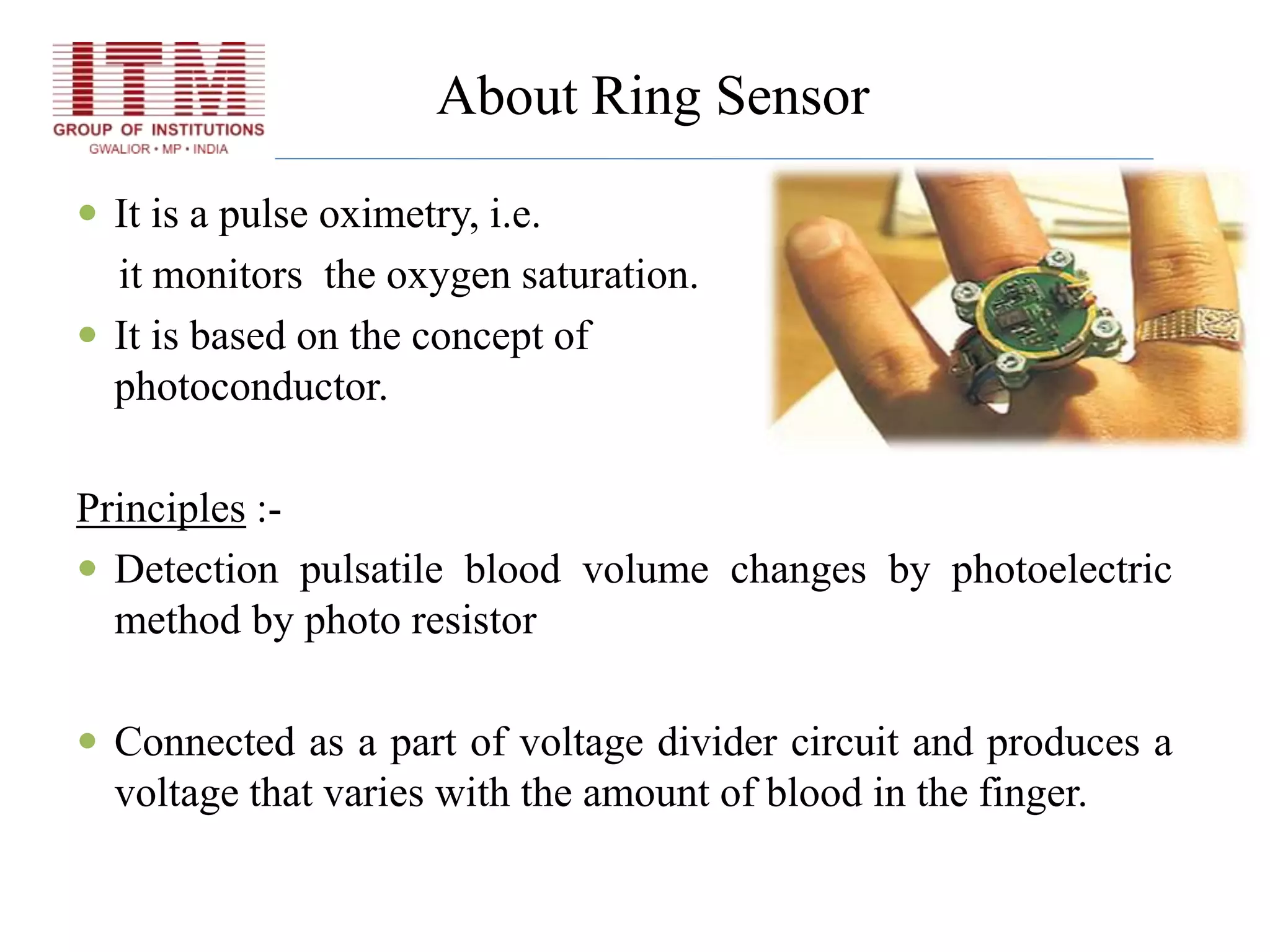
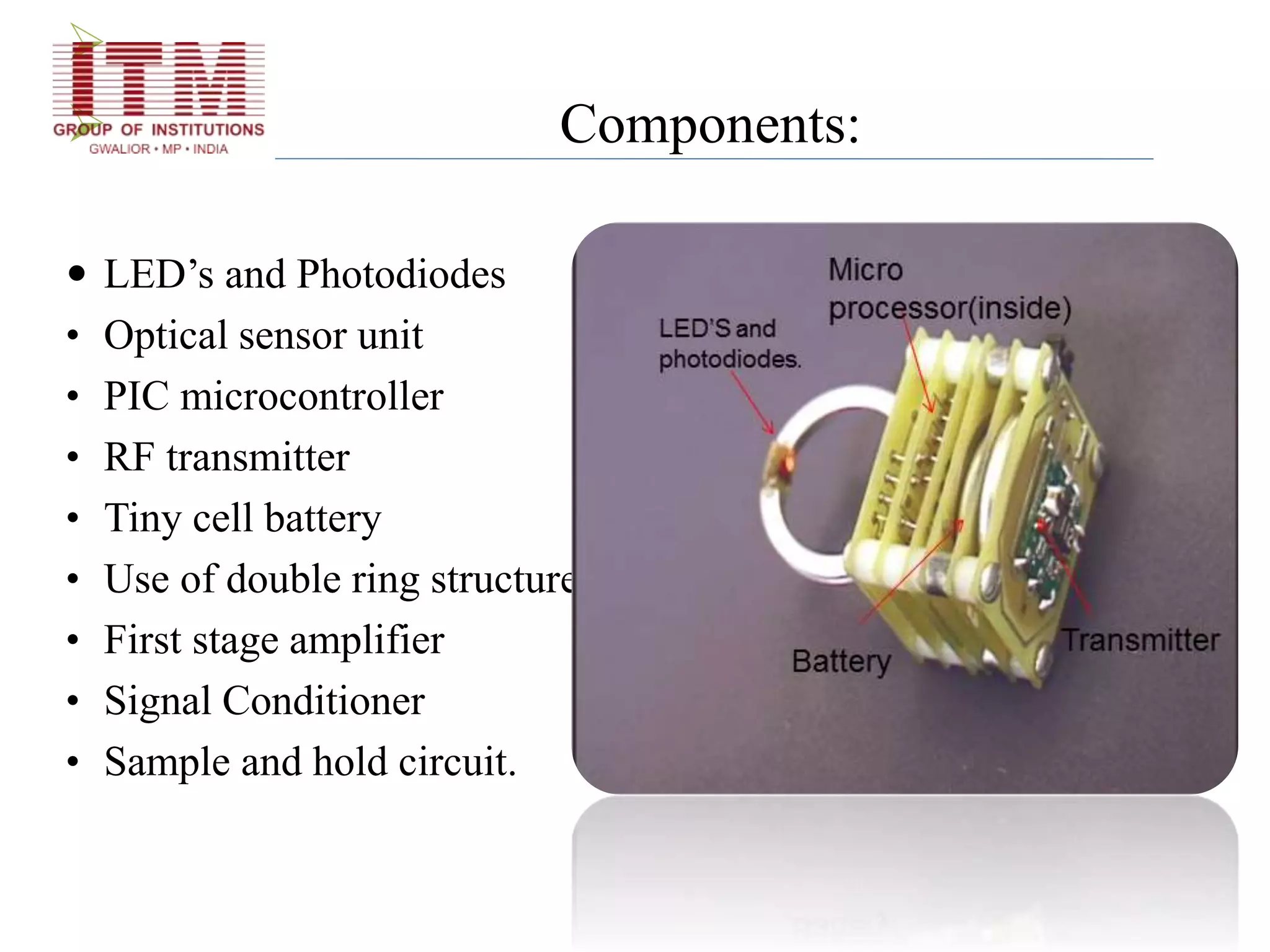
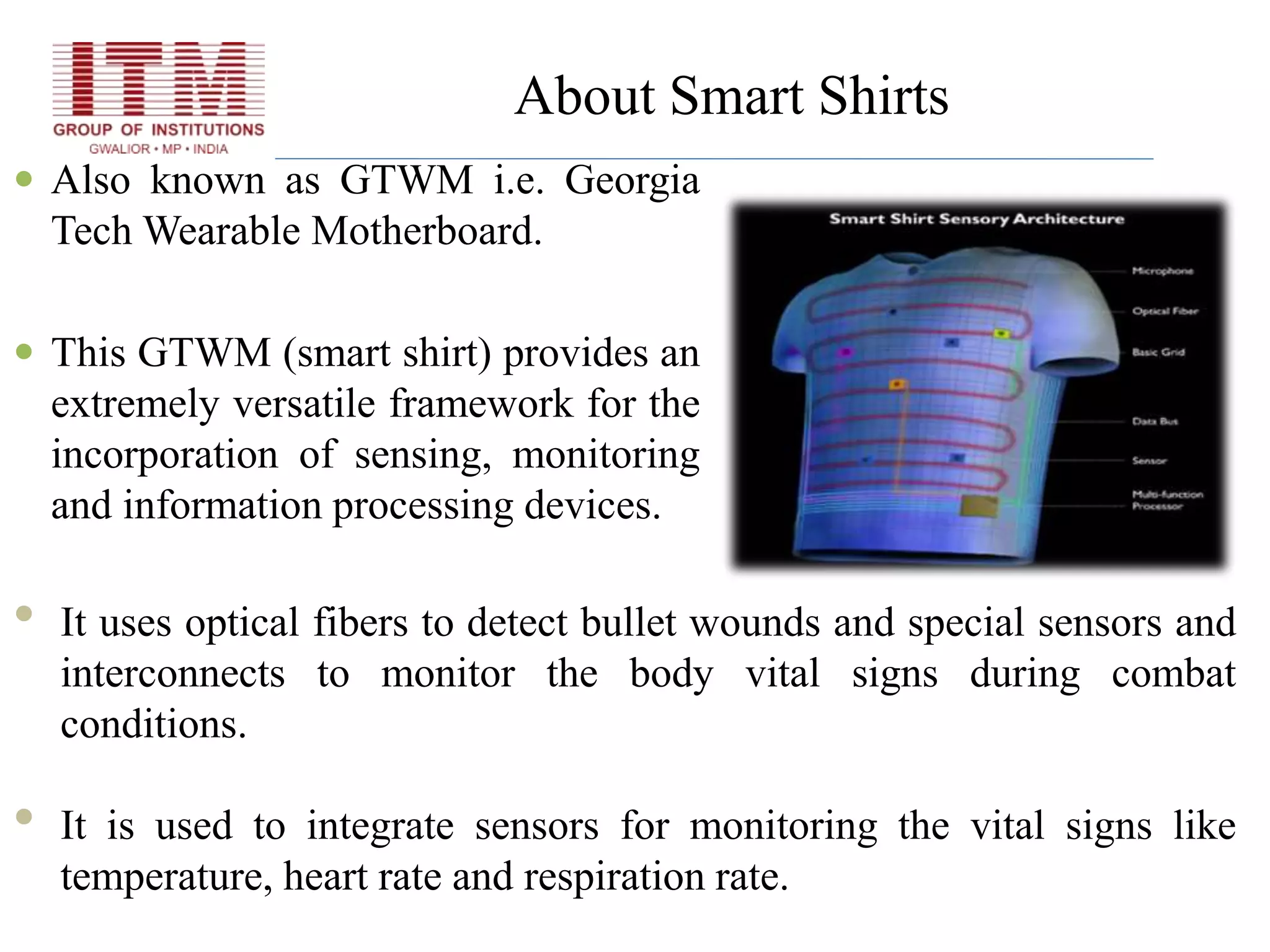
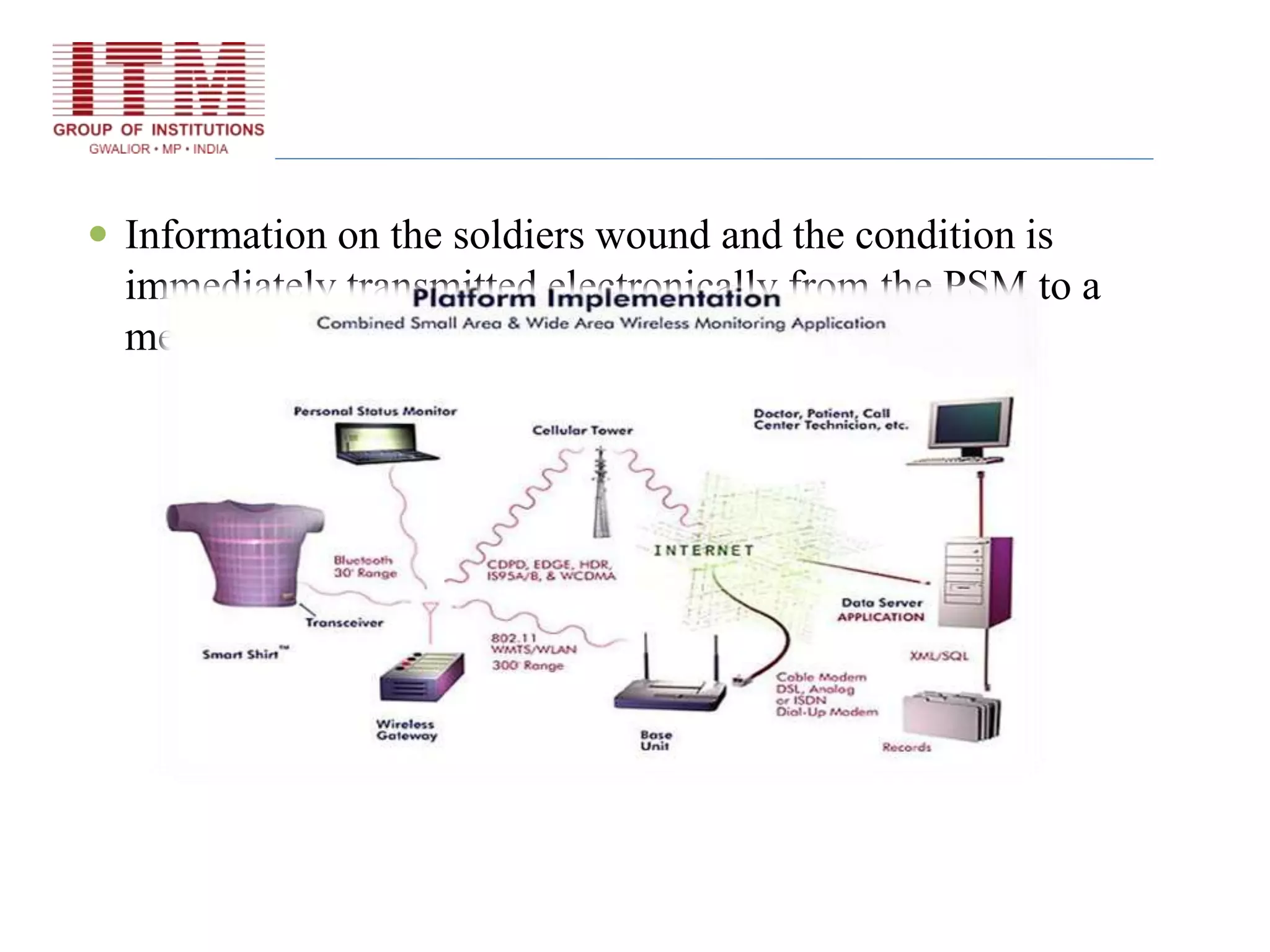
The document discusses wearable biosensors, which are devices that monitor physiological signals continuously through components like biological elements, transducers, and electronic devices. It highlights various types, such as ring sensors that track heart rate and oxygen saturation, and smart shirts for monitoring vital signs in combat or emergency situations. While these technologies offer advantages like continuous monitoring and ease of use, they also face challenges such as high initial costs and limited physiological parameter tracking.